YOU ARE LEARNING:
Wires, Fuses and Plugs

Wires, Fuses and Plugs
This lesson looks at the components in a plug; the live wire, the neutral wire, the Earth wire, and the fuse.
The image shows the inside of a plug.
Notice there are 3 wires and a fuse.
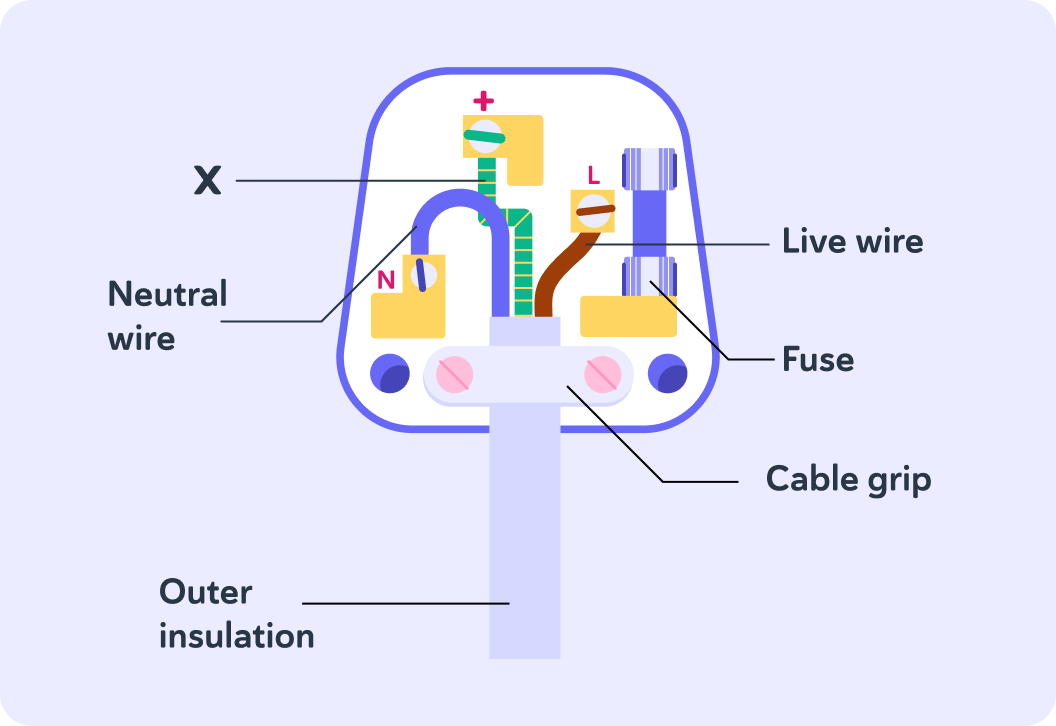
Do you know what the name of the wire labelled X is? Sometimes known as the ground wire, it is a safety wire which directs current away from components in order to prevent dangerous electric shocks or fires.


Which of the 3 wires actually carries the current?
A) Earth B) Live C) Neutral
Answer A, B or C.


Which of the 3 wires is a safety wire to ensure the appliance does not conduct electricity?
A) Earth B) Live C) Neutral
Answer A, B or C.


Which of the 3 wires is there to complete the circuit?
A) Earth B) Live C) Neutral
Answer A, B or C.


So there are 3 wires in the plug.
The earth wire (green and yellow) is the safety wire to prevent the appliance conducting electricity.
The live wire (brown) carries the electrical current.
The neutral wire (blue) completes the circuit.

If the earth wire was faulty, what would happen if the live wire was loose, and somebody touched the case of a plug?

Which two wires in a plug form a complete circuit with a household appliance? Select the correct two from the list below.

You can select multiple answers
If mains electricity has a voltage of 230 V, what is the potential difference across the live and neutral wire going to be?

Have a good look at this table.
It shows the potential differences across the wires in a plug.
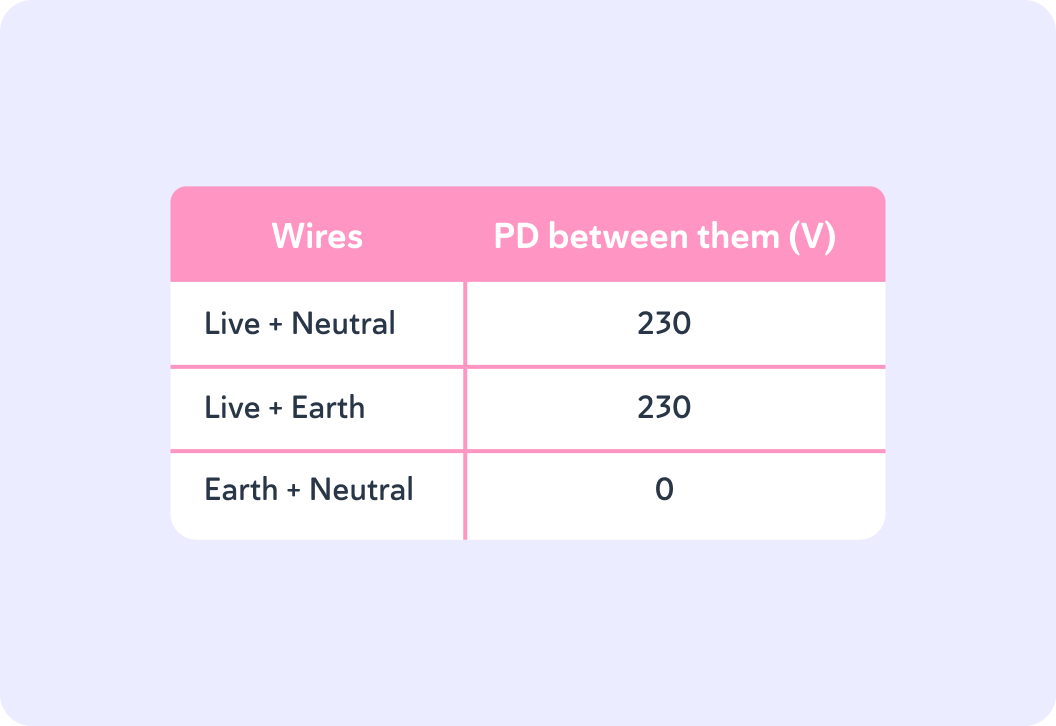
Why is there 0 V between the earth and neutral wire?
A) They both carry the current. B) Neither of them carry the current.
Answer A or B.


The live wire is the only wire to carry the current, and therefore it is the only wire to have a potential difference across it.
This is why there is a difference of 230 V between that wire and the other two.

Why are there fuses in plugs?

Fuses prevent circuits from overheating if the current gets too high. The fuse contains a very thin wire with a low melting point. How does that tiny wire prevent overheating?

The role of the fuse is to prevent the components overheating and potentially catching fire. The fuse contains a very thin section of wire with a low melting point. If too much current travels through it, the tiny wire will break and the circuit will be incomplete. This means that the current can no longer travel through the circuit.
