YOU ARE LEARNING:
The Eye and Its Structure
The Eye and Its Structure
The eye is a sensory organ that allows us to see. We will examine its structure and components.
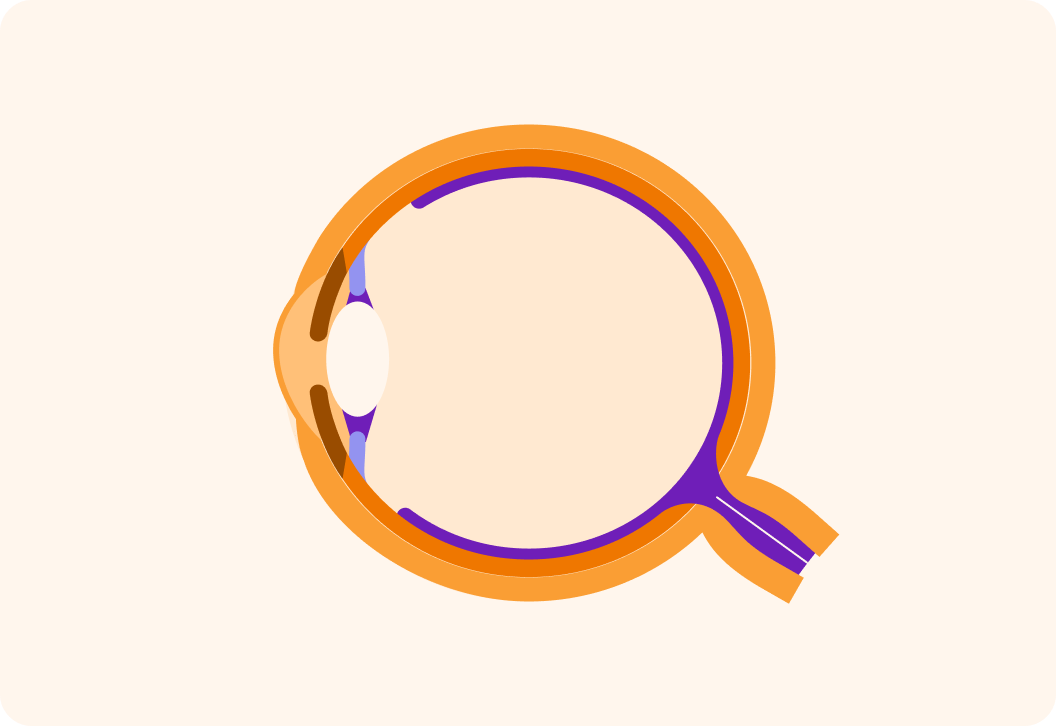
This is an image of an eye from the side. Is the eye a cell, a tissue or an organ?
A) A cell
B) A tissue
C) An organ


Ultimately, it is the eye that allows us to ______ things.

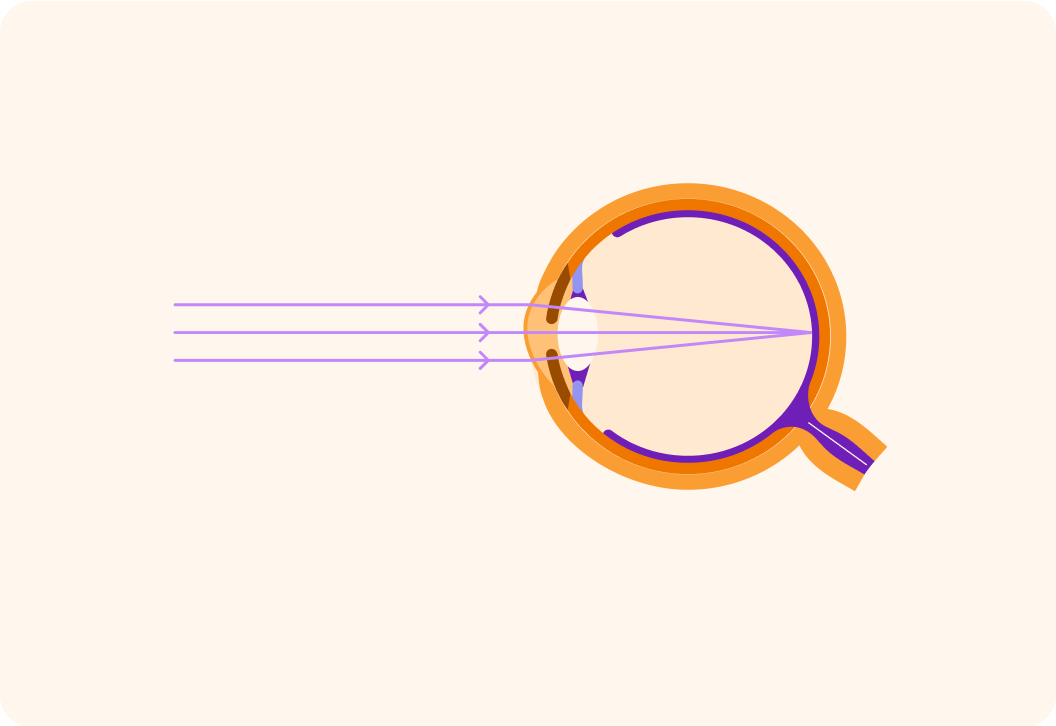
The eye takes in rays of _________, focuses them and sends a message to the brain.


