YOU ARE LEARNING:
How Do Vaccines Work?

How Do Vaccines Work?
Vaccines involve introducing weakened pathogens to the immune system, which allows it to learn which antibodies to produce to destroy the pathogen. If the same pathogen attacks, the immune system can respond quickly.
A vaccine is typically an injection consisting of a dead or weakened pathogen, whose __________ create an immune response in the body.

What substances are created by lymphocytes that recognise antigens and destroy pathogens?

Vaccines provide the body with a weakened pathogen, whose antigens will give the immune system the opportunity to produce antibodies, without the person getting ill with the disease. If the same type of pathogens infect the person again, they will not get ill. This is called immunity.
Vaccines give the immune system a "practice run" to create antibodies to a particular pathogen. How do vaccines prevent us getting ill from a particular disease?

When pathogens enter the body through a vaccine, two types of white blood cell work to remove it from the body. Which two are they?

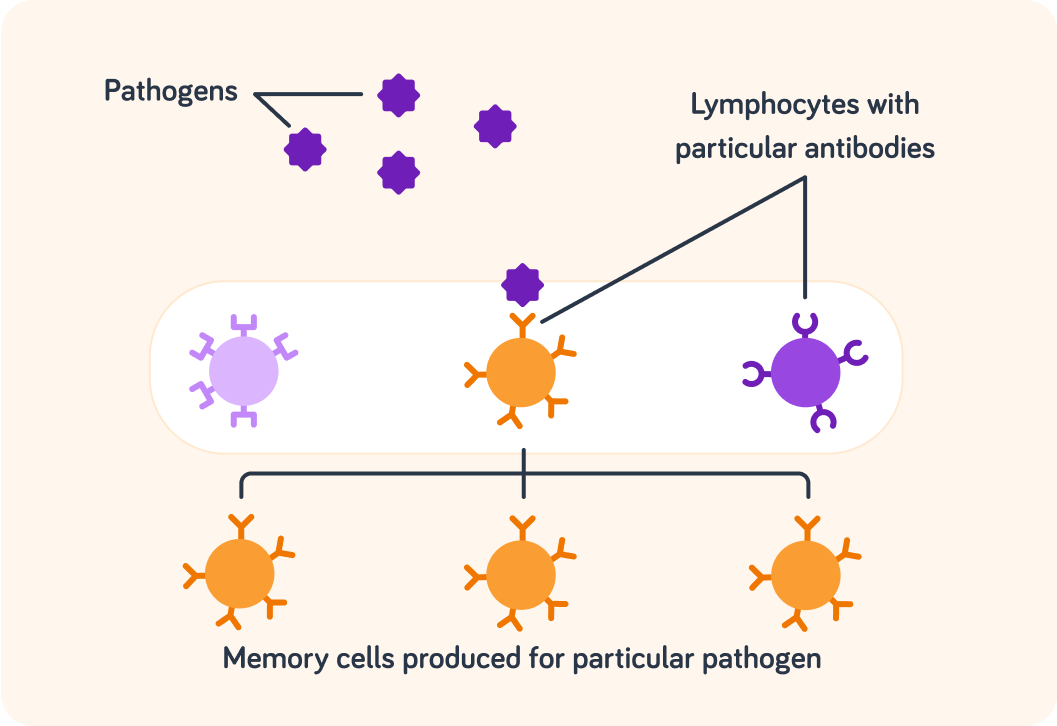
The lymphocytes leave a form of antibody-producing white blood cells in the blood that "remember" specific pathogens and release specific antibodies to attack them. What are these antibody-producing cells called?


What do memory cells give us? Pick the most correct answer.

If someone was vaccinated for disease A, and produced memory cells, would they protect the person if they became infected with disease B?

Which of these statements are correct about vaccines?

You can select multiple answers
