YOU ARE LEARNING:
Blood Vessels
Blood Vessels
The distinct structure of blood vessels, including arteries, veins and capillaries, are related to their function.
Blood vessels are the method by which blood travels around the body to our tissues. They come in three forms: Arteries, veins and capillaries.
Each vessel has a specific structure related to its function. Arteries and veins are essentially opposites of each other. What do you think their two functions are?

Veins carry blood towards the heart. Remember it like this: Veins enter the heart. Arteries carry blood away from the heart. Remember it like this: Arteries carry blood away from the heart.
Capillaries are tiny vessels that branch out from the main system to form a network.
So veins carry blood towards the heart. Do you think this blood is generally oxygenated or deoxygenated?

Arteries, on the other hand, carry blood away from the heart, after it has visited the lungs. Do you think the blood in the arteries is generally oxygenated or deoxygenated?

We have used the terms "generally oxygenated" and "generally deoxygenated". That is because there are two exceptions to the rule, which we will visit in another lesson. Nevertheless, please keep it in mind.
Structure A is an artery, which carries blood away from the heart.
We will look at how the artery is adapted to do that job really well.

Compared to the other blood vessels, arteries have a thick, elastic wall. Bearing in mind they receive blood straight out of the heart, why do you think that is?
A) To push blood back into the heart. B) To withstand the strong pressure of the blood coming out of the heart. C) To ensure blood doesn't move back into the heart.


Arteries have a small lumen compared to their thicker walls. Looking at the picture, what do you think a lumen is?
A) The hollow space inside a blood vessel. B) The outer coating of the blood vessel. C) The length of a blood vessel.


Which two of these options do you think we find in artery walls that makes them strong and flexible?

You can select multiple answers
Structure B is a capillary
Arteries branch into capillaries, carrying oxygenated blood from the heart. Capillaries then join back into veins after the oxygen has been given to tissues. We will look at how the capillary is adapted to do that job really well.

Capillaries are extremely small vessels. Why do you think that is?
A) They are filters, so need to be small to filter large components out of the blood. B) Capillaries are found in the heart, so need to be small to fit in the heart. C) Capillaries carry blood to all cells in the body, so they have to be tiny, like cells.


Capillaries exchange substances with cells. They give them oxygen and nutrients and take away waste products. How do you think this happens?
A) Each cell has its own capillary joined to it. B) The substances move through the walls of the capillary and cell walls. C) The capillaries open into cells and substances are sucked between them.


Due to the substances moving through the permeable capillary walls, the walls must be very thin.
In fact, the capillary walls are only a single cell thick to maximally reduce the diffusion distance.

What do you think capillaries give to cells and what do you think they take away from them? Pick all the option you think are correct.

You can select multiple answers
Structure C is a vein
Veins carry blood back towards the heart. We will look at how the capillary is adapted to do that job really well.

Veins take blood back to the heart. This might mean travelling for example up your leg. Do you think the pressure in veins is "high", "low" or "neither"?


Veins have thin walls
This is because they don't have to withstand a very high pressure from the blood, like arteries do.

Veins have large lumens
This helps to keep the pressure in veins low. Imagine squeezing toothpaste through a small hole compared to a larger hole. You'd need more force to get it through the smaller hole. Likewise, larger lumens in veins allows blood flow at lower pressure.

Lastly, veins have valves in them which open in one direction only. Why do you think veins need valves and arteries don't?
A) To ensure it is only blood that is travelling in the veins. B) To prevent blood from travelling backwards. C) To separate each section of the vein.


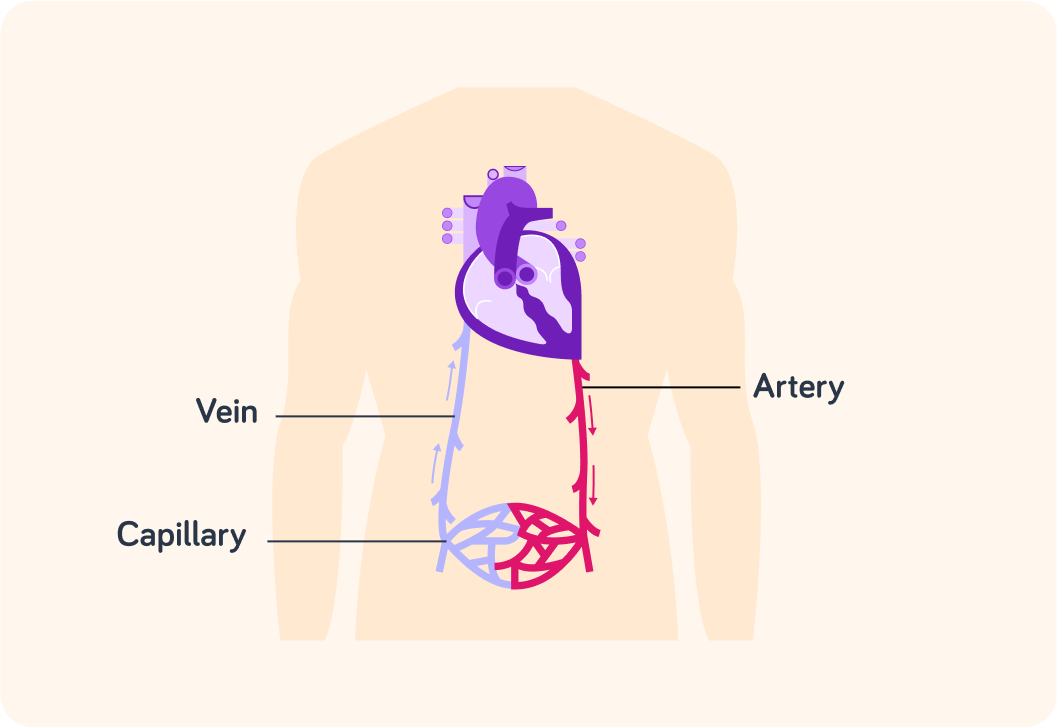
Here you can see all three types of blood vessels
The arteries take oxygenated blood away from the heart, branch into arteries which provide substances to the cells and collect waste products via capillaries. Then they form veins which travel back to the heart with deoxygenated blood.
Arteries are...

Capillaries are...

Veins are...

To sum up:
Veins enter the heart (carry blood towards the heart).
Arteries carry blood away from the heart. Capillaries are the small channels that surround each cell.
