YOU ARE LEARNING:
Physical Barriers
Physical Barriers
Physical barriers are the first form of defence the body has against pathogens. They help to trap pathogens and include the skin, and tiny hairs in the nose and airways.
On a daily basis, your body defends itself against attacks microorganisms that could cause disease. We call these microorganisms pathogens. The first set of defences your body has against pathogens are non-specific physical and chemical barriers. In this lesson, we will look at physical barriers.
Which two of these do you think are physical barriers to disease? Pick all the options you think are correct.

You can select multiple answers
The skin is a physical defence to pathogens. It stops pathogens from entering your bloodstream.
If cut, your skin will form a scab to prevent pathogens entering and infection occurring.
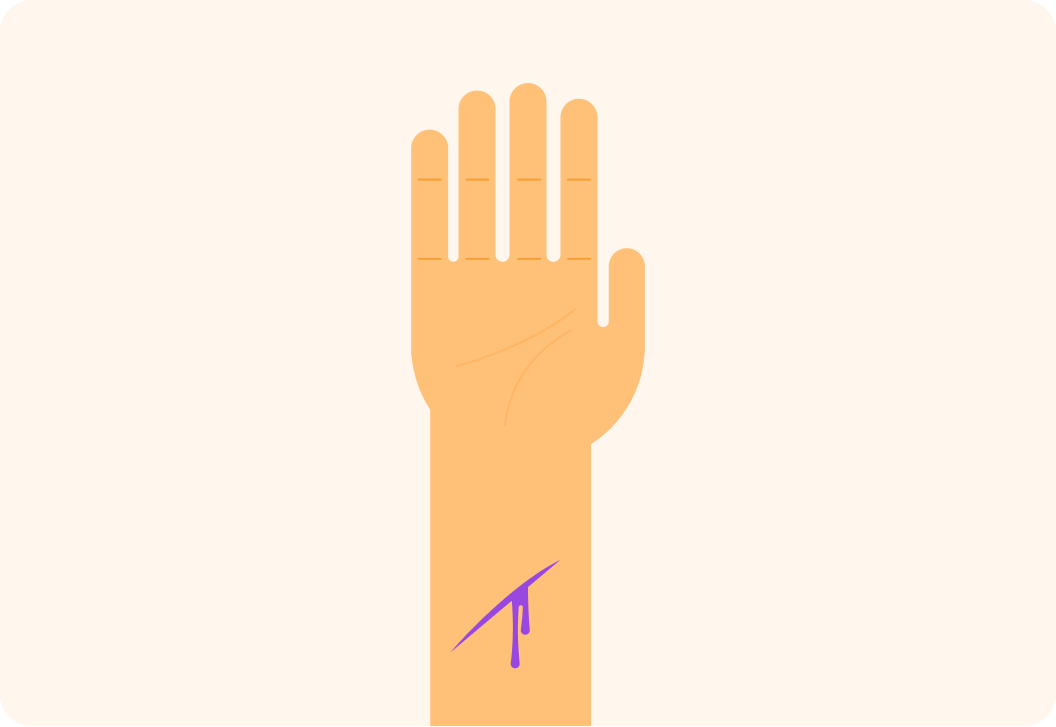
Our skin also produces antimicrobial substances. What do you think these are for?
A) Removing dirt from our skin. B) Killing pathogens. C) Keeping our skin moisturised.
Answer A, B or C.


The nose is another physical barrier.
Goblet cells are important cells in physical defence. They line the airways and produce a substance which catches pathogens. What do you think this substance is?

Hairs and mucus trap pathogens that get breathed in through the nose.
It's a bit like how a spider weaves its web to catch flies.
When you're ill, you produce much more mucus in your nose compared to normal (often producing a blocked or runny nose). Why do you think this is?

Mucus is also produced in the trachea and bronchi.
These are the pipes that take air down into the lungs.
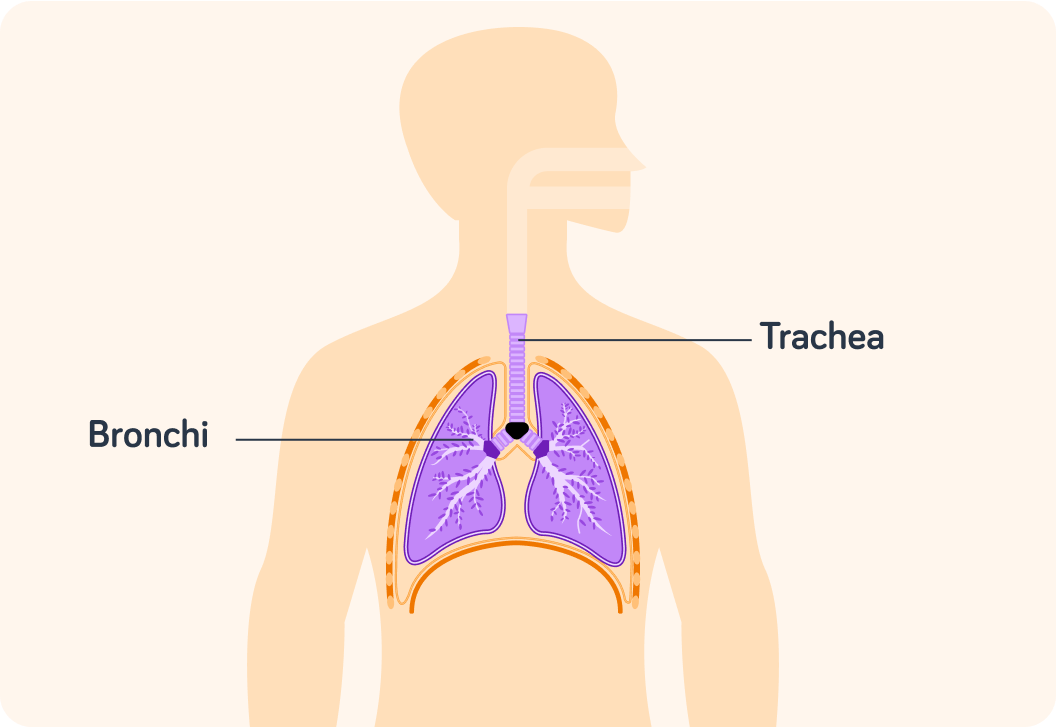
The cells that line these pipes are called "ciliated cells". They have very small hair-like structures poking out of them. Do you know what these structures are called? You might know from a previous lesson.


Cilia help to push mucus to the throat, where it can be swallowed into the stomach. In which direction do cilia push mucus?
A) Upwards B) Downwards C) Neither
Answer A, B or C.


Imagine standing in a line of 50 people, and passing a football up the line from start to finish. Now imagine the people are cilia, and the football is a ball of mucus. Cilia work to pass mucus back up towards the throat by passing a ball of mucus from one cilia to the next.
So, to recap, which of these are physical barriers to pathogens?

You can select multiple answers
Which two of these statements are correct?

You can select multiple answers
