YOU ARE LEARNING:
Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic Cells

Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic Cells
Eukaryotes are a type of organism cell that has a nucleus. Prokaryotes are a type of living cell that has no nucleus, rather its DNA is free in cytoplasm.
This is an example of a eukaryotic and a prokaryotic cell
The eukaryotic cell is to the left, and the prokaryotic cell is to the right. This lesson will look at 4 big differences between them.
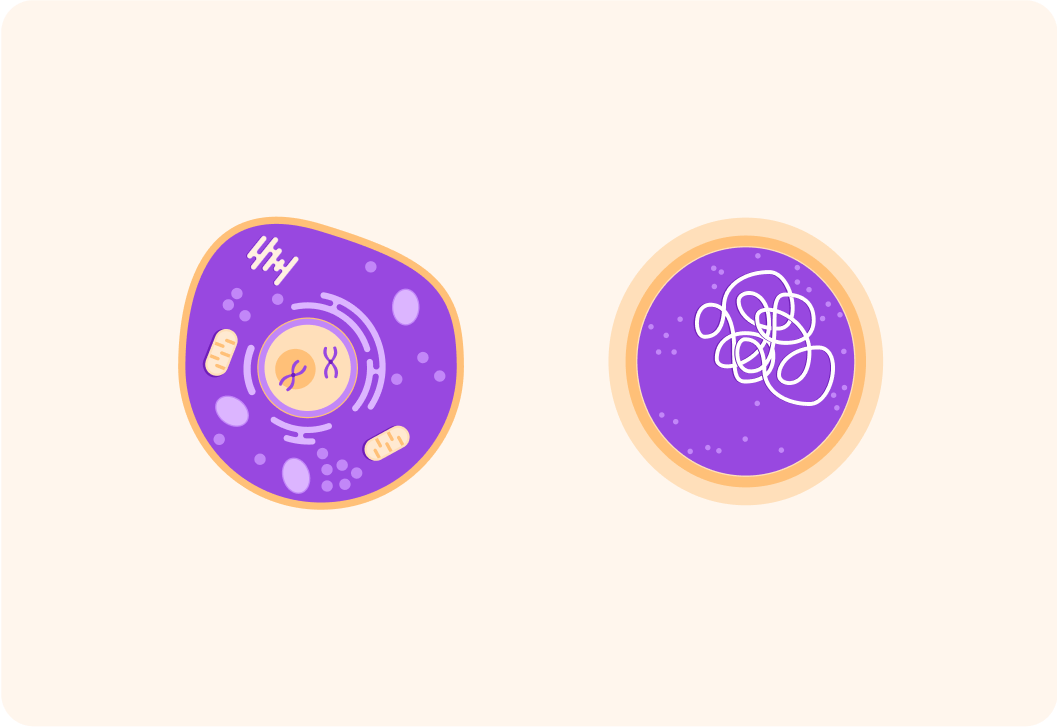
First of all, eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells belong to different kinds of organisms.
Eukaryotic cells belong to multicellular organisms. What do you think that means?

Multicellular organisms are also called eukaryotes. Pick the four options that you think are eukaryotes.

You can select multiple answers
Now, prokaryotes are unicellular organisms which means...

What kind of organism do you think a prokaryote is?

