YOU ARE LEARNING:
Competition

Competition
To survive and reproduce, organisms require resources from their environment. In order to achieve this, they may have to compete with other organisms that want the same resource. Those that are better adapted to acquiring the resource will be successful.
To survive, every organism must have a sufficient supply of key materials from their environment. Which of these materials must a tree have from its environment to survive and grow?

You can select multiple answers
This diagram shows what a typical plant, like a tree, needs to survive and reproduce.
It needs resources from both the living (biotic) and non-living (abiotic) parts of its ecosystem.
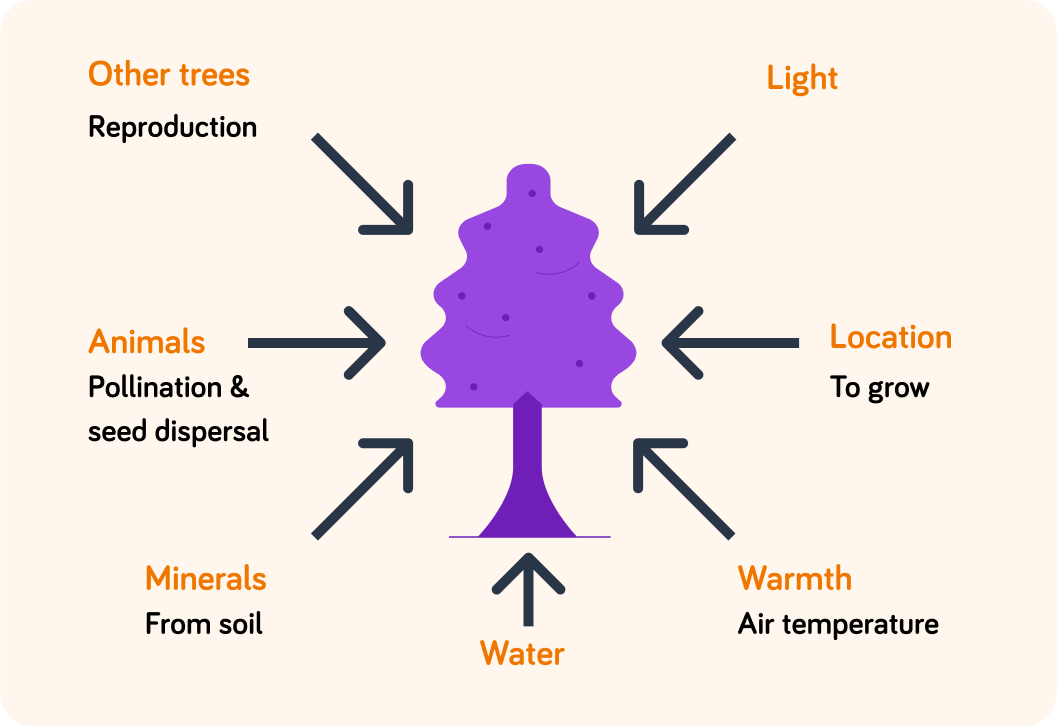
Which of these resources is an example of a biotic factor?
A) Animals B) Warmth C) Light D) Location E) Water


In a forest, each tree must compete for access to resources. Which of these resources would a tree be competing for?

You can select multiple answers
Also animals must have access to biotic and abiotic resources from their ecosystem to survive. Which of these resources, however, are not required directly by animals?

