YOU ARE LEARNING:
Estimating the Area Under a Curve

Estimating the Area Under a Curve
In many situations, the area under a curve can tell us important information. We can estimate it by finding the areas of shapes which fit under the curve.
The area under a curve can be an important quantity to calculate. For example, in a speed-time graph, it represents the distance travelled.
Sometimes the area under a graph will be able to be calculated exactly because it is some kind of polygon such as a triangle, rectangle or trapezium.
Remember the formula for the area of a triangle
We will use triangles as a shape to estimate the area under a curve.

What is the area of a triangle with base 10 and height 5?


This is the formula for the area of a rectangle
We can also use rectangles as shapes to find the area under a curve.

What is the area of a rectangle with base 6 and height 8?


Trapeziums are also useful for finding the area under a curve
This is the formula for finding the area of a trapezium, where a and b are the lengths of the parallel sides.
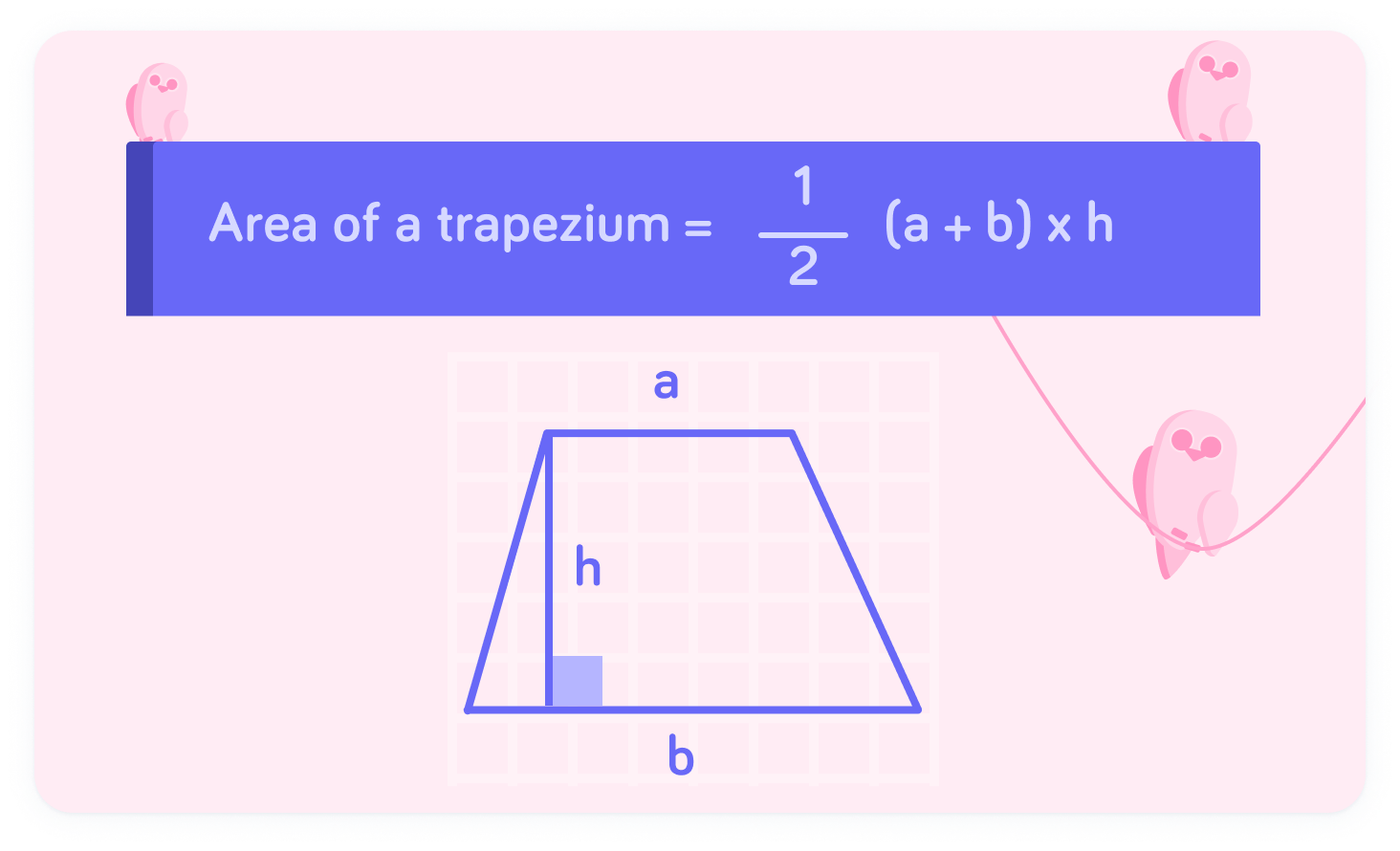
What is the area of a trapezium where a=3, b=5 and h=6?


However, if the graph is curved we will have to estimate the area using either a triangle, rectangle or trapezium or a combination of them.