So eukaryotic cells belong to multicellular organisms
These are animals and plants
Prokaryotic cells belong to unicellular organisms
For example bacteria.
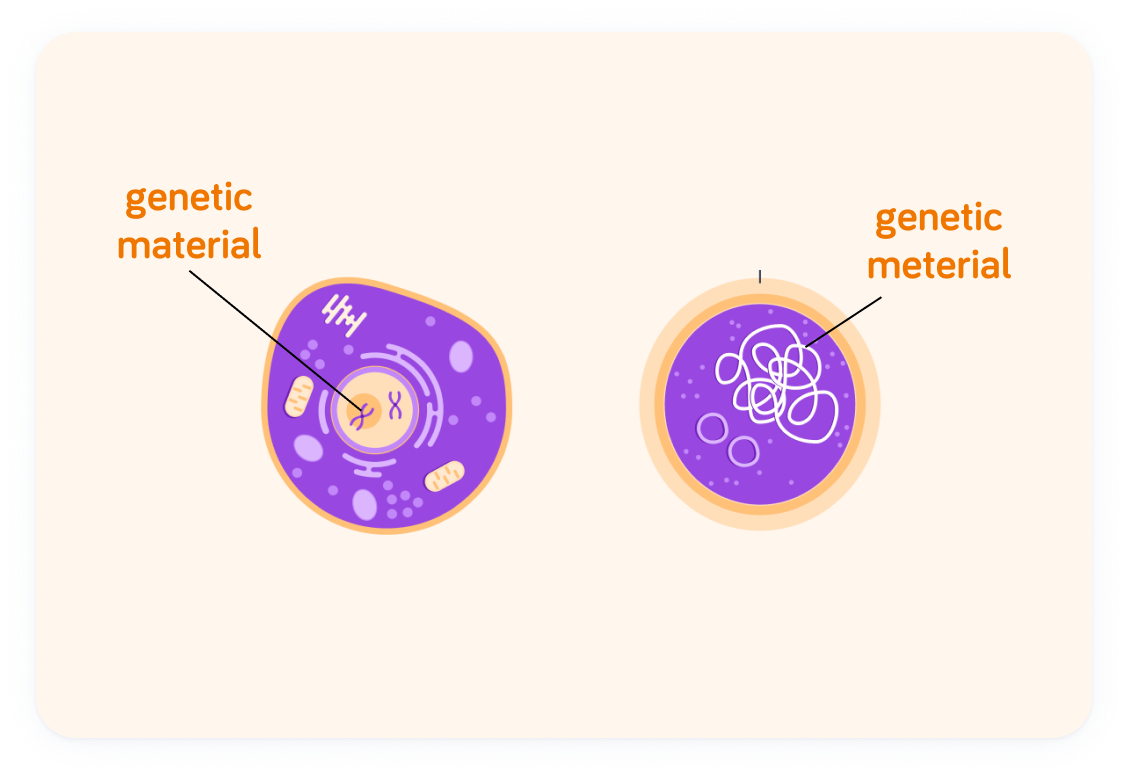
The second big difference is to do with the genetic material in the cells
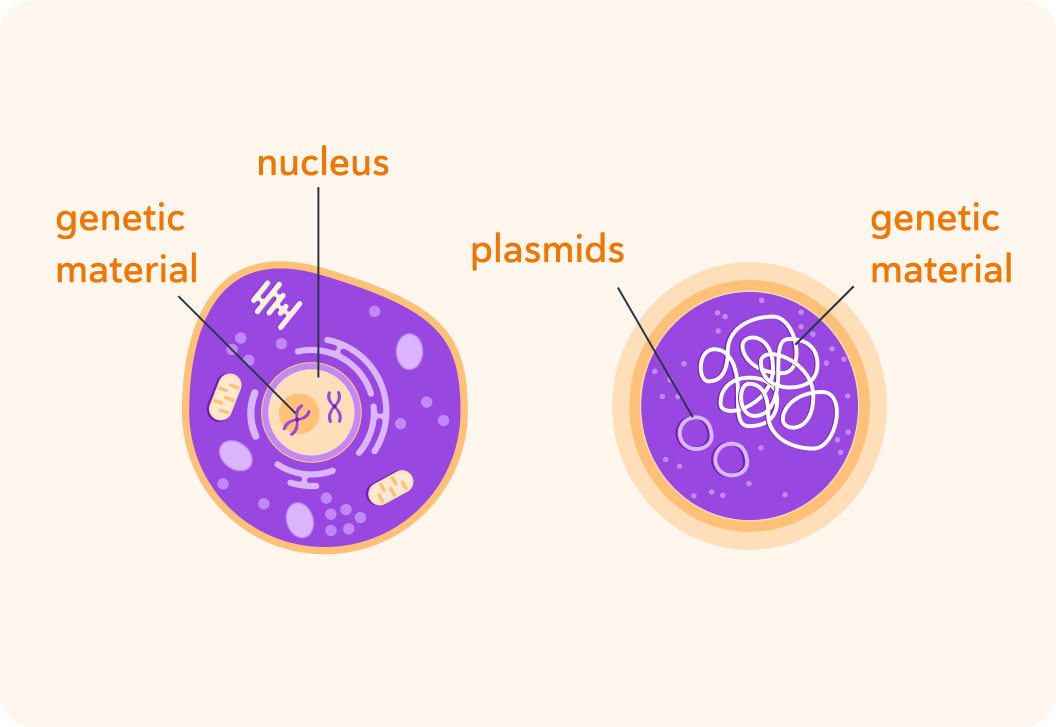
In animal and plant cells (eukaryotes), the genetic material is stored in the cell nucleus.
Which of these statements is true?


