YOU ARE LEARNING:
White Blood Cells
White Blood Cells
White blood cells are involved in the immune system to destroy pathogens that have entered the body.
Blood is a tissue. **** It has a group of similar cells working to serve particular functions. We have already looked at red blood cells and plasma. In this lesson we will look at white blood cells and **** platelets.
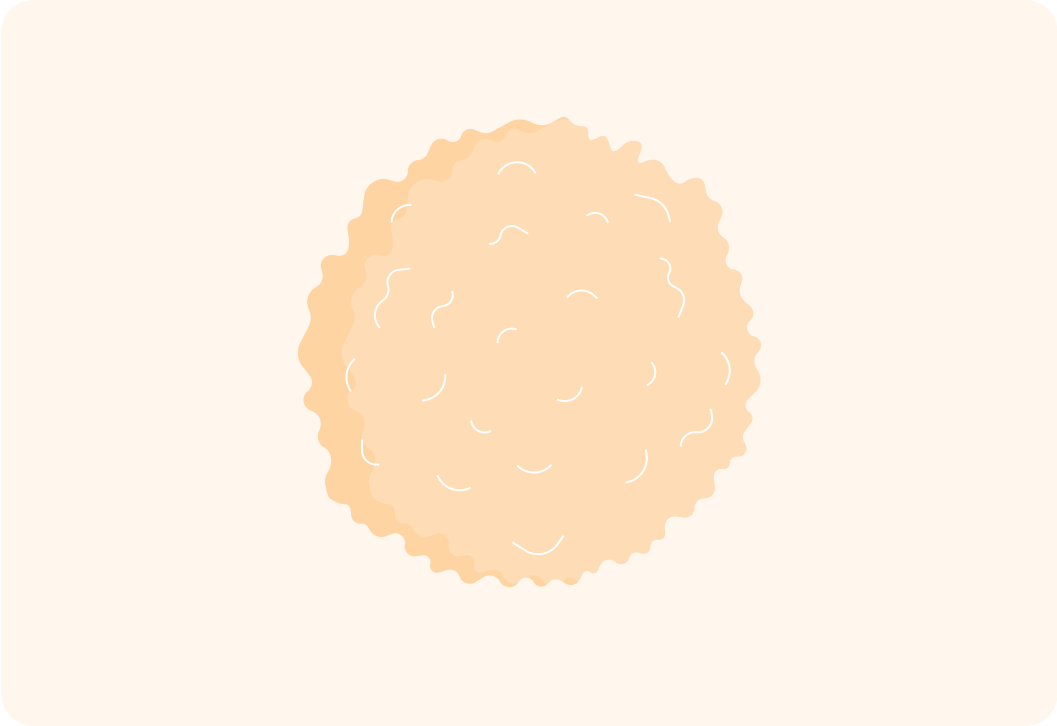
This is a white blood cell
This is how it would look in real life under a microscope.
There are several types of white blood cells. One type removes pathogens, which are harmful microorganisms in the blood, through a process called phagocytosis. What do you think these white blood cells are called?

The term phago- comes from Greek and means "to eat". Putting the terms phago- and -cyte together, what do you think phagocytosis is?

The other white blood cells are called lymphocytes. What do you think they do?

Lymphocytes also produce antitoxins. Now, anti- means "against", so what do you think lymphocytes do?

So white blood cells make weapons that the body needs to fight disease. Do you think they have a nucleus?

Imagine you are looking down the middle of an artery, which travels away from the heart.
If we used a microscope, this is what we might see. It's kind of like looking down the middle of a tiny straw.
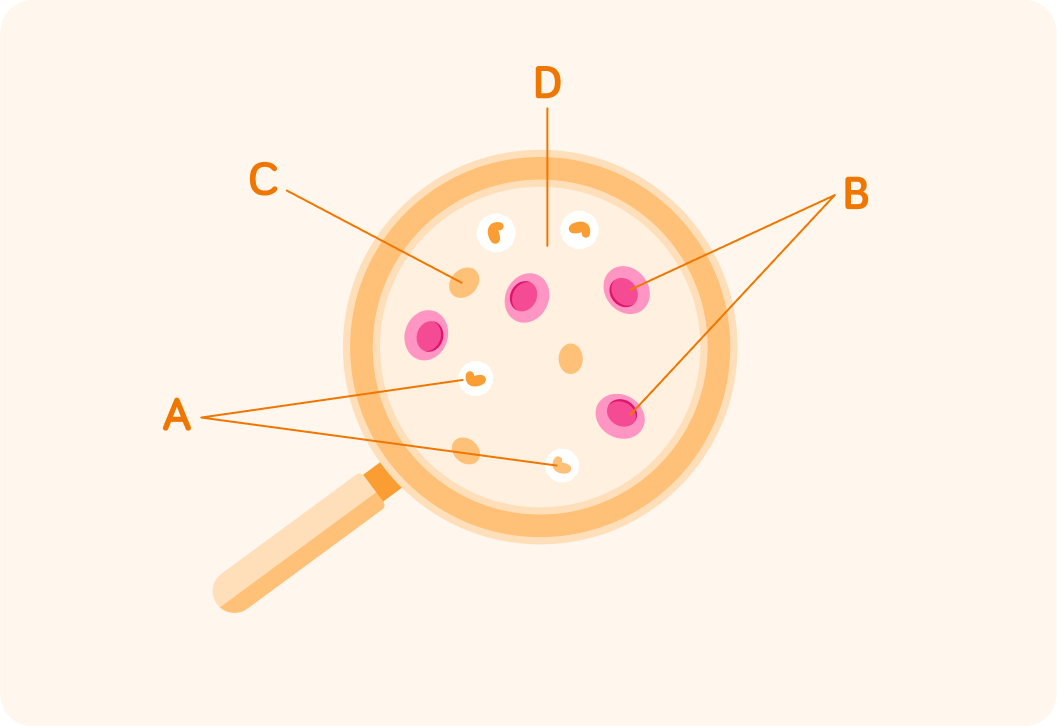
Which label do you think points to white blood cells?


Platelets are the components that help with blood clotting at wounds. Which label do you think points to platelets?


Platelets are the last blood component we will look at. They are fragments of cells that are responsible for patching up wounds to stop the blood pouring out. They cause clotting. They are basically a natural plaster.
In addition to stopping blood pouring out of a wound, what else do you think they do?

Do you think platelets have a nucleus?

If someone with a lack of platelets cuts themselves, what do you think would happen to them?

To sum up
Red blood cells...
are the biconcave discs with no nucleus. They contain haemoglobin to carry oxygen to the cells.
Plasma...
is the straw-coloured fluid part of blood that carries substances around the body such as nutrients, hormones, antibodies, proteins and urea.
White blood cells...
produce antibodies and antitoxins to fight infection. They produce stuff, so they do have a nucleus.
Platelets...
are responsible for clotting the blood when we get a cut. We can think of them as the body's natural plaster.
