YOU ARE LEARNING:
Leaf Structure

Leaf Structure
The structure of a leaf is in such a way as to maximise its ability to carry out photosynthesis.
What is the process called where plants use sunlight to turn carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen?

Plants use a special enzyme called chlorophyll to perform photosynthesis. Chlorophyll gives plants their ________ colour.

So chlorophyll makes plants green and helps them photosynthesise. In which green part of the plant do you think photosynthesis mostly takes place?

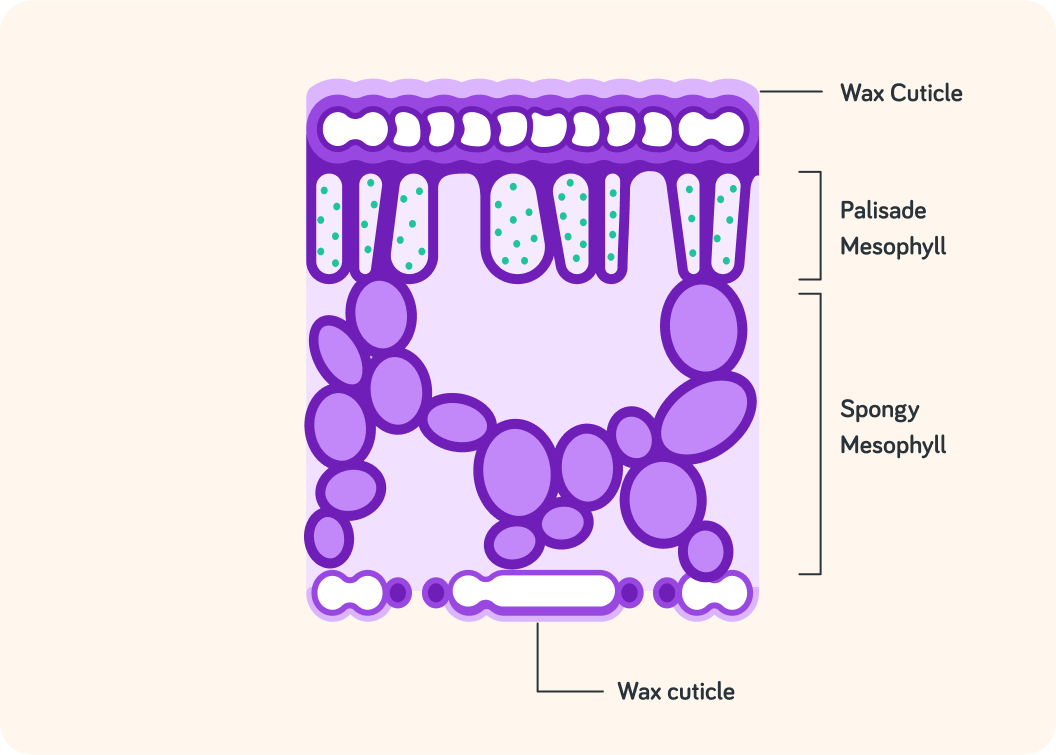
This shows what a leaf looks like on the inside
It has lots of layers that work together to make the leaf really good at photosynthesising.
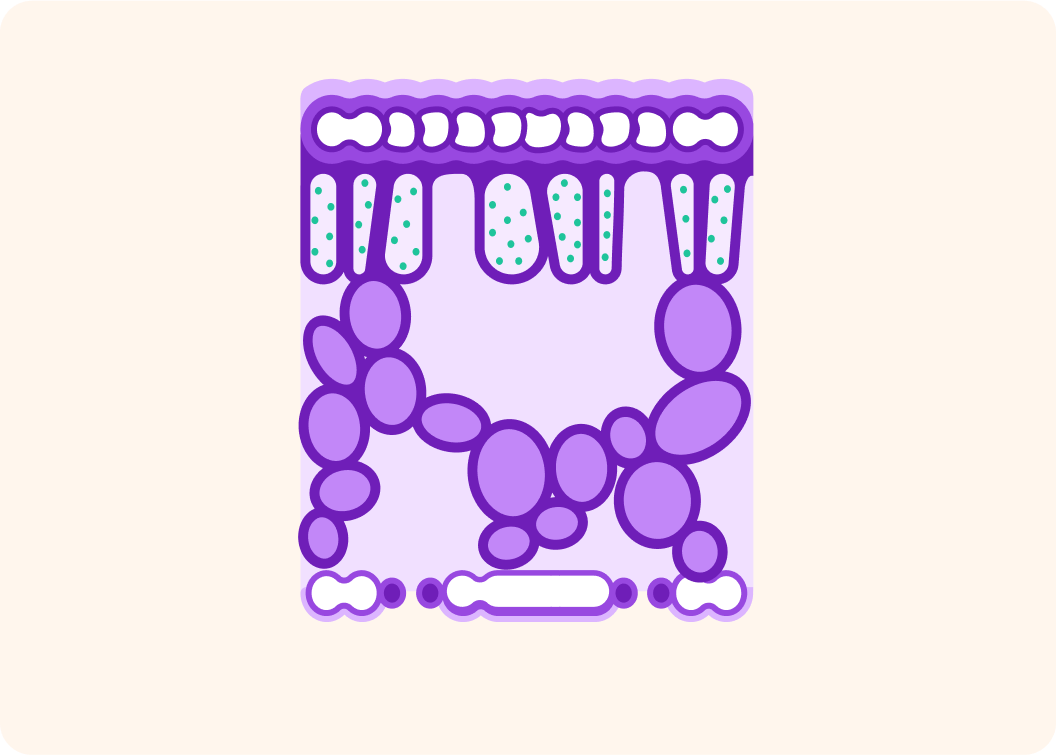
What are the two "ingredients" again that the plant needs to perform photosynthesis apart from sunlight?