So the eye is a very complex organ, made up of lots of different types of tissue.
It takes in light, focuses it and sends the information to brain. That, ultimately, allows us to be able to see.

It is the retina in the eye that is sensitive to light
It has two different types of receptor cells that can detect light: Rod cells and cone cells.

One of these types of receptor cells are responsible for colour vision. Which ones do you think that is?
A) Rod cells B) Cone cells


When do you best see colour?
A) During the day B) In the night


The cone cells are responsible for colour vision and they work best in bright light
People who are colour blind have issues with their cone cells.

Rod cells, on the other hand, do not help us see colour. When do you think they work best?
A) In bright light B) In dim light


Rod cells don't help us see colours like cone cells
On the other hand, they help us be able to see even in dim conditions where cone cells don't work very well.

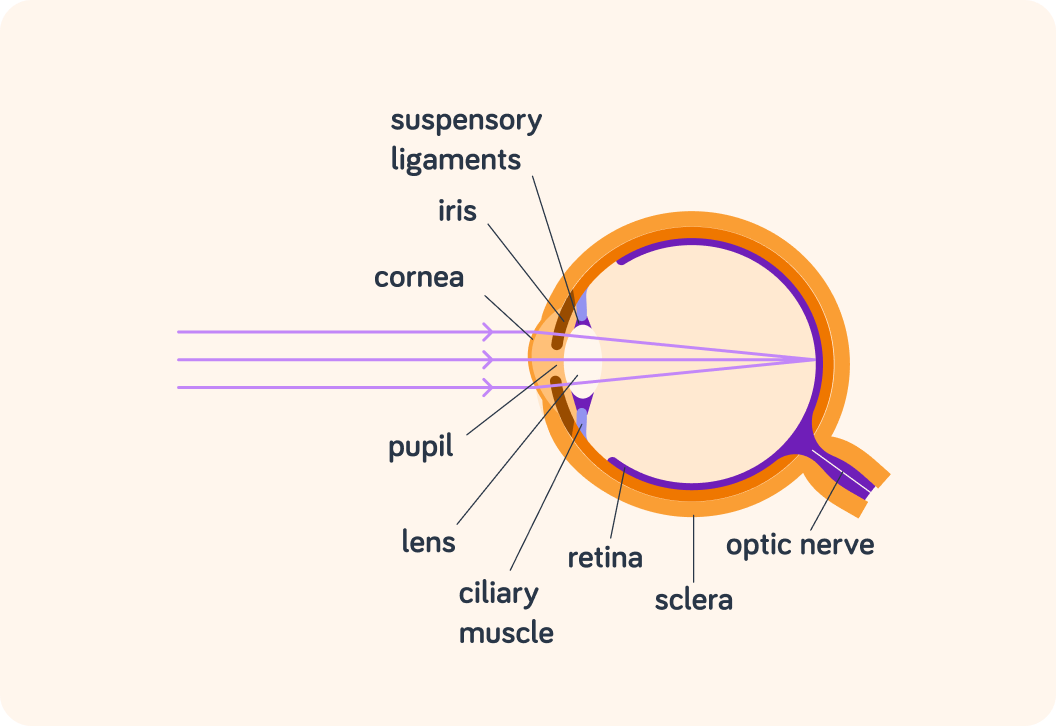
Light first enters the eye through the ___________.

