YOU ARE LEARNING:
The Water Cycle

The Water Cycle
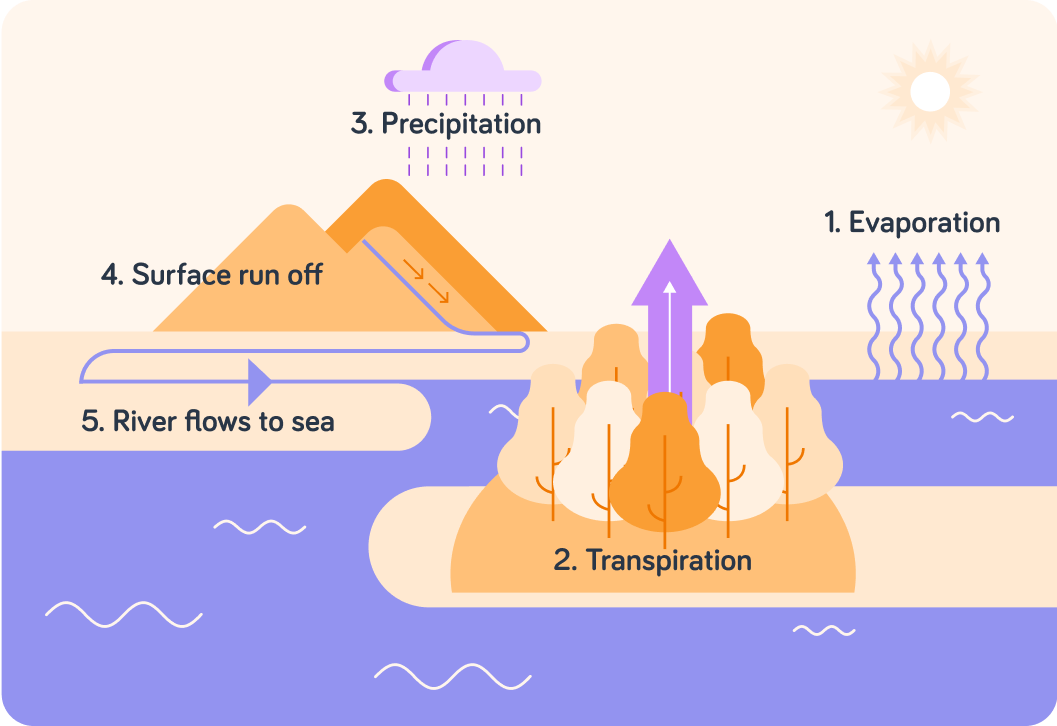
A continuous cycle of evaporation and precipitation ensures a constant supply of water across the Earth.
Where is the largest store of water on the planet?

Why is this source of water in the seas and oceans of no use to the vast majority of land based plants and animals? Pick all the options you think are correct.

You can select multiple answers
The water cycle allows water from the oceans to be available to plants and animals across the continents. It also removes the salts from sea water to provide fresh water to the land. Some specialist plants can use the salt water directly. These plants live on the coast in sand-dunes, salt marshes etc. We call them halophytes.
The heat from the sun warms the upper layers of the seas and oceans.
This causes the water to evaporate from the surface.
This water forms the clouds, but why do the clouds not contain salt?
A) The temperature is not high enough to evaporate salt molecules. B) The salt is too heavy to stay up in the clouds.


Eventually the clouds become too saturated with water vapour and the water falls to Earth as precipitation. Some of this will fall over the land. Which of these are classed as precipitation?

You can select multiple answers
Which of these are examples of how water returns to the oceans in the water cycle?

You can select multiple answers
Once the water is on the ground, gravity will make it start to flow back towards the seas and the oceans. Remember that land is generally higher than the oceans. Surface runoff and flow of water in water courses takes the water back to the seas.
Plants take up water through their roots. It is pumped up the plant's roots and stems to be used for different purposes. Which structures in a plant provides the suction power to pull water up the plant?

When water moves from roots to leaves in a plant, large amounts of water evaporates out into the atmosphere as fresh water.
We call that transpiration.

Transpiration can add large volumes of fresh water back into the atmosphere from the soil. How much water per hour do you think a large oak tree can add to the air on a hot summer's day?

What happens to water that is returned to the atmosphere via transpiration?