Plant leaves are built to be extremely good at performing photosynthesis
That means they can hold the right amount of carbon dioxide and the right amount of water.

The outside layers of the leaf is the wax cuticles. Why do you think it's good for plant leaves to have waxy outer layers?
A) Wax is necessary for photosynthesis. B) Wax reduces water loss from the leaves. C) Wax makes insects stick to the plants.

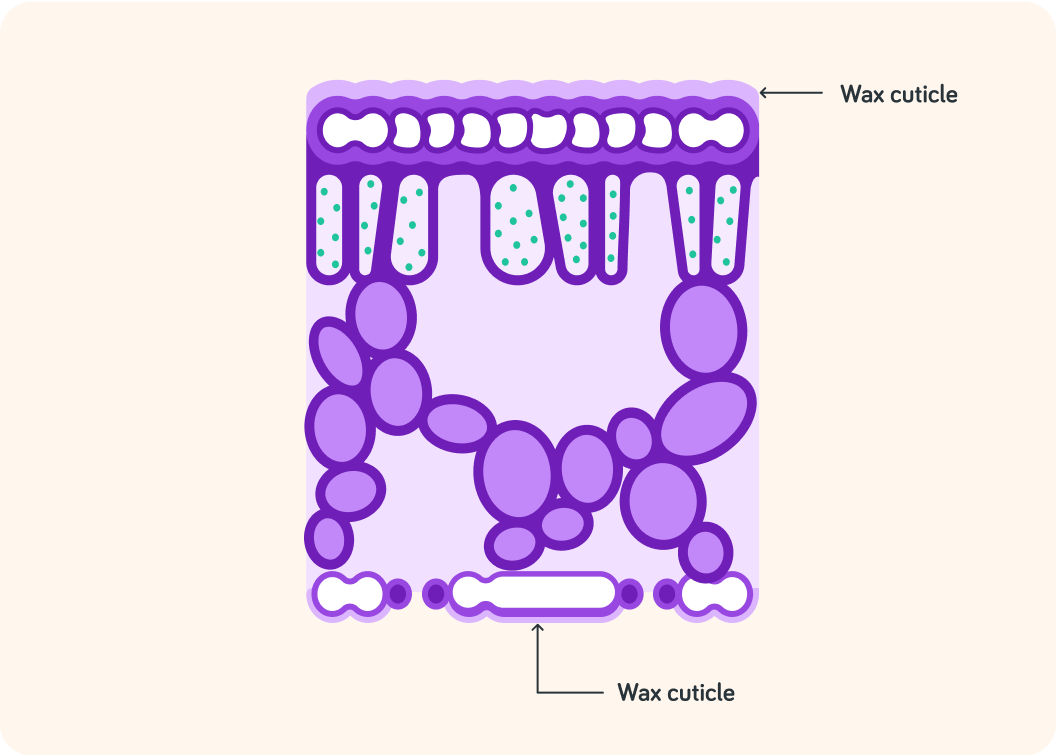
So the wax cuticles help reduce water loss from the leaves, but where does the water come from in the first place?
A) Plants suck up water via their roots. B) Plants drink water via holes in their leaves. C) Plants produce their own water in the leaves.