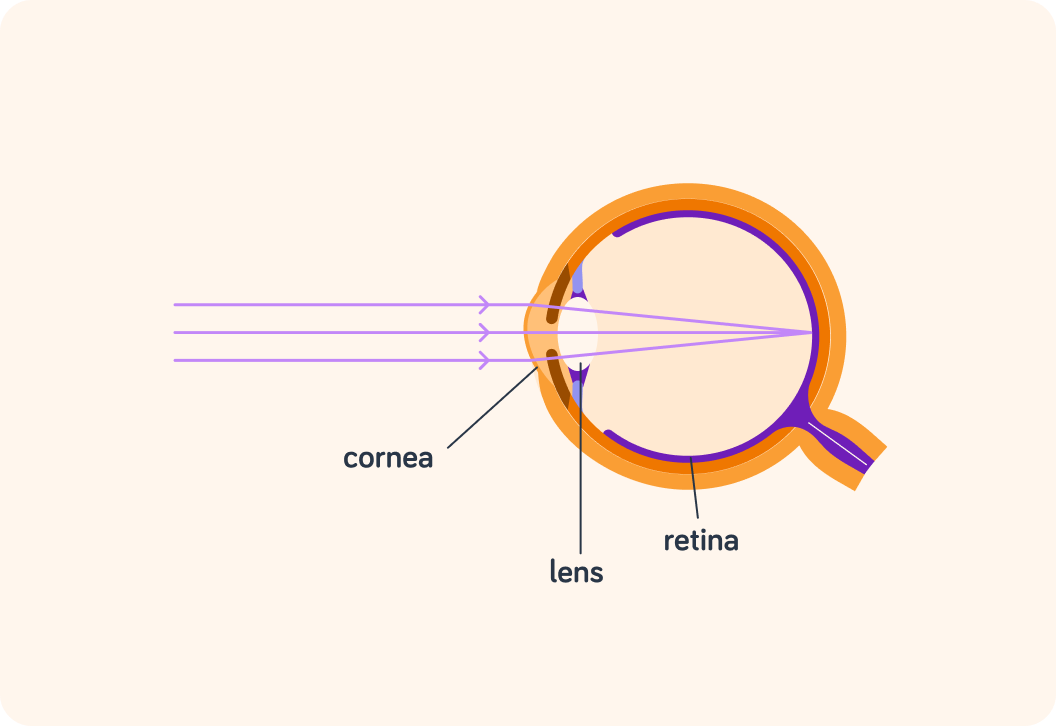
After the cornea, the next thing the light hits is the ________.


Now, think about a camera. What does a lens do to an image?
A) It colours it. B) It focuses it. C) It animates it.


Just like the lens in a camera, the cornea and lens in your eye focus light that comes in to form a clear image.
They "refract" (bend) the light so that it meets in one spot on the retina.

What is the black circle in your eye called?

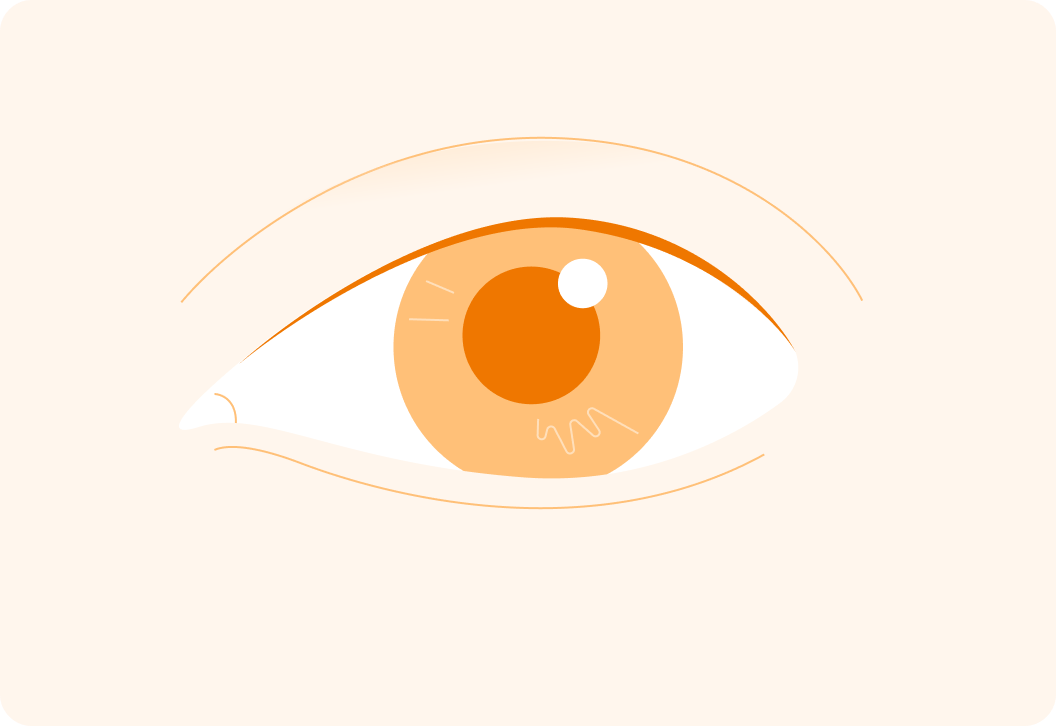
Your pupil can change size. It is normally bigger or smaller in darker conditions?
A) Bigger B) Smaller


