electricity
Particles can either be positive, negative or neutral. The dynamics of charged particles is what gives rise to electricity.
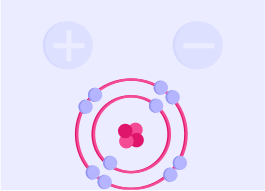
Positive and Negative Charges

Static Electricity

Conductors and Insulators

Static Charge in Real Life

Electric Fields
Current is the movement of charged particles, most commonly electrons moving through a metal.
The voltage or potential difference is the driving force behind a current. It is the energy per charge.
All components have some resistance, which is the electric "friction" obstructing the flow of a current moving through a material.
Circuits allow current to flow through components, providing energy to devices.

Circuit Diagrams

Diodes and LEDs

Series Circuits

Parallel Circuits

Total Resistance in Series and Parallel Circuits

Ammeters in Series

Electrical to Thermal Dissipation

E = IVt
Mains electricity is the alternating current (AC) electric power supplied to homes and businesses.
Power is the rate of energy transfer, and in the UK, energy is distributed by the National Grid.
Signals can either be digital or analogue. Digital signals can be used for logic gates.