The wax cuticles help reduce water loss from leaves
The water in the leaves originally gets sucked into the plant via its roots. It gets transported to the leaves via special vessels called xylem ("zy-lem"). More on those in later lessons.

What is the big middle layer in the leaf called?

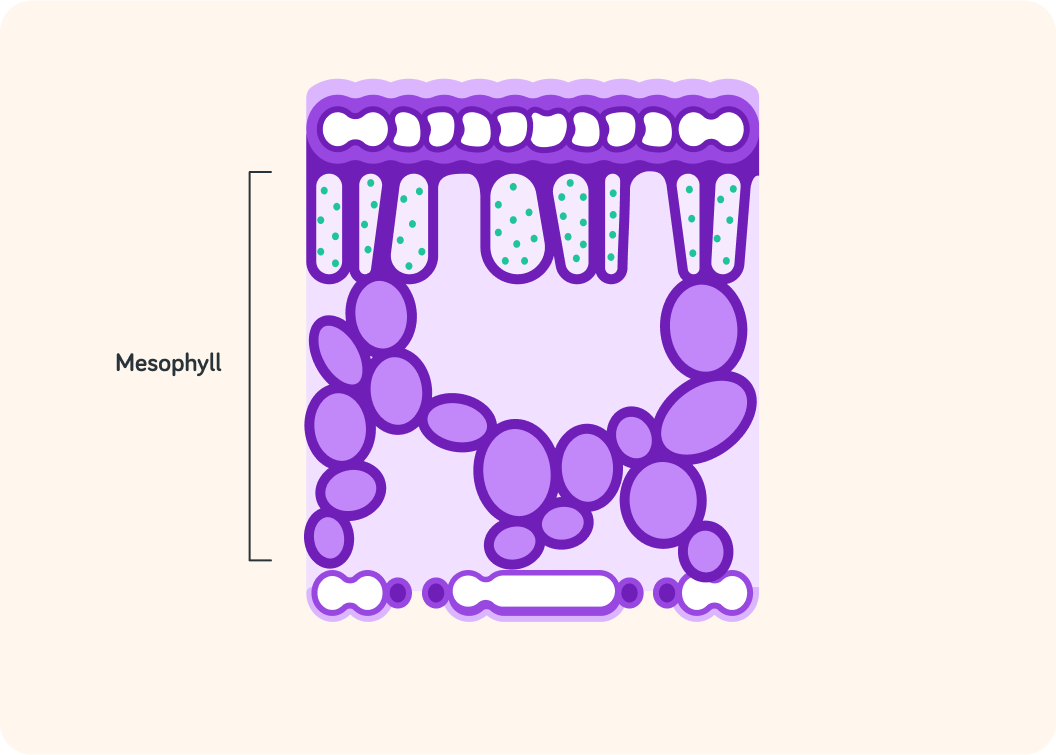
Actually the mesophyll is divided into two layers
Spongy mesophyll and palisade mesophyll.
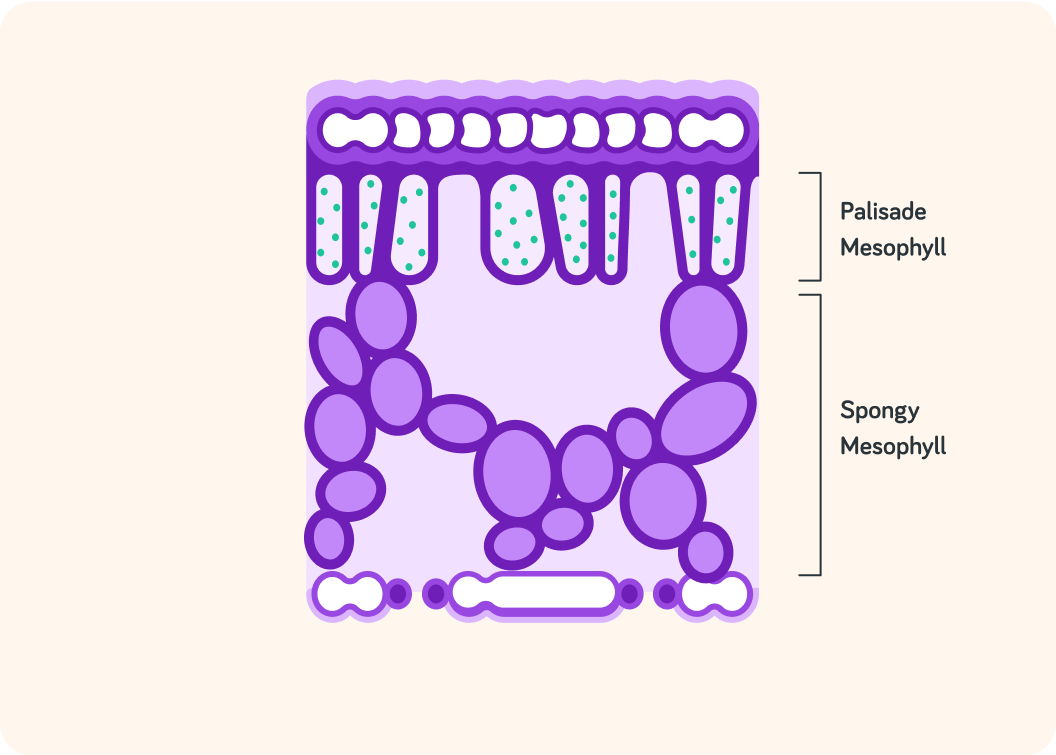
The spongy mesophyll has a lot of air pockets in it. Why is that important?
A) So that the leaf does not get too heavy. B) So that water can get into the leaf. C) So that carbon dioxide can get into the leaf.