The bigger the pupil is, the more light is let into the eye.
The darker the conditions, the bigger the pupil to allow us to see better.
The brighter the conditions, the smaller the pupil to protect the eye from too much light entering it.

What do you think the pupil actually is?
A) A blind spot B) A patch C) A hole


So the pupil is actually a hole. But a hole in what?


The pupil is a hole in the iris
The iris is a coloured, circular muscle that controls the size of the pupil.
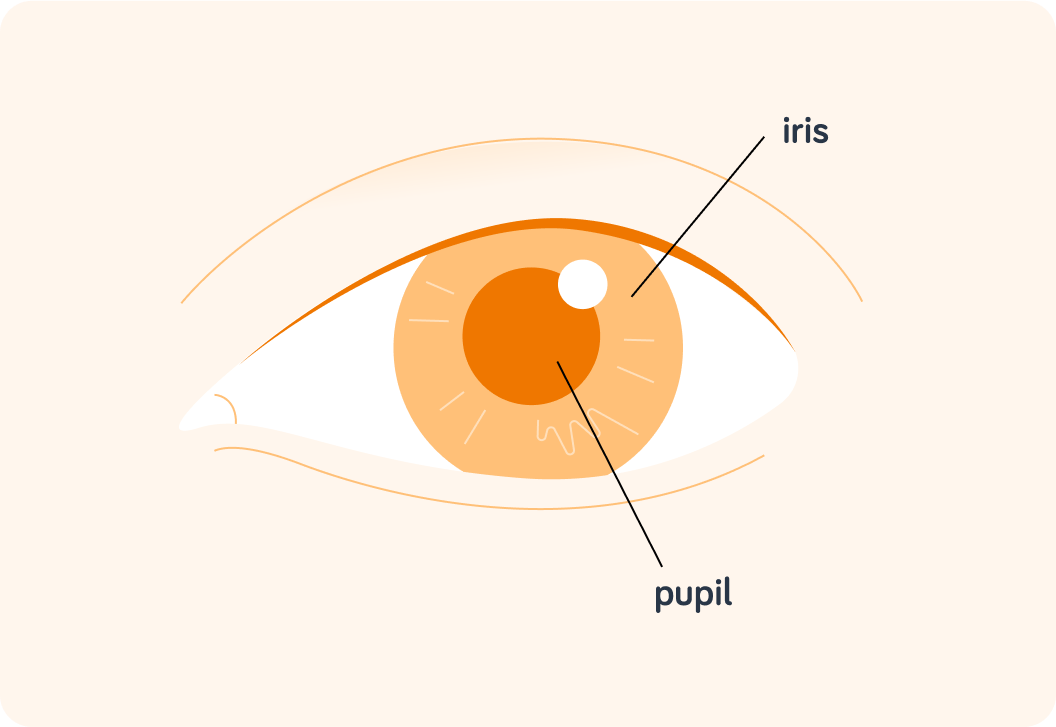
If someone suddenly turns on a bright light in the middle of the night, what do you do? Do you open or close your eyes?
A) Open them B) Close them


When a bright light is all of a sudden turned on, we want to shield our eyes from the light
This is because our eyes haven't adjusted to the bright light at all. The iris hasn't had a change to contract to make the pupil smaller, so there is way too much light entering the eye.

The iris is not the only muscle in the eye. What is the other muscle in this diagram called?

