YOU ARE LEARNING:
Total Resistance in Series and Parallel Circuits

Total Resistance in Series and Parallel Circuits
This lesson compares the total resistance in a series circuit and a parallel circuit. Adding resistors to a parallel circuit will reduce the total resistance, unlike in series circuits.
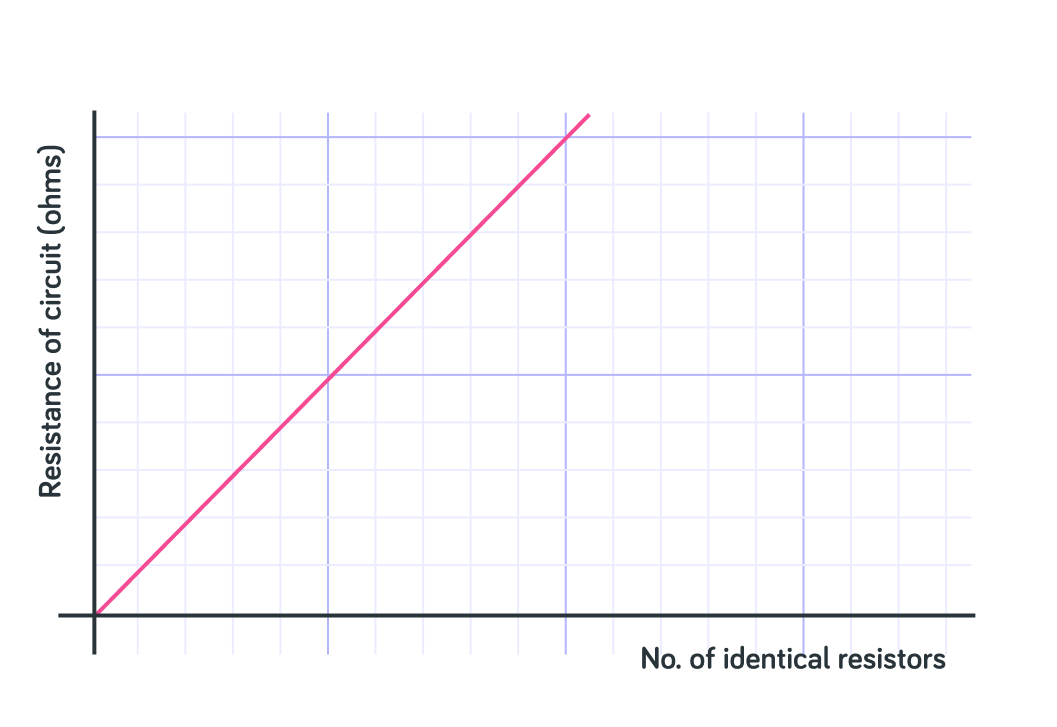
In a series circuit, the more resistors you add the ________ the total resistance of the circuit.

In a parallel circuit, the more resistors you add, the ________ the total resistance of the circuit.

If you increase the number of resistors in a parallel circuit, the total resistance of the circuit decreases, because...

Which of the following is the correct formula for calculating resistance in a circuit?

What would the total resistance be in this circuit?

