YOU ARE LEARNING:
Calculating Work Done
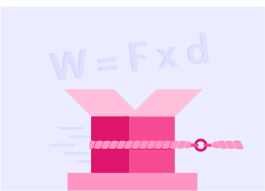
Calculating Work Done
We will apply the Work Done equation to calculate the energy transferred in a system, to illustrate how much force is applied to what distance.
Which of the following is also a correct equation for work done?

If you increase the force, what happens to work done?

If you increase the distance that a force moves an object, what happens to work done?

Remember that work done is the same as the energy required to move an object over a certain distance, by applying some force. This distance is in the direction of the force.
If you increase the force and/or the distance, it increases the amount of work done. This can be calculated using the formula E=F×d where E is work done (or energy) in Joules, F is force in Newtons, and d is distance in metres.
You can also use the formula W=F×d because work done and energy transferred is ultimately the same thing.
What is the work done in a system, if a block is pushed with a force of 100 Newtons for 2 meters?

What is the force used in a system where work done takes 1000 Joules, as a block is moved 10 meters?

A man lifts a 5 Newton block to a height of 5 metres. What is the work done by the man?

A man pushes a block with a force of 10 Newtons for a distance of 7 metres. What is the work done?

If the work done in a system increases by 50 Joules, what does the energy transferred in the system increase by?

Work done by a force in a system is the same as the energy transferred in that system. Therefore, if you increase or decrease work done, the energy will increase or decrease by the same amount.