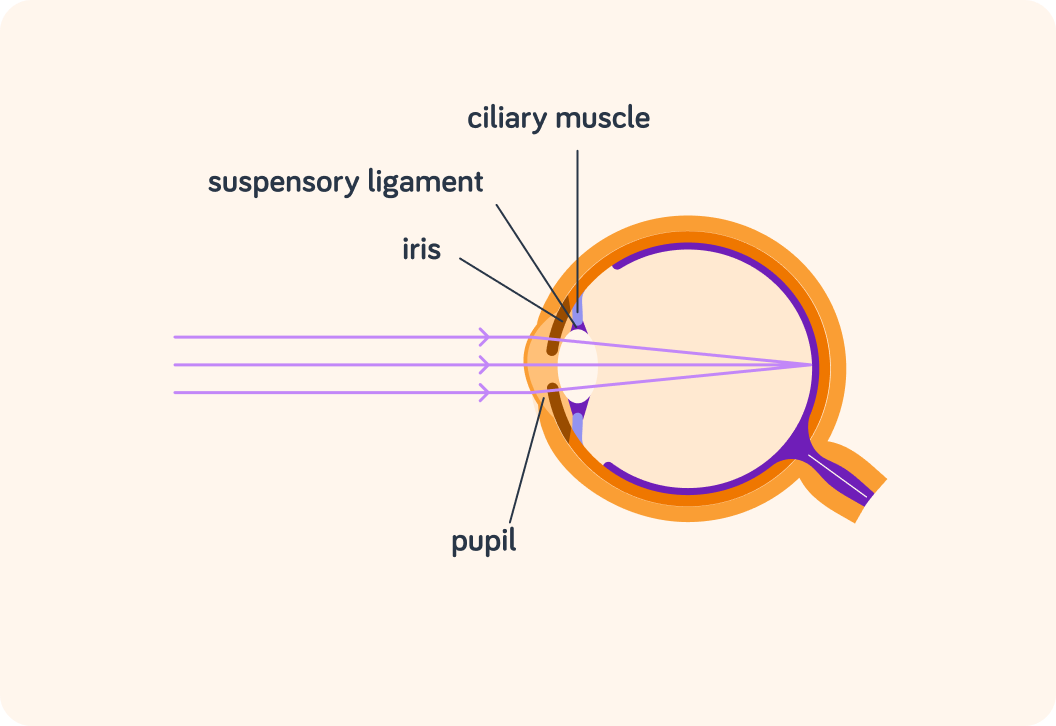
The ciliary muscle can contract and relax just like any other muscle. When it does that, it helps the eye focus by changing the shape of the ___________.


What's the name of the structure that connects the ciliary muscle to the lens?


So the lens changes shape by the ciliary muscle either contacting or relaxing
This helps the eye focus light on the retina.

Now, when the light is detected at the retina, it creates an electric impulse. What makes sure that impulse is carried to the brain?

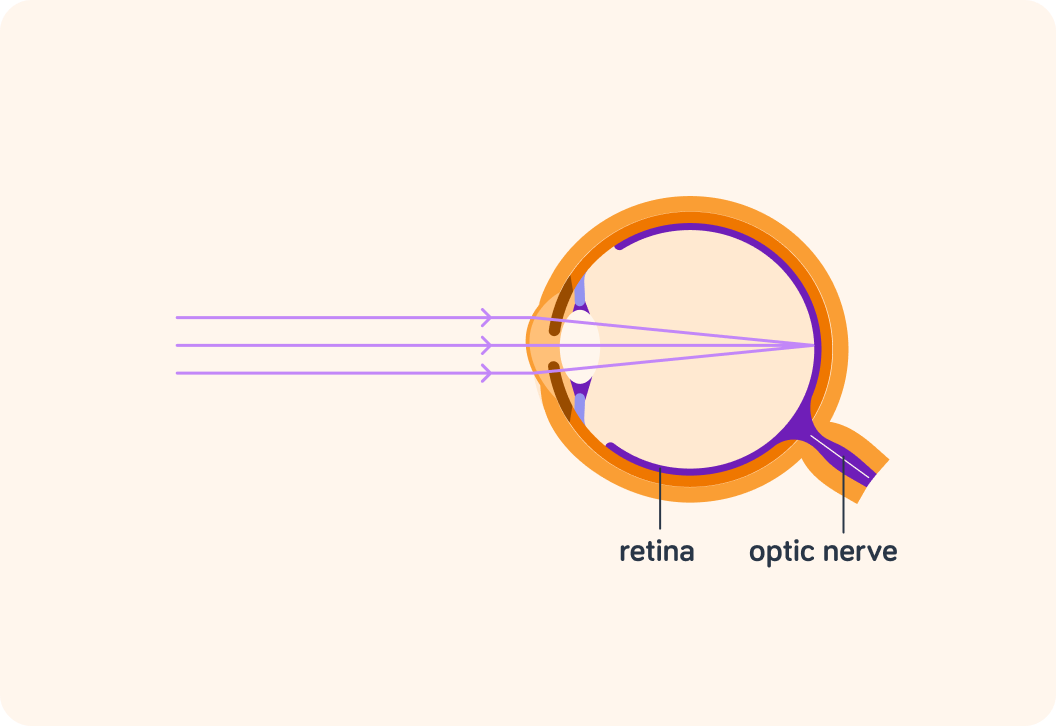
True or false? If the optic nerve is destroyed, you can still see.


