YOU ARE LEARNING:
Anti-Microbial Resistance

Anti-Microbial Resistance
Unfortunately, although antibiotics have helped save millions of lives, there is always pressure to produce new types of drugs, due to anti-microbial resistance. This is when microbes like bacteria become resistant to commonly used antibiotics.
Anti-microbial resistance is when microorganisms become resistant to the substances that are meant to kill them. What is one common example?

Take a look at how this chest infection is passed from person to person.
The purple bacteria are normal. The orange bacteria are resistant bacteria. Each person has taken antibiotics to cure their infection, but some bacteria live on in the next person who contracts the illness, nonetheless.
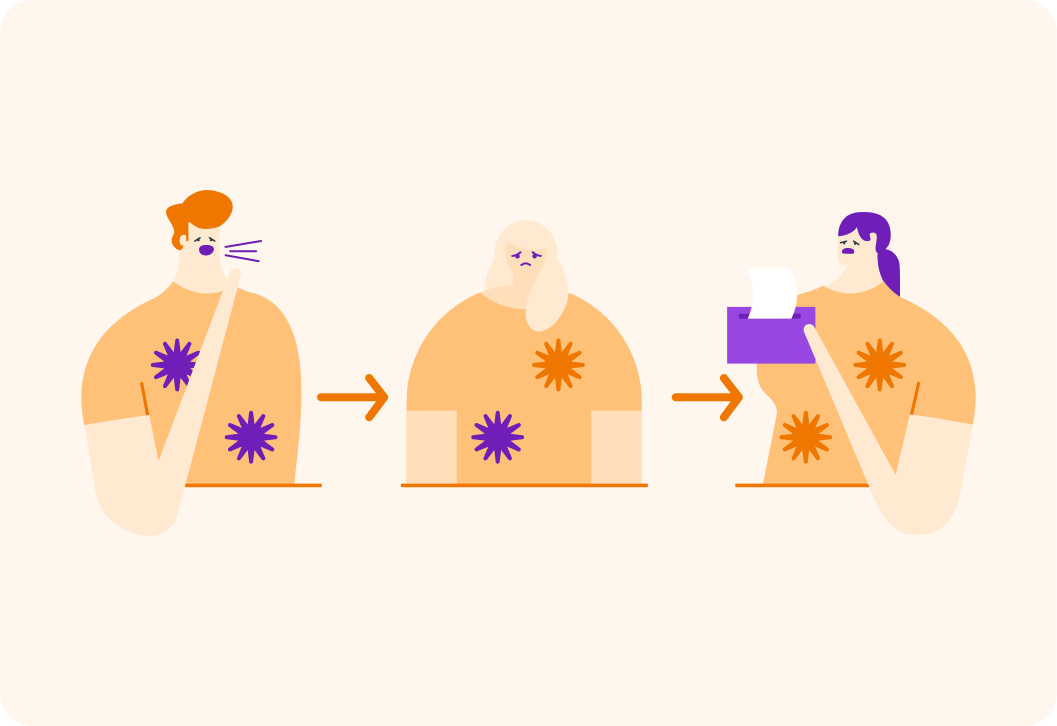
What do you notice about the bacteria?
A) The bacteria don't change between people. B) The resistant bacteria are becoming more numerous from person to person. C) The bacteria become less resistant the more people they infect.
Answer A, B or C.


Bacteria can become resistant to antibiotics naturally, through natural selection.
But misuse of antibiotics, such as not finishing a full course of antibiotics or taking the wrong antibiotic, can speed up this resistance.

Do you think the first person in this diagram used antibiotics properly? Answer yes or no.


Antibiotic resistance is a big concern! Why?

One form of resistant bacteria is MRSA (methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus). This bacteria is resistant to most antibiotics, including the very strong antibiotic methicillin.
It takes a few steps to produce an antibiotic resistant bacteria. First, there has to be a change in the DNA of the bacteria. What is a change in DNA called?

This mutation may change the traits of the bacteria. This could mean that they got better at defending themselves when antibiotics try to kill it.
If normal bacteria without the mutation get killed by antibiotics, will this be an advantage or a disadvantage to the resistant bacteria?

Without the non-resistant bacteria, the resistant bacteria will have less competition and more resources available. This means they can reproduce better and rapidly! We would have to be able to produce a new form of antibiotic to kill them.
However, we only have a limited number of antibiotics. If we run out of antibiotics to kill a particular bacteria, then we will struggle to defend against that bacteria.
What do you think we can do to reduce antibiotic resistance? Pick all the options you think are correct.

You can select multiple answers
Antibiotic resistance that can affect the global human population. Imagine a superbug that was resistant to all antibiotics! Humans travel all over the world today, so this superbug would be able to spread very quickly from country to country. Millions upon millions of people could get seriously ill and we might not be able to help them.