The palisade mesophyll is close to the surface of the leaf so it can easily absorb sunlight. It also contains most of the leaf's chloroplasts. So this is where the leaf performs ______________.


To recap! Plant leaves are built to be extremely good at performing photosynthesis
Photosynthesis requires water and carbon dioxide, so plant leaves makes sure that both are available in the leaves.
Water
Water enters the leaf from the roots via vessels called xylem.
The wax cuticles on the outside of the leaf makes sure that water isn't lost from the leaves too quickly.

Carbon dioxide
Big air pockets in the spongy mesophyll allows plenty of room for carbon dioxide inside the plant.
It is then used for photosynthesis in the palisade mesophyll which contains most of the leaf's chloroplasts.

But how does carbon dioxide get into the leaf in the first place?
The answer is in the lower epidermis layer.
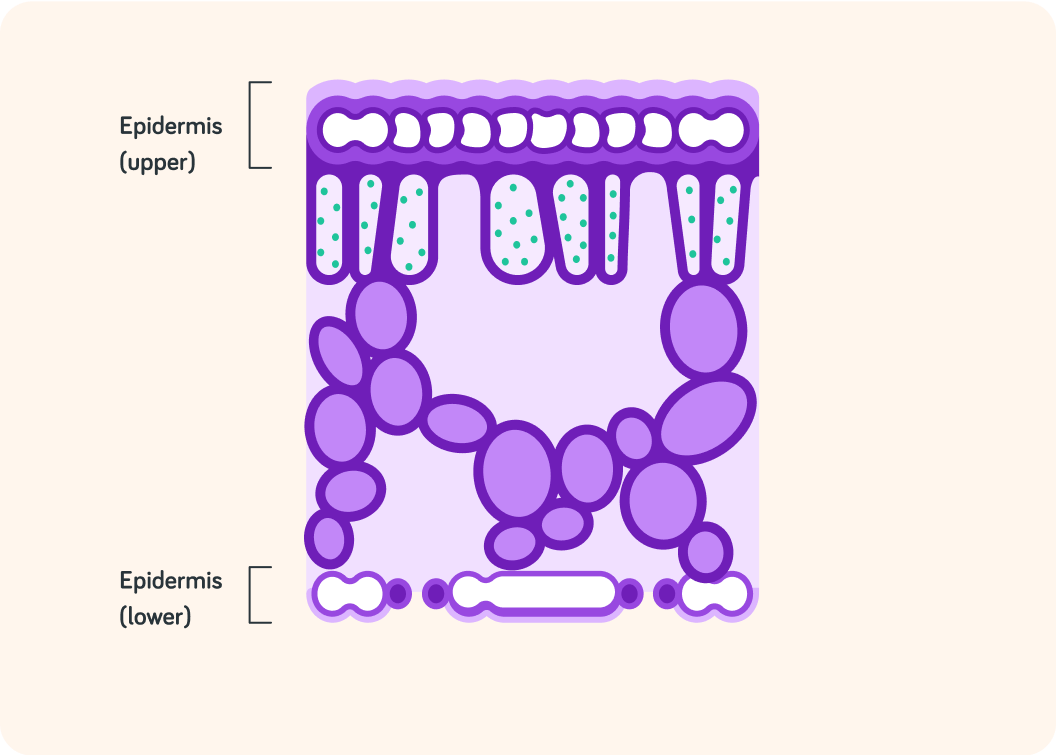
Have a close look at the lower epidermis. How do you think carbon dioxide gets in?


What is one of these little openings called?

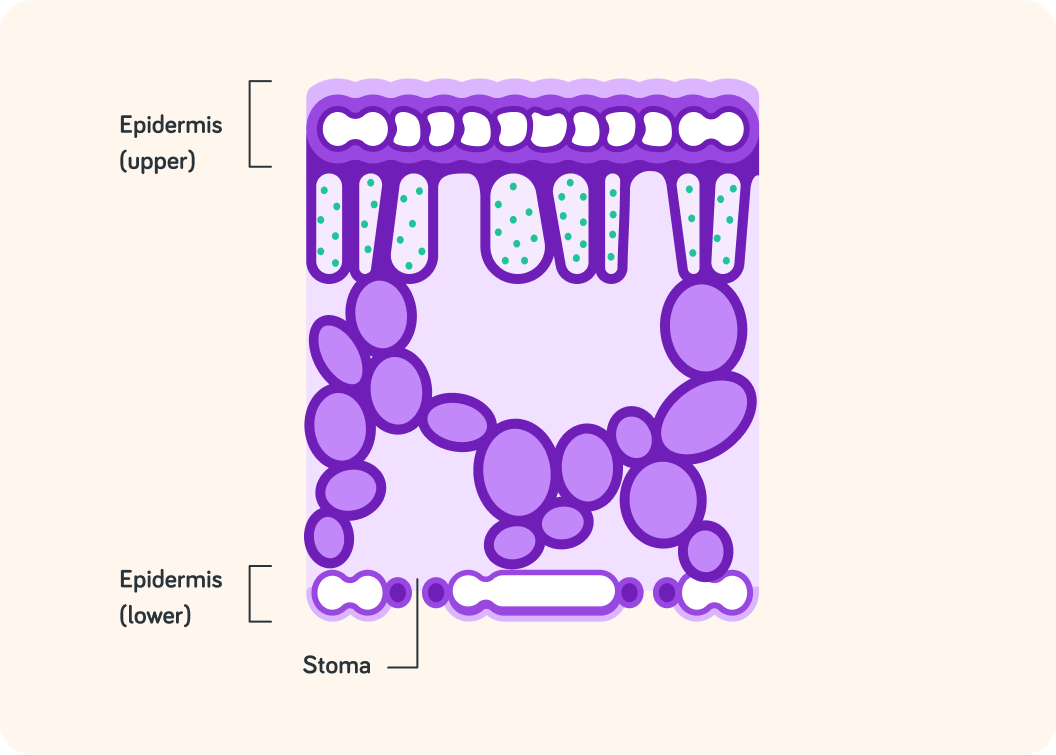
So air (and carbon dioxide) get into the leaf through stomata
Stomata are little openings in the leaf's lower epidermis.