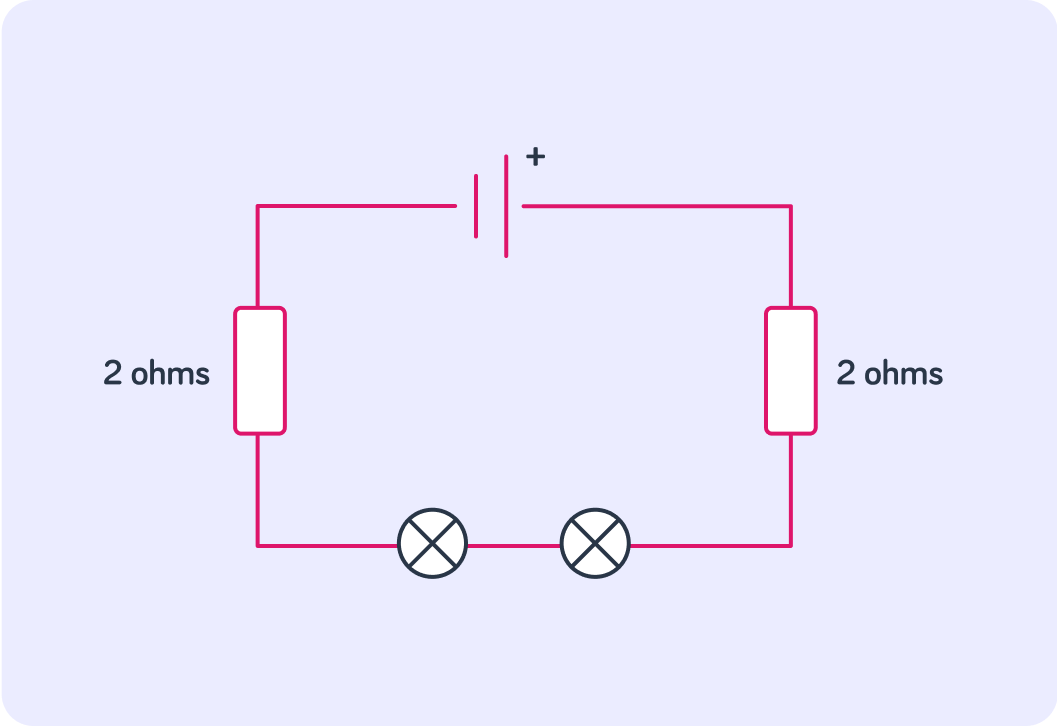
To calculate the total resistance in a series circuit, we simply add together the resistances of each component.
We do not need to worry about the current or voltage for calculating total resistance.

This is the same circuit, but this time we have added the resistors and bulbs in parallel.
This time we do need to take into account the current and the voltage.
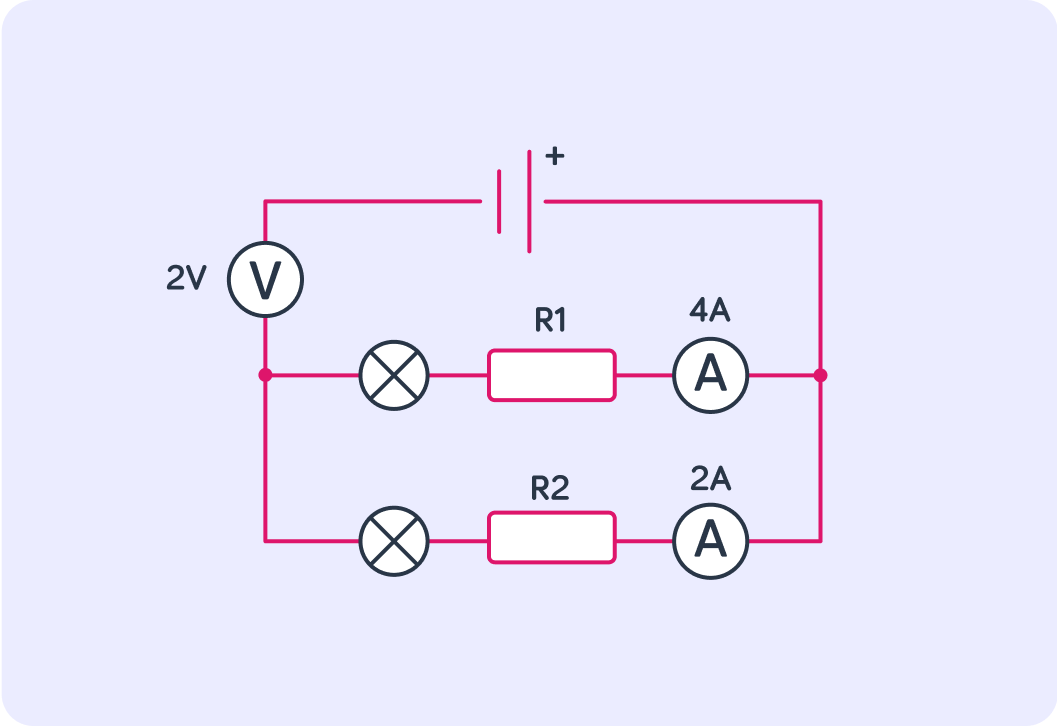
Using R=IV, calculate the resistance across R1.


