YOU ARE LEARNING:
Mutations
Mutations
Mutations in DNA can occur through different methods, such as radiation or chemical mutagens. The different mutation types, from deletion to substitution, have varying effects on amino acid production.
A mutation is a change in DNA. Do you think these changed are planned or random?

Do you think mutations occur continuously or only very rarely?

Which of these do you think increases the chance of a DNA mutation occurring? Pick all the options you think are correct.

You can select multiple answers
Mutations change the bases in DNA. If this change of DNA occurs in a gene, how does this affect the gene?

When a DNA mutation occurs on a section of coding DNA (a gene), the gene will be changed, causing a genetic variant. Genes are read by molecules to code for proteins, so this can affect the phenotype of an organism.
Will it always affect the amino acid (and the protein that gets produced) if a gene is changed?

The amino acid lysine has the DNA triplet code TTT and TTC. So, if the DNA code changes from TTT to TTC, the same amino acid will be produced. This gives flexibility. However, even if a mutation does change an amino acid, it may not actually affect a protein's overall appearance or function.
What do you think such mutations are called, which change a base, but don't affect the amino acid or protein produced?

If a mutation is not a silent mutation, so if it does have an effect, what do you think it could do? Choose all the options you think are correct.

You can select multiple answers
There are different types of mutations, including insertions, deletions, and substitutions. Luckily though, most mutations do not have a huge effect on the workings of our bodies.
What do you think an insertion mutation might be?

What do you think deletion mutations are?

Which of these is an insertion? A, B or C?

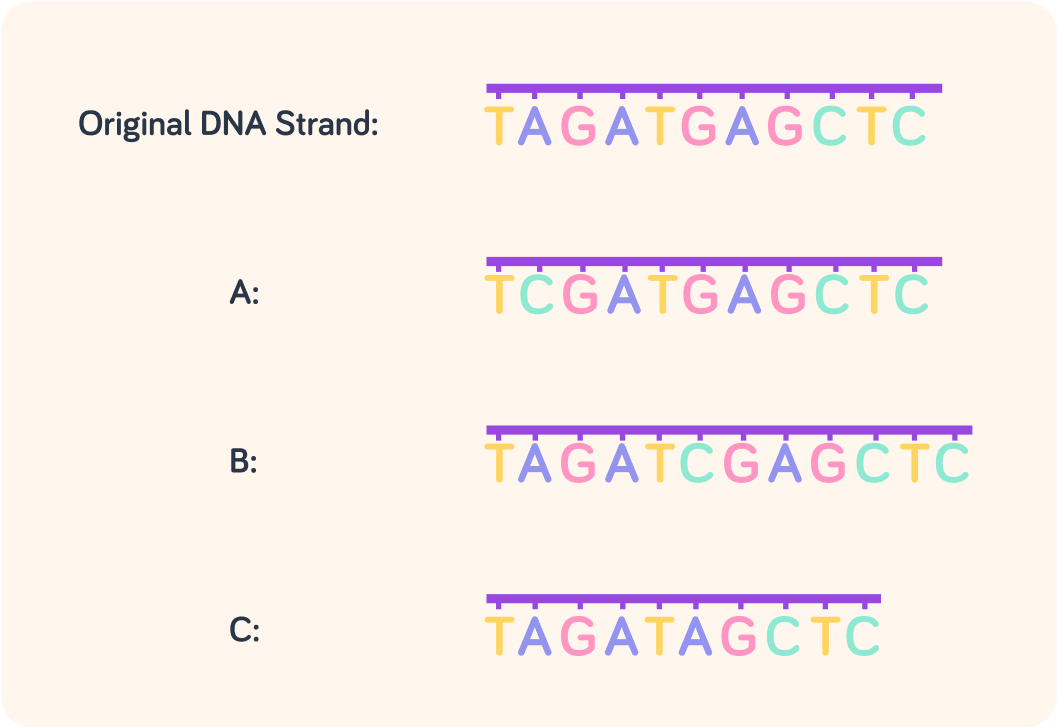
Which of these is a deletion? A, B or C?


Example A is another type of mutation, where one base in the DNA is changed for another. What do you think this mutation is called?
A) Swap mutation B) Substitution mutation C) Imitation mutation


So, insertion and deletion mutations not only change the order of bases in DNA, they also change the length of the DNA strand. Substitution mutations do not change the length of DNA.
Do you think insertion and deletion mutations are considered more dangerous than substitution mutations?

To sum up, take a look at this image.
This is a step by step walkthrough of what might happen in a deletion mutation. Similar scenarios can be imaged for substitution and insertion.
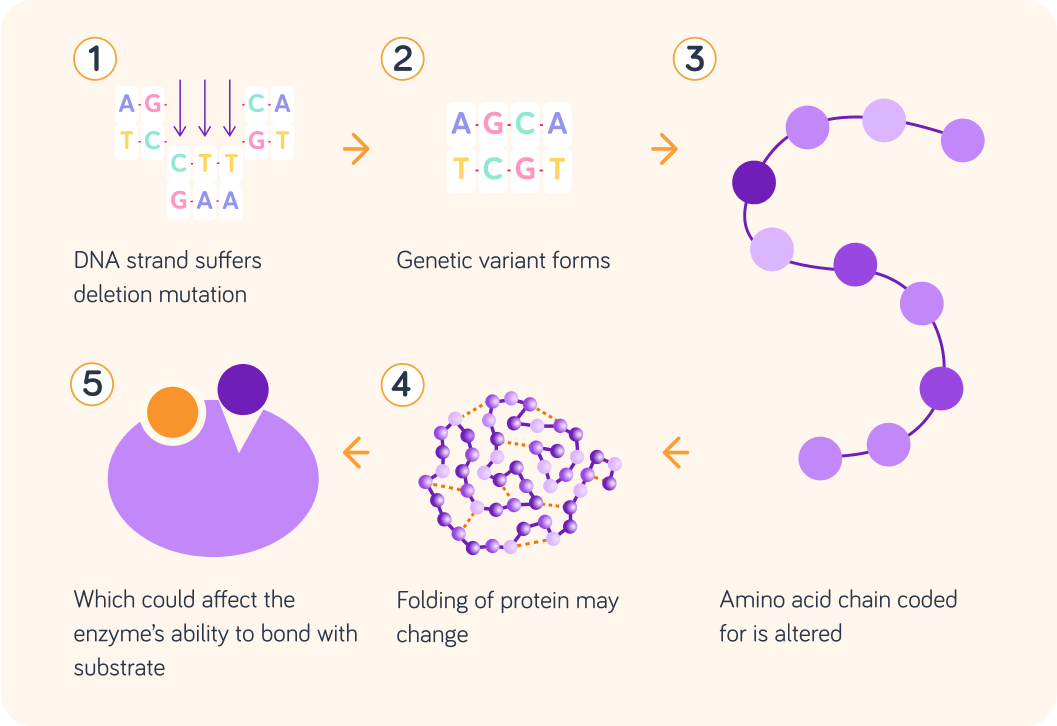
- A mutation deletes a section of bases in DNA.
This is a random occurrence that deletes one or many bases in DNA.

- The mutated DNA strand results in a genetic variant forming.
A genetic variation is a change in the DNA sequence of our genomes.

- The bases in the variant gene may produce different amino acids.
If the codons are changed, different amino acids will be coded for.

- Amino acids could affect the folding of the protein peptide.
The bonds between amino acids across from each other in the protein can affect the folding.

- Different folding can affect the structure of the enzyme that is produced.
This may affect the enzyme's ability to interact with the substrate.

