YOU ARE LEARNING:
Producing Antibodies
Producing Antibodies
Monoclonal antibodies are artificially produced using a scientific method, which this lesson will discuss.
Antibodies attach to cell surface proteins called antigens. If the body detects antigens on foreign substances in the body, such as pathogens, it triggers an immune response.
Do you think antibodies can detect substances other than pathogens?

Monoclonal antibodies are an extremely useful tool.
Antigens are basically present on every cell - not just on pathogens.
In humans, that could be things like blood cells, cancer cells or hormones.
However, antigens only trigger an immune response when the body recognises them as not its own - so when they are foreign. Which of these is an example of a time where we want to fight cells or molecules that are not foreign in our bodies?

Many things can go wrong in our body that makes us ill.
Things like blood clots, or mutations forming cancerous tumours affect countless people. Monoclonal antibodies can be developed to detect certain antigens, to help diagnose and treat us from different illnesses.
Scientists use animals to produce monoclonal antibodies. Which animal do you think they use?

Mice can be used to create antibodies.
Immune systems will create antibodies against substances that are foreign to them.
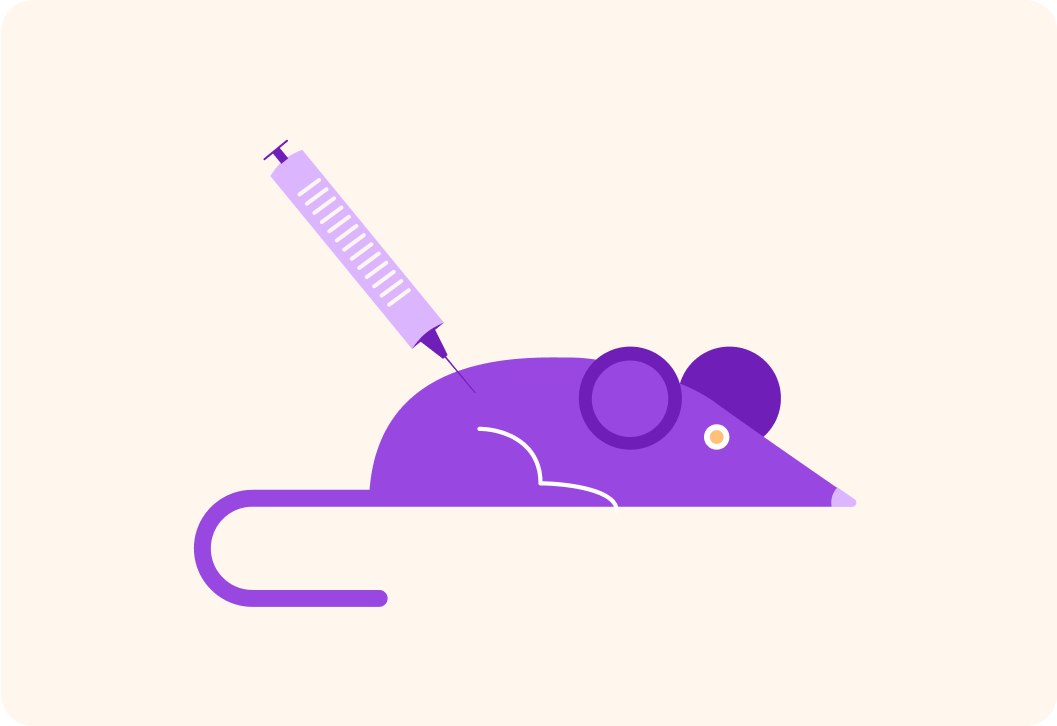

For example, if we inject a mouse with a human hormone, what will the mouse's immune system do?
A) It will start to fight the human hormone. B) It won't see the human hormone as a threat, so it won't respond. C) It will see the human hormone as a threat, but it won't be able to do anything to fight it.


The human hormone is foreign to the mouse.
So the mouse will begin to releases B-lymphocytes, which produce antibodies specific to the antigen. Scientists can then harvest those antibodies from the mouse.

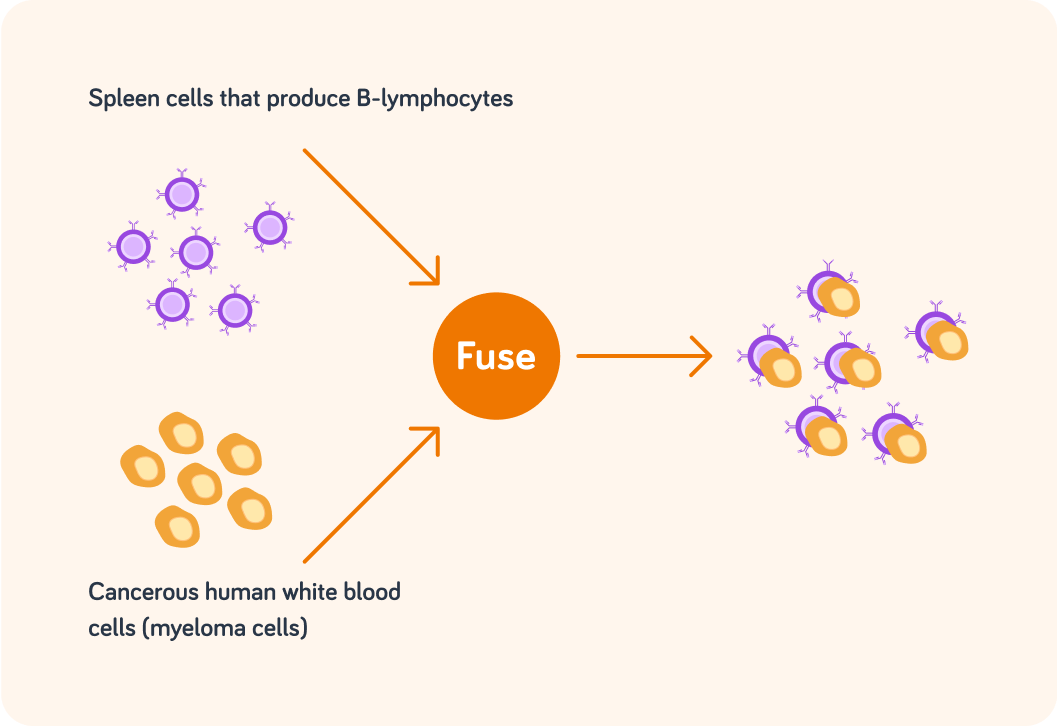
Scientists harvest spleen cells from the mouse. It is these spleen cells that produce lymphocytes. Which of these statements is correct?

Lymphocytes do not divide easily. This makes it difficult to produce them on a large scale. Scientists have a way around this, however.
Which of these cells are known for dividing very quickly?

The spleen cells can be fused with human cancerous white blood cells.
The cancerous white blood cells are called myeloma cells.
This combination produces a new kind of cell. What do you think they are called?
A) Hybridoma cells B) Mixture cells C) Intermediate cells
Answer A, B or C.


What do you think hybridoma cells do?

To sum up!
A mouse is injected with a foreign substance.
The mouse then produces antibodies specific to the antigen on the foreign substance.
The mouse's spleen cells produce the antibody-producing lymphocytes.
Scientists collect spleen cells from the mouse.
The harvested cells are fused with cancerous white blood cells (myeloma cells).
These are called hybridoma cells. As they divide, they produce millions of antibodies.