So the prokaryotic cell has no nucleus. The genetic material is stored simply in the cell's ___________.


The genetic material in prokaryotic cells sit in one big scrunched up loop
But some bacteria also have plasmids that are little rings of DNA outside the main loop of genetic material.
The third difference is to do with the cell wall. Do all eukaryotic cells (animal and plant cells) have a cell wall?

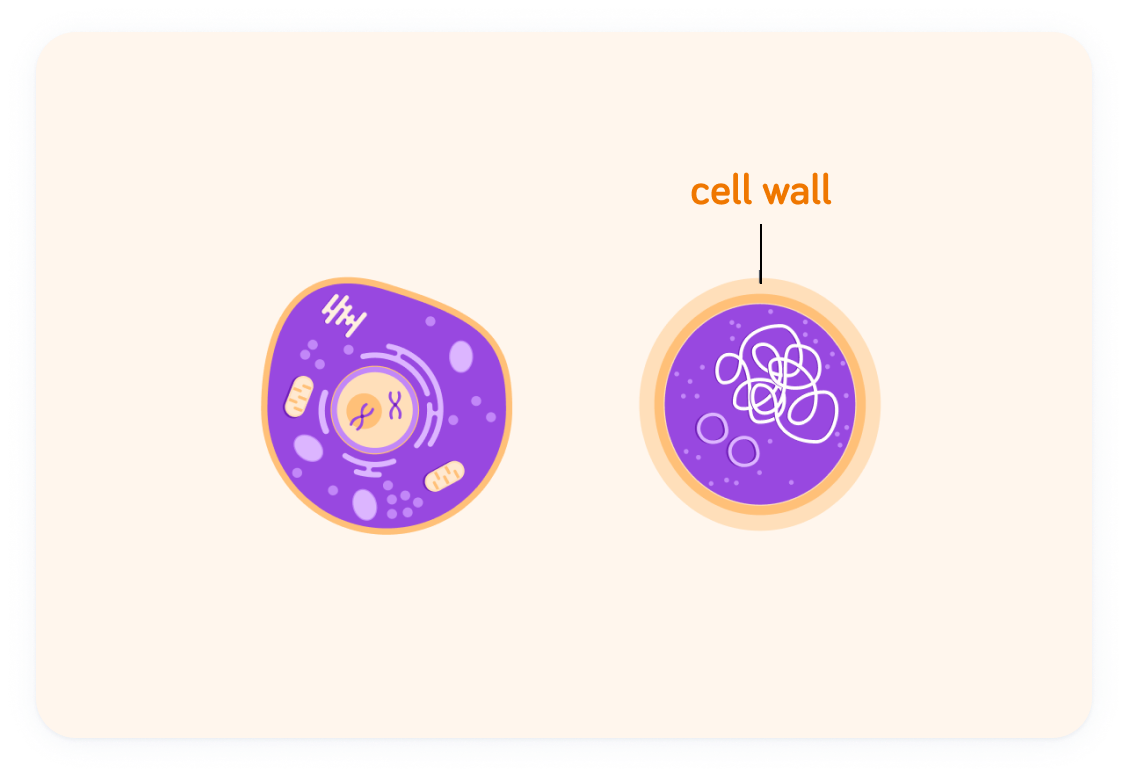
All prokaryotic cells have a cell wall
Eukaryotic cells only have a cell wall if they are plant cells - not if they are animal cells.

