YOU ARE LEARNING:
Tissue Culture
Tissue Culture
Cells from a plant can be collected, and used to grow identical plants from. This is important for micropropagation, commercial use, or preserving rare plant species.
Farmers and plant breeders have always tried to improve their crops to achieve higher yields, disease resistance, and even brighter and longer lasting flowers. If a breeder created a new variety, how ****** did they used to produce more copies of this new plant?

Conventional breeding (sexual reproduction) means that genes are mixed from two parents. This means it is hard to control the outcomes in the next generation. What word is used to describe this "range" of outcomes?

In evolution, variation between offspring is desirable, but for a plant breeder variation can be a problem. Why do you think that is?

What method of reproduction does a plant breeder want to use to ensure they obtain seedlings that are all identical to their parent?

Unfortunately, only a limited number of plant species naturally reproduce via asexual methods.
Have a guess at which of these common plants can reproduce asexually. You might have some in the house or in the garden.

You can select multiple answers
If you look at a field of daisies, there may appear to be hundreds of individual plants.
In reality, though, there are probably only 3 or 4 genetically different plants there! The rest are clones. We can use this natural ability of plants to grow asexually by using a tissue culture.
Tissue culture
A small cutting is taken from the parent plant that has the desired characteristics.
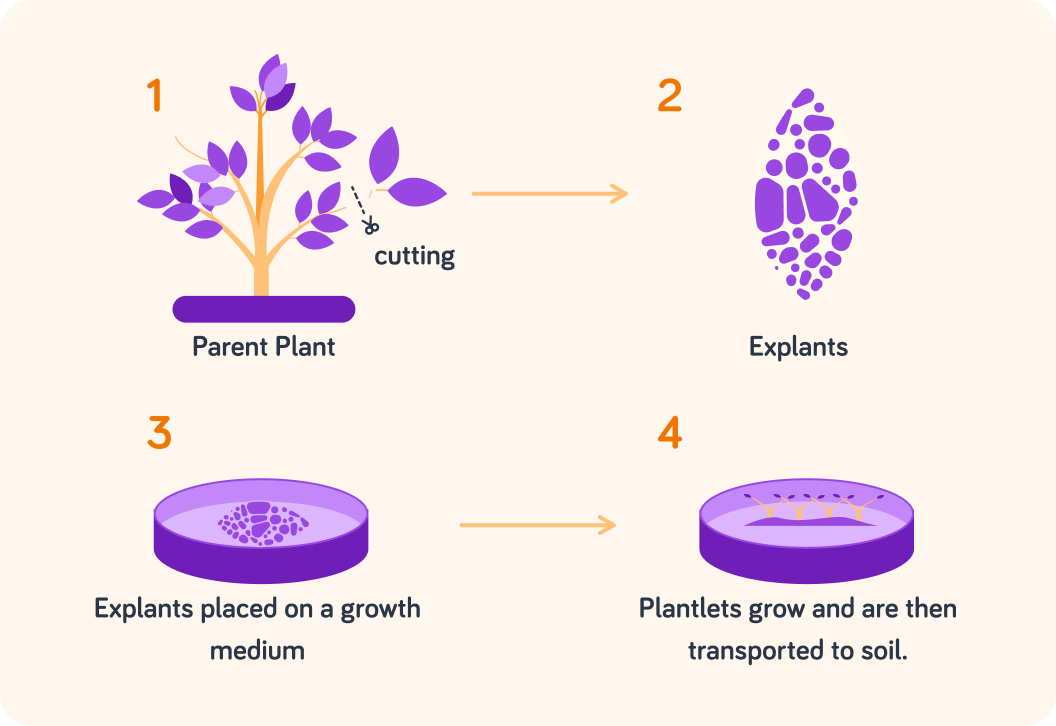
The cutting is divided into small bundles of cells ("explants"). This has to be done in a sterile environment. Why do you think this is so important?
A) To prevent the explants from going mouldy. B) To prevent fungi or bacteria growing on the growth medium. C) To prevent the final plant from being infected.


The explants are placed on a growth medium ("agar") with nutrients, growth hormones and water. These are placed in the warmth to grow. What else will they need to grow?


Once they have grown into small plants ("plantlets"), they can be transplanted to soil.
After this, they grow like a normal seedling from a seed.

What is true about each of the plantlets?

Another term for this process is micropropagation.
Which of these would be a use of microproagation?

You can select multiple answers