Without the optic nerve sending the impulse to the brain, you will not be able to actually see anything
Light will enter your eye still and focus on the retina, but you don't recognise that until the impulse reaches the part of our brain that is responsible for vision. If they don't get there, you won't actually "see".

Finally, what do we call the outside layer of the eye? It's the only thing in this diagram that hasn't been mentioned yet.

The sclera goes all around your eye and when you look in the mirror you can see quite a bit of it. What colour is it normally?


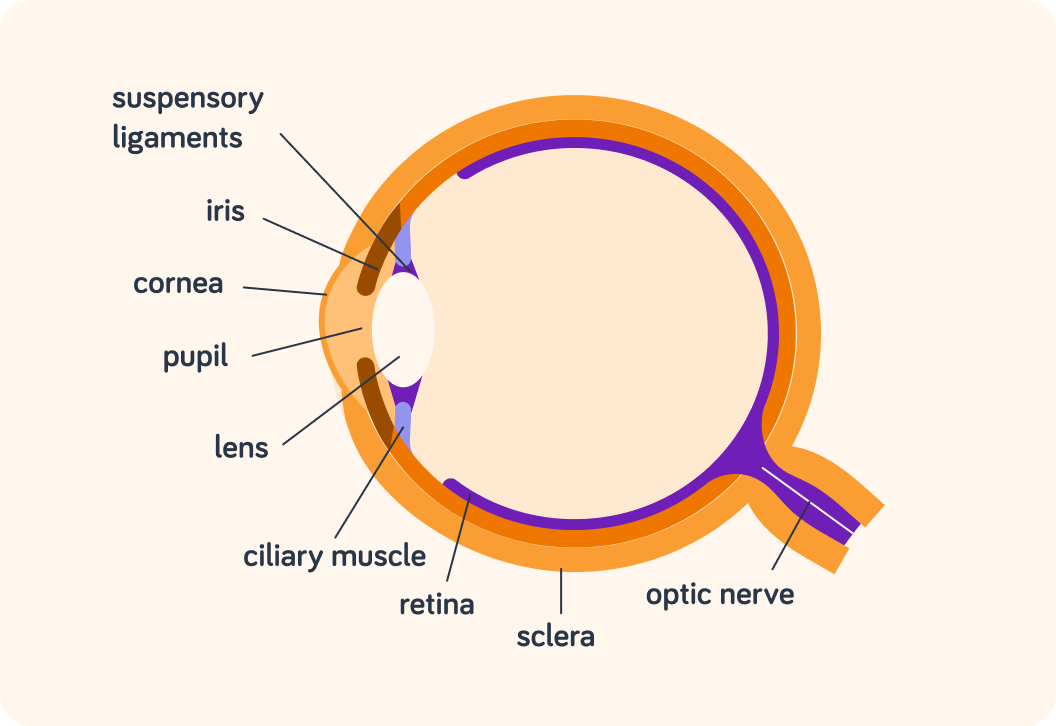
So to summarise, light enters you eye through the pupil
The cornea and the lens focus the light with the help of the ciliary muscle and the suspensory ligament.
The pupil can change size
In dim conditions, the iris will relax so more light is allowed in through the pupil. In bright conditions, the iris will contract to make the pupil smaller and protect the eye from too much light entering it.

When the cornea and lens have focused the light, it hits the retina
The retina has cone cells that are responsible for colour vision and rod cells that make us better able to see things in the dark.

An electric impulse is created which the optic nerve carries to the brain
You only actually experience "seeing" things when the impulse has reached the visual centre at the back of your brain!

The white part of your eye is part of the sclera
It goes all around the outside of your eye. You only see a small part of it when you look in the mirror.

