YOU ARE LEARNING:
Absorption

Absorption
We will look at how food travels through the digestive system, and the adaptation of the small intestine for absorption.
Once food has passed through the upper parts of the digestive system, it has been converted into small molecules that can be absorbed and used by the body. Proteins, for example, have been converted into what?

Once digestion is complete the products must be absorbed into the blood and the lymph systems for transport to the body's cells for use.
The products of digestion, including water, move through the lower gut (ileum, large intestine, rectum). They are pushed along by the walls of the intestine. What type of tissue creates this movement?

The digestive system is, in very simple terms, a long tube of muscles.
Some of of these muscles run along the tube, while others run around the tube. A wave of contractions spreads along the walls of the digestive system and pushes the digested food along, much like a Mexican wave.
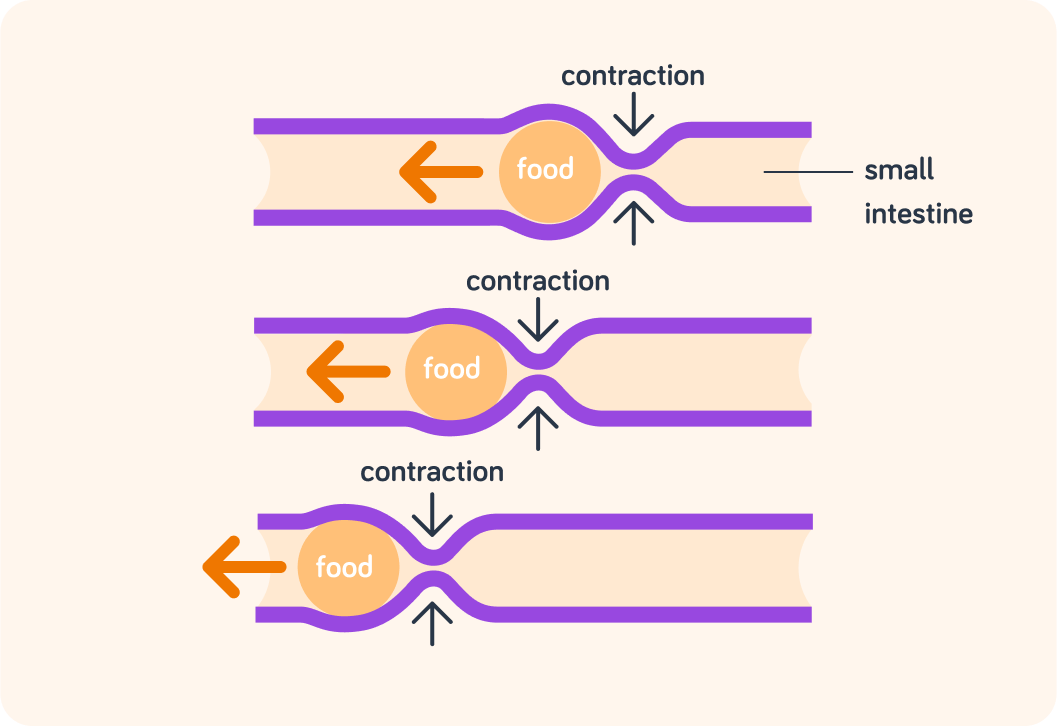
Which part of the upper digestive system uses this movement method to push food along from the mouth?


These waves of muscle contractions push the products of digestion through the gut in a process known as peristalsis. This happen in all parts of the digestive system, including the oesophagus.
The small intestine, from the stomach to the start of the large intestine, can be divided into two sections. One is the duodenum. Which one is the other much longer part?

The ileum is the section of the digestion system where the products of digestion are transferred from the inside of the gut to the blood and lymphatic systems. This is a slow process so the ileum is very long to help give enough time for absorption. How long do you think it is in an adult?

The inside of the ileum is not a flat smooth surface like it is in other parts of the digestive system.
The insides are folded into finger-like projection that stick out into the flow of digested products as they move through the ileum.

The finger-like projections are called "villi" (a single one is a "villus"). They produce a large surface area to allow more absorption of chemicals by active transport and which other slow passive process, do you think?


Each villus has three important adaptations that improve the efficiency of the uptake of the products of digestion.
The first adaptation ensures there is only a short distance for the chemicals to move from the gut into the blood and lymph. Which adaptation is this?
A) Lacteal
B) Rich blood supply C) Epithelium walls are only one cell thick


Fatty acids and glycerols cannot be dissolved into the plasma of the blood very well, so the second adaptation of the villus is the lacteal. The lacteal is a small branch of the lymphatic system that carries the fatty acids and the glycerols from the gut to the body so they don't enter the blood. What chemicals are fatty acids and glycerols digestive products of?
A) Carbohydrates B) Fats and oils (lipids) C) Proteins


The third adaptation is the rich blood supply. Each villus has a network of capillaries inside to help speed up the absorption of two major products of digestion. Which ones?
A) Fatty acids and glucose B) Amino acids and glycerols C) Amino acids and glucose


The capillaries from the villi combine to form the hepatic portal vein which carries these products to the liver for processing, before they can circulate around the rest of the body.
One important part of the diet does not get fully absorbed until it hits the large intestine. What is this vital chemical?