This is a close-up of a stoma
By the way, you say "one stoma" and "many stomata".
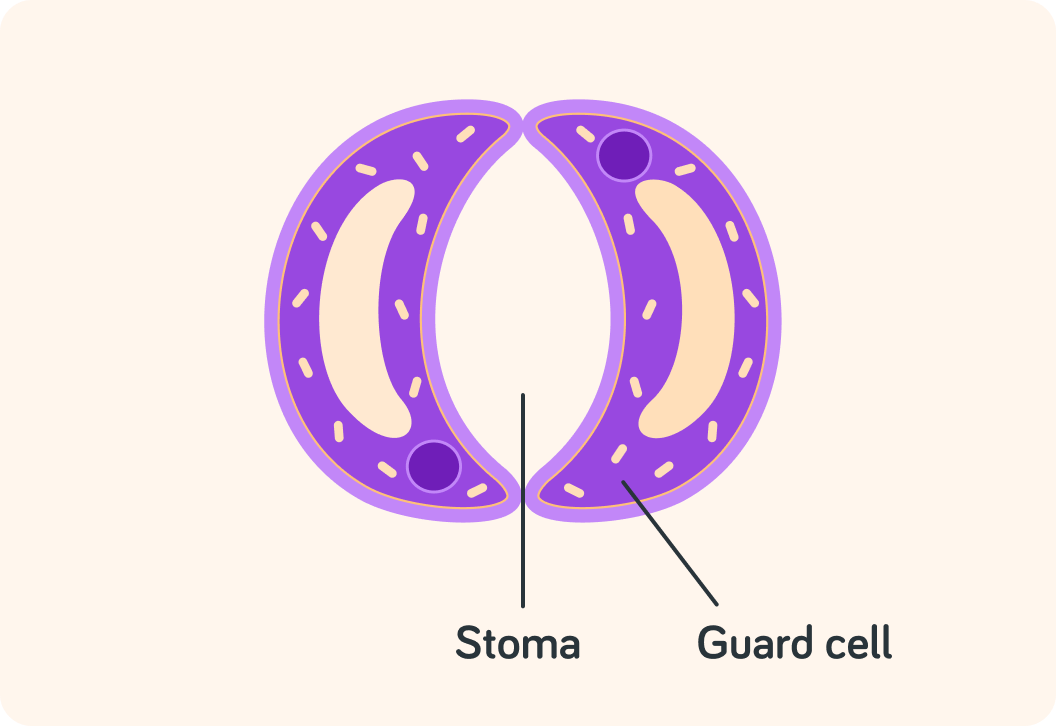
The guard cells on either side of the stoma are like "gate keepers". What do you think that means?
A) They keep insects from entering the leaf. B) They decide if it's water or air that enters the leaf. C) They can open and close the stoma.


So when the stoma is open, carbon dioxide can enter. Why do you think the guard cells sometimes decide to close the stoma?
A) To prevent water loss through the stoma. B) To prevents insects from entering the leaf. C) To prevent pesticides from entering the leaf.