Now calculate the resistance across R2.


What is the total current in the circuit?


What is the total resistance of the circuit? Give your answer correct to 2 decimal places.


The total resistance of the circuit is 0.33Ω which is not the same as the sum of both of the resistances across the two resistors, which would be 0.5Ω+1Ω=1.5Ω.
So if these resistors were connected in series, the total resistance would be higher than when they are connected in parallel.

So in series circuits, all the current flows through one pathway. This means that the total resistance equals the sum of each of the resistors' resistances.
In parallel circuits, every time you add a resistor, you create another pathway for the current to flow which increases the amount of current. Remember R=IV - if you increase the current I that means that you will decrease resistance R.
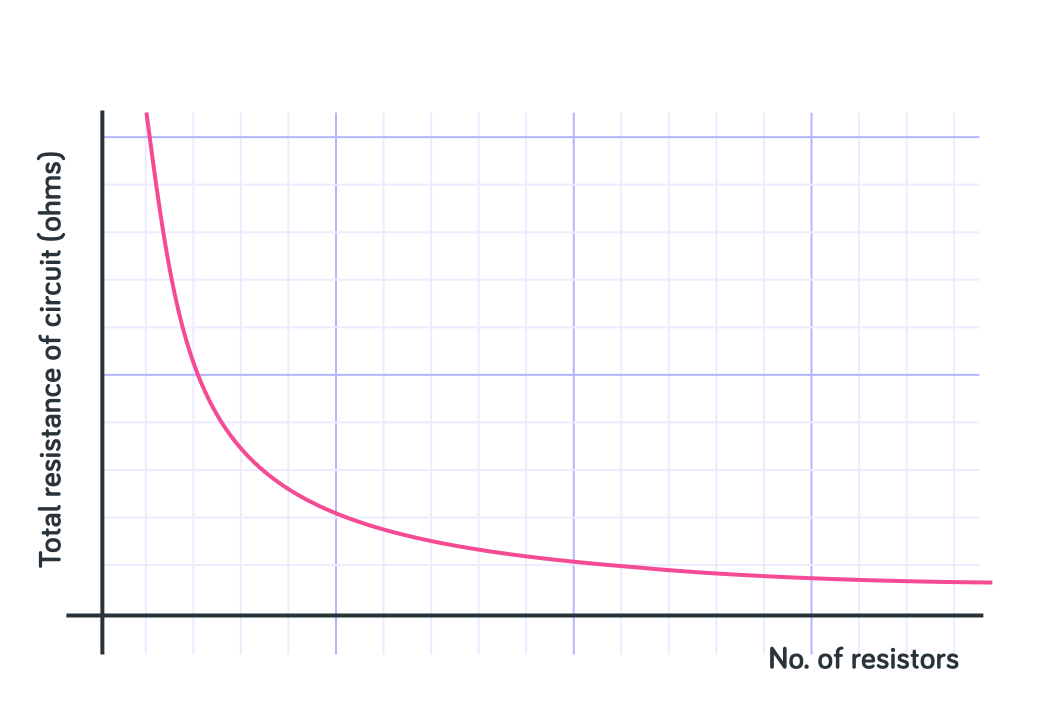
Does this graph show the relationship between resistors and total resistance in a 'series' or 'parallel' circuit?

Here you can see the graph for the resistance for a PARALLEL CIRCUIT.
As you increase the number of resistors, the total resistance of the circuit drops.