You can select multiple answers
Animals need shelter from the elements and from predators.
Rabbits have a burrow to sleep and breed in. They also need shelter from predators when they are out foraging for food. For example, they can hide in long grass or between the fallen branches of trees.
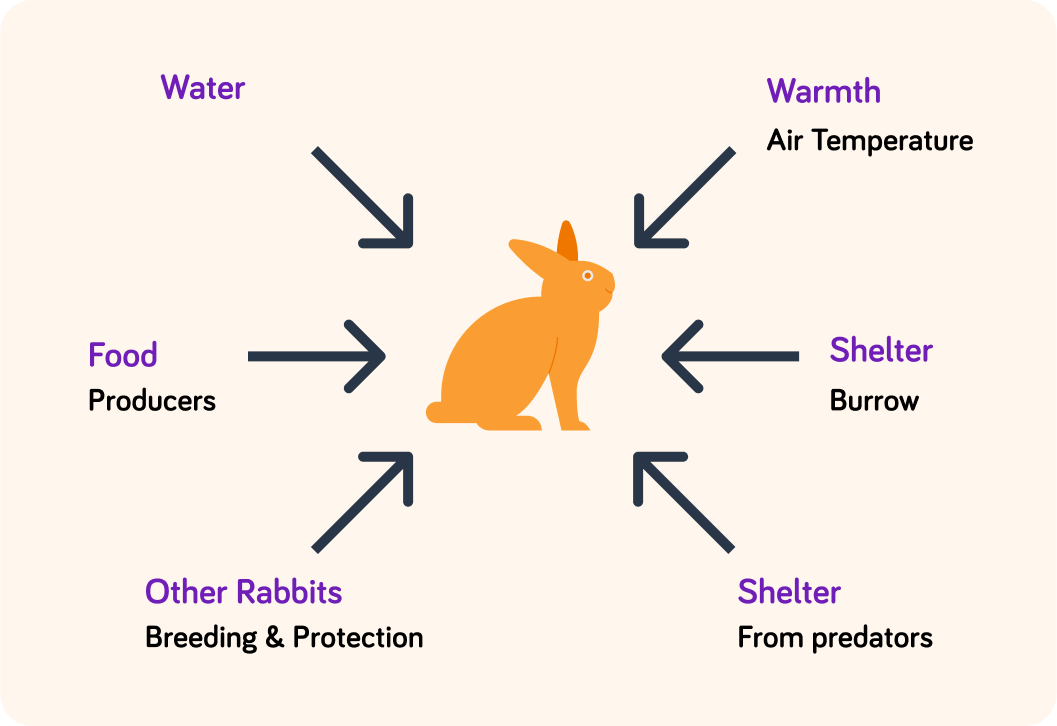
Which factor (biotic or abiotic) do they not need to compete with other rabbits for?


Competition for resources is an important process that helps to determine the abundance and distribution of all species. If a species is successful in competing for resources, more individuals of that species will likely survive, as they have access to more food, space to live etc. They will likely also reproduce more, because reproduction needs a lot of nutrients and energy. Sometimes they also push out species that are less successful, like the grey squirrels have pushed out the red squirrels in many places in the UK.
Example of competition: Squirrels
Grey squirrels and red squirrels both like the same habitats.
They love temperate forests with access to nuts, especially acorns. They are in competition with each other to survive.
Which of these resources might they be competing for? Pick all the options you think are correct.

You can select multiple answers
In the UK, only one of these factors is in short supply most of the time. This is the key factor. Which one do you think that might be?

So, it's a simple game: The more acorns you collect, the more survival points you win.
Red squirrels only eats ripe brown acorns that appear in mid- to later autumn. Grey squirrels eat ripe brown and unripe green acorns that appear in late summer into early autumn.
Which species has the highest chance of survival if they are competing in the same location?

So grey squirrels out-compete red squirrels for food.
They have all but replaced the native red squirrels in almost all habitats in the UK, except in northern Scotland where the red squirrel's thicker fur allows them to survive in the colder climate better than the grey squirrels.
To survive and out-compete other species for key resources, organisms have to adapt to their environment. If they are successful, they can pass these adaptations on to their offspring.
Adaptions that help individuals survive so that they can pass those adaptations on to their offspring is also referred to as survival of the fittest. What process is this a key part of?

Example of adaptation: The bluebell (Hyacinthoides non-scripta)
Bluebells cover the ground of deciduous forests in ** early spring.
They appear before most of the trees are in leaf and before most other flowering plants start to set flowers.
Which of these factors might they compete with other plants for in the forest?

You can select multiple answers
They avoid some of this competition, so they have access to pollinators and plenty of light, but what is the adaptation that has allowed them to avoid competition for these key resources?

Survival is complex! If you want to survive life, do it differently, do it better, do it faster and do it before others. These are the key reasons for most biological adaptions to the environment.