The guard cells close the stoma by filling their ____________ with water.
A) vacuoles B) nuclei C) cell membranes

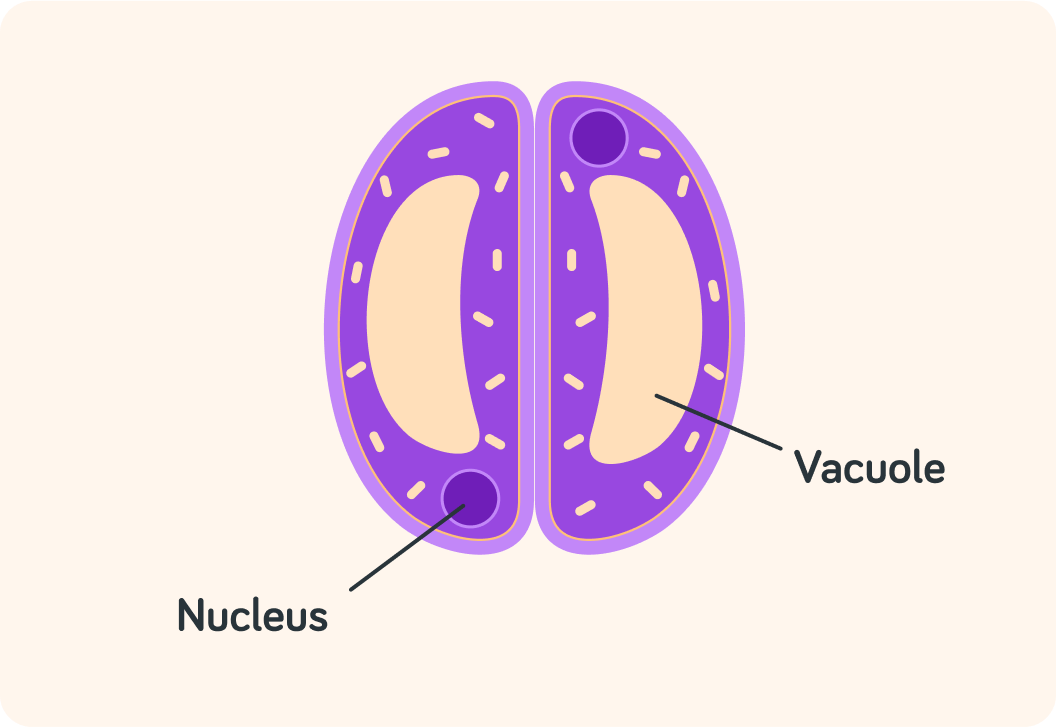
The guard cells are like "gate keepers"
They can close the stoma if too much water is evaporating through it. They do that by filling their vacuoles with water so the stoma closes up.
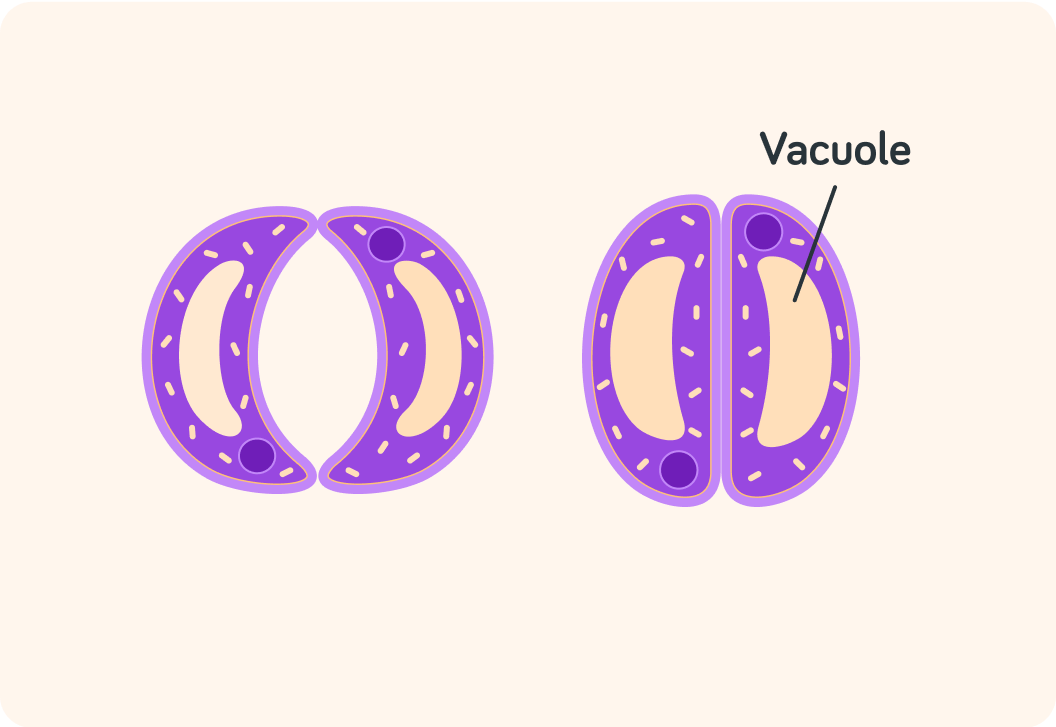
So there are lots of different cells and tissues in a plant leaf. That means that a plant leaf is an _____________.

