YOU ARE LEARNING:
Resistance, Length and Diameter
Resistance, Length and Diameter
The resistance of a wire is directly proportional to its length, and inversely proportional to its cross-sectional area or diameter.
What is the role of the wire in a circuit?

Although we want the wire to transport the current around the circuit, it will inevitably cause some ____________ to the current that flows through it.

If a current flowing through a wire experiences resistance, how will the length of the wire affect the amount of resistance the current experiences?

This graph shows the relationship between the length of the wire and resistance.
As the current flows through a wire it experiences resistance. Therefore, the longer the wire, the greater the resistance to the current.
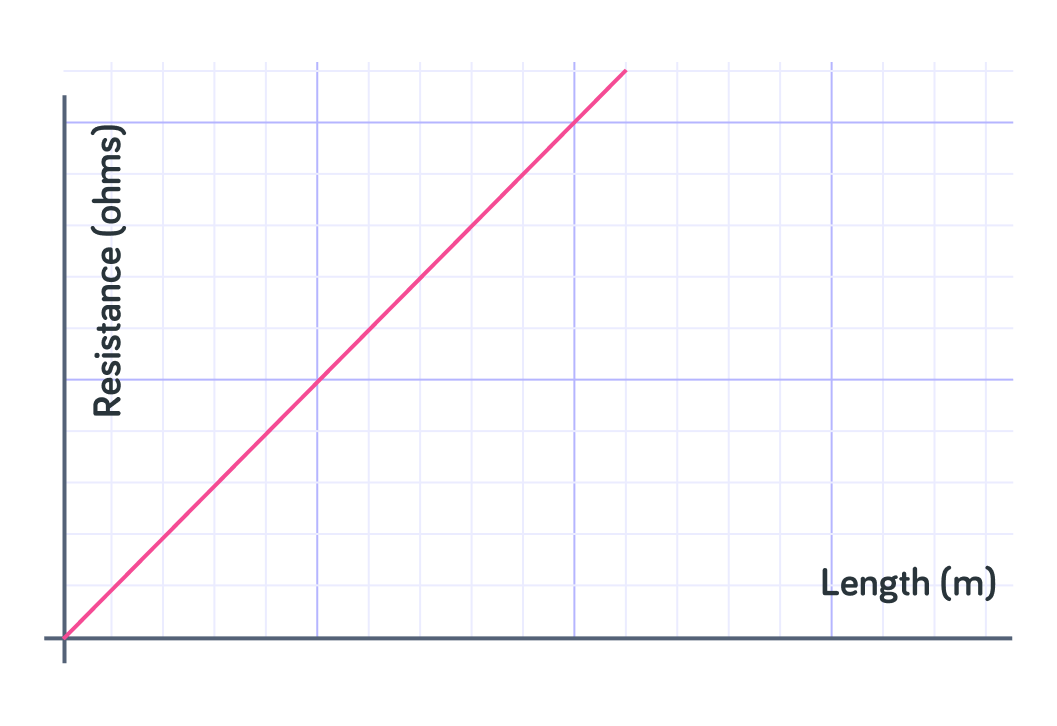
The relationship between the length of a wire and the resistance is directly __________.

The relationship between the resistance and the length of the wire is directly proportional. This means that for every set amount you increase the length of the wire, the resistance increases by a set amount too. This is shown by a straight line that goes through (0,0) on a resistance vs length graph.
If the current flows through the wire, what will happen to the resistance if you increase the cross-sectional area of the wire? In other words, you make the wire thicker.

This graph shows the relationship between the cross-sectional area of the wire and the resistance. The relationship is _____________ proportional.

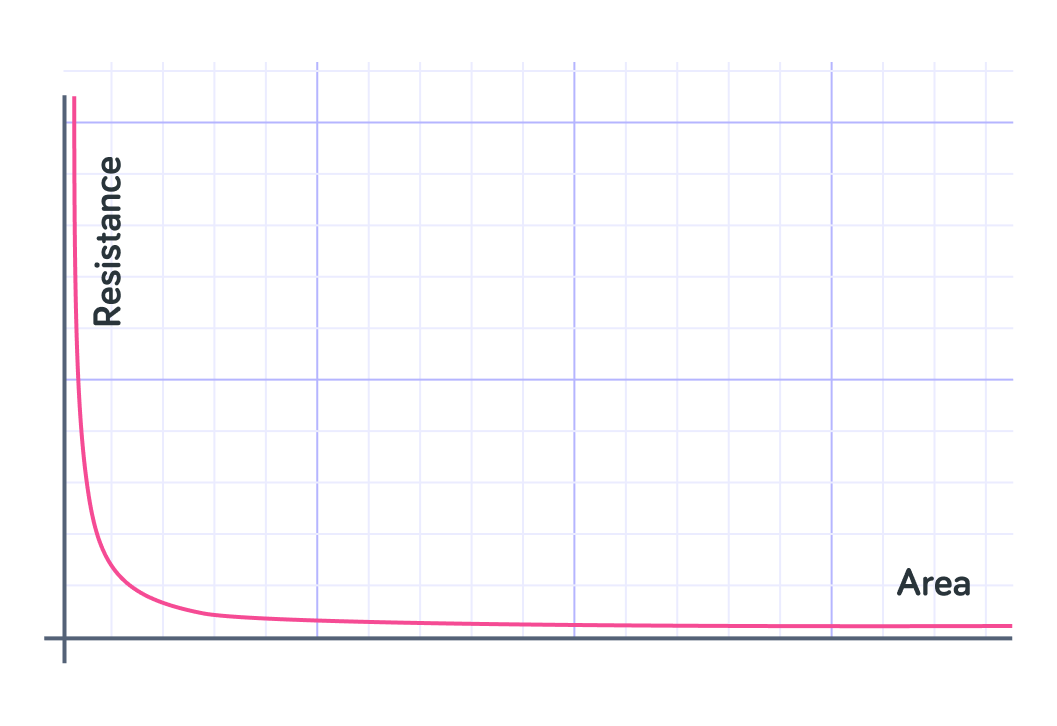
The relationship between the cross-sectional area of the wire and resistance is inversely proportional. As you increase the cross-sectional area of the wire the resistance decreases.
