YOU ARE LEARNING:
Ionisation Potential and Penetrating Power

Ionisation Potential and Penetrating Power
Each type of nuclear radiation is ionising to a different degree, which affects their ability to move through matter.
Radiation is ionising if it has the ability to add or remove ____________ from atoms and molecule.

If an atom has an equal number of electrons and protons then it is electrically neutral (uncharged). Ionisation causes atoms to gain or lose electrons. Which statement correctly describes the change in overall charge of ionised atoms?

What are the four types of ionising radioactive decay?

You can select multiple answers
The rest of this lesson will look at each type of directly ionising radiation, their ionisation potential and penetrating power. The lesson will not tell you about neutron emission, because neutron emission is not directly ionising.
Alpha decay
An alpha particle has a relative atomic mass of 4, and an electrical charge of +2. Can you remember what an alpha particle actually is?

An alpha particle is simply a helium nucleus.
It consists of two protons and two neutrons, so it has a relative atomic mass of 4, and an electrical charge of +2.
Alpha particles have the highest electrical charge out of all the radioactive decay. Do you think these are the most or the least ionising out of all the types of radiation?

Penetrating power
Penetrating power is the ability to travel (or penetrate) through materials without getting absorbed.
Alpha particles also have the most charge and the largest mass out of all the radioactive decay. Do you think these are the most or the least penetrating out of all the types of radiation?

Alpha particles have a relatively large mass and a strong charge, so they transfer their energy easily to materials.
This makes them good at ionising, but it also means that they don't penetrate very well. Alpha particles are easily absorbed by the thickness of skin, a few centimetres of air or a thin piece of paper.
Beta decay
What is a beta particle?

In one word, what is the difference between a β− particle and a β+ particle?

Beta particles have less charge than alpha particles.
This means that beta particles are less ionising. However, beta radiation is more penetrating than alpha radiation. Beta particles can pass through skin, but they are absorbed by a few centimetres of body tissue or a few millimetres of aluminium.
Gamma radiation
What is the net electrical charge of a gamma ray?

Do you think gamma rays are weakly or strongly ionising?

What is the relative atomic mass of a gamma ray?

Do you think gamma rays are weakly or strongly penetrating?

Gamma rays are weakly ionising because of their penetrating power.
Because they are electromagnetic waves of a very short wavelength, they are not easily absorbed by materials, so they are not very good at ionising materials. On the other hand, they can easily travel through the materials, so they are very hard to stop.
So ionising potential and penetrating power...
depend on charge and mass, respectively.
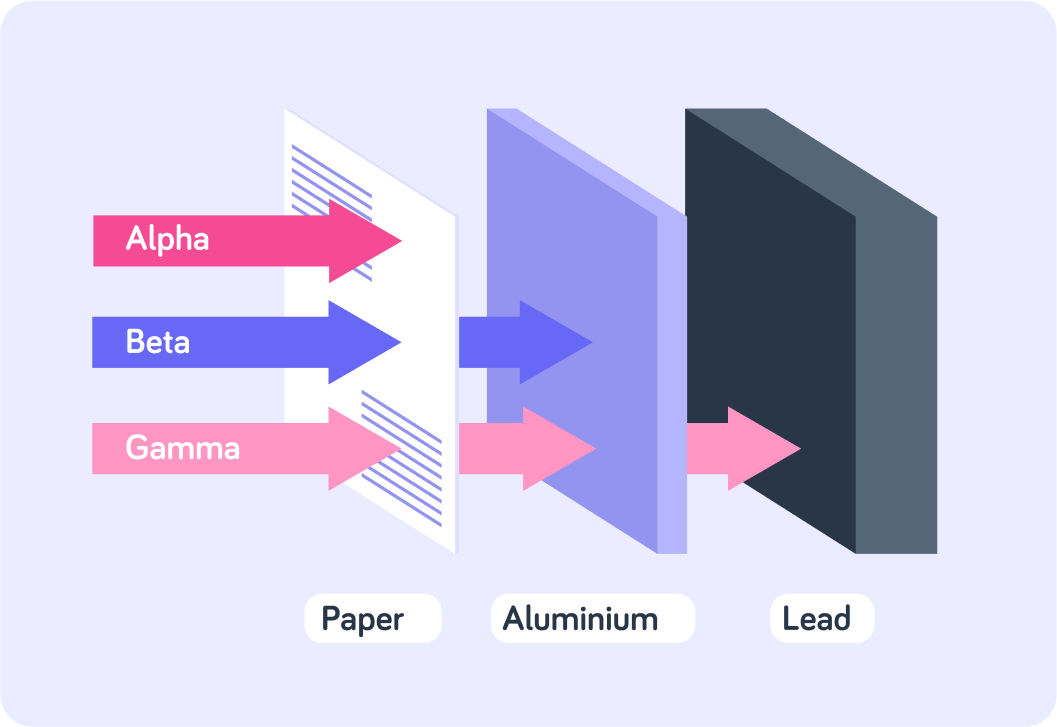
This image summarises the penetrating power of the 3 types of ionising radiation. Which is the most penetrating?


Which type of radiation is the most ionising?