Summary! A plant leaf is an organ
It consists of may different types of cells and tissues, organised into layers. That makes the leaf very good at performing photosynthesis.
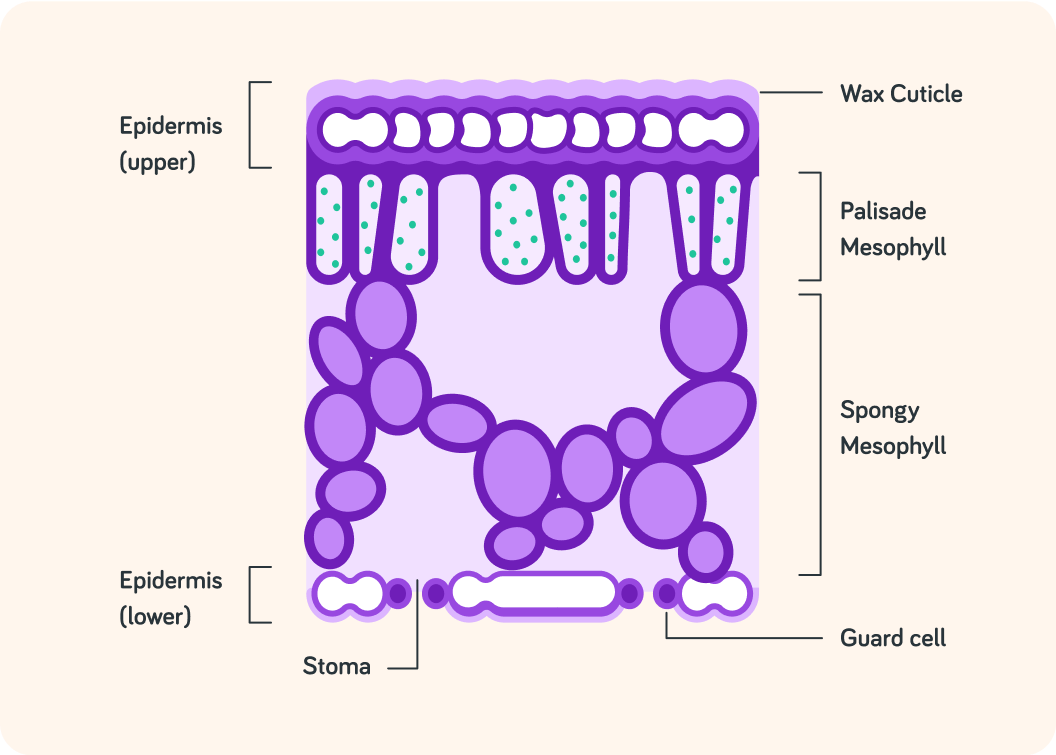
Photosynthesis requires water
Water enters the plant via the roots, but the leaf's wax cuticles make sure that the leaf doesn't lose water too quickly.
Also, guard cells on either side of the stomata can close the stomata if the leaf is losing too much water anyway.

Photosynthesis also requires carbon dioxide
Air (and carbon dioxide) enters the leaf through open stomata in the lower epidermis and is kept in the air pockets in the spongy mesophyll.

Photosynthesis mainly takes place in the palisade mesophyll
This layer can easily absorb sunlight and it holds most of the leaf's chloroplasts which is the organelles that allow plants to perform photosynthesis.