The fourth and final difference between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells is to do with their size
One of them is much smaller than the other!
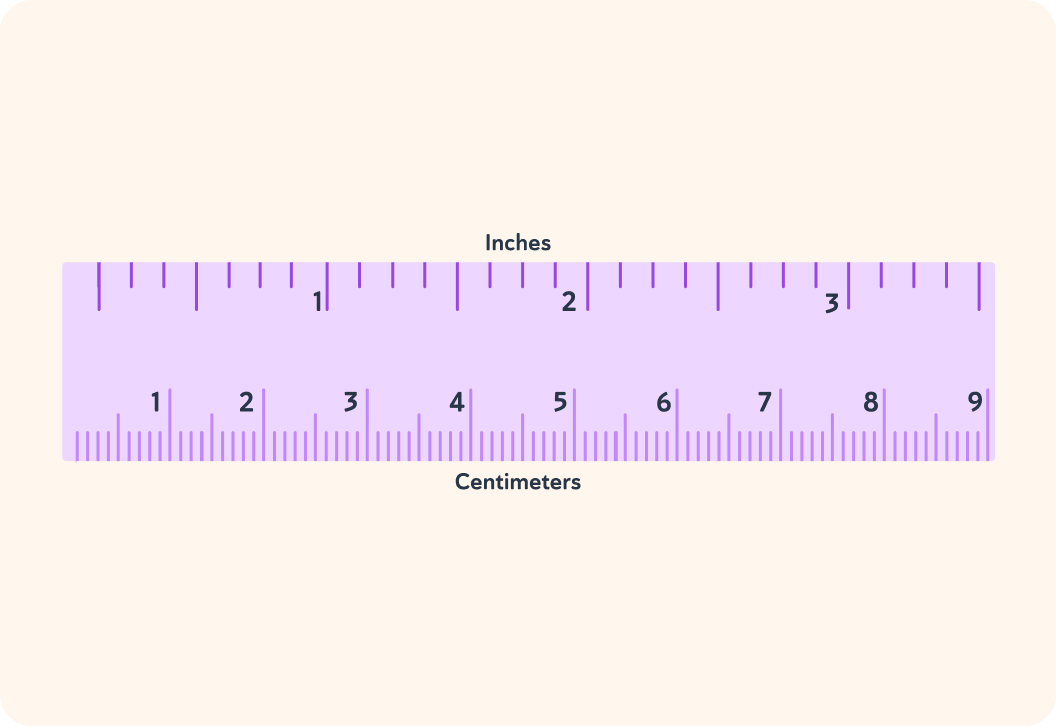
A eukaryotic cell is between 0.1 and 0.01 millimetres. How many eukaryotic cells does that mean you can fit in a millimetre?


Do you think prokaryotic cells are bigger or smaller than eukaryotic cells?


Prokaryotic cells are much much smaller than eukaryotic cells!
You can fit 10-100 eukaryotic cells in a millimetre. You can fit 500-1000 prokaryotic cells in a millimetre.

To summarise! Eukaryotic cells and prokaryotic cells belong to different kinds of organisms
Eukaryotic cells belong to multicellular organisms (plants and animals). Prokaryotic cells belong to unicellular organisms (for example bacteria).

Prokaryotic cells don't have a nucleus
The genetic material is one big loop that is stored in the cell's cytoplasm. Some bacteria also have little rings of DNA in the cytoplasm - plasmids.

All prokaryotic cells have a cell wall
Eukaryotic cells only have a cell wall if they are plant cells. Animal cells don't have a cell wall.

Prokaryotic cells are much much smaller than eukaryotic cells!
You can fit 10-100 eukaryotic cells in a millimetre. You can fit 500-1000 prokaryotic cells in a millimetre.

