YOU ARE LEARNING:
Endocrine system 2: Structure

Endocrine system 2: Structure
There are several endocrine glands in the body, the structure of which we will study.
The endocrine system provides the body with one of its two coordination and control mechanisms. This system secretes chemicals from glands into the blood that affect the function of target organs in the body. What are the chemicals called that are secreted by endocrine glands?

The diagram shows the location of the major endocrine glands in the body.
The hypothalamus and the pituitary glands work closely together to control the system.
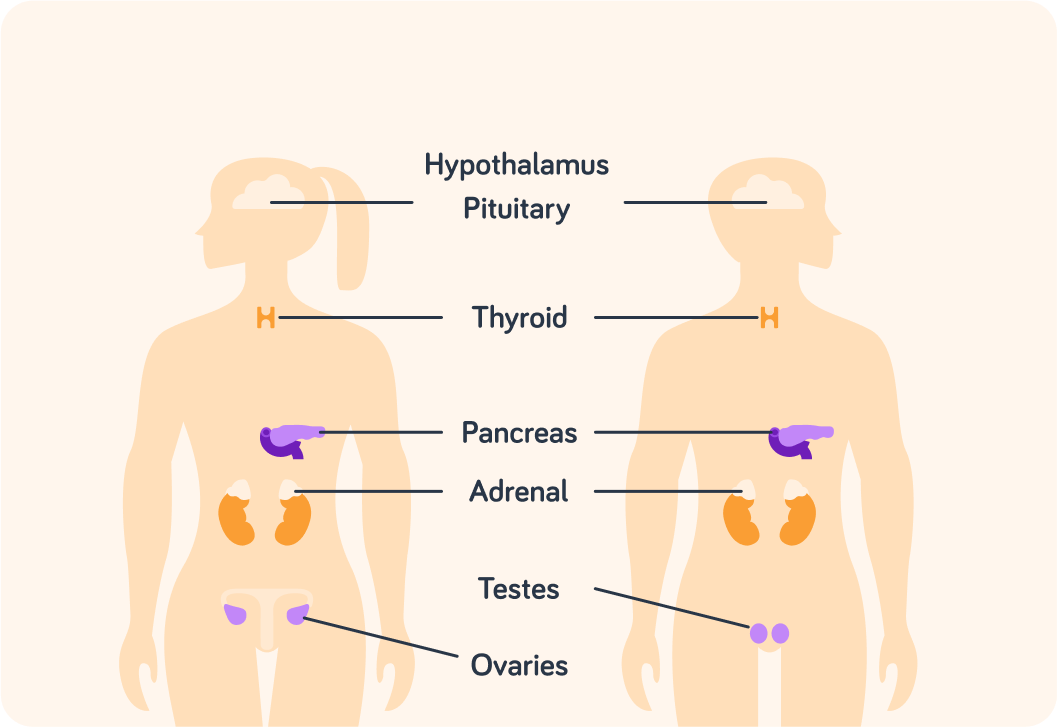
Above what organ do you find the adrenal glands?


At the base of which organ do you find the pituitary and the hypothalamus?


Which glands are not found in men? Pick all the options you think are correct.

You can select multiple answers
Which gland is found in the middle of the neck?

Where do we find the pancreas?

The endocrine system allows the body to respond to changes. Hormones change the function of their target organs. This might be to respond to an external stimulus, such as being frightened.
Getting a fright is one kind of stimulus. Other stimuli might be from internal changes in the body, for example a drop in blood sugar levels if you have not eaten for a while. In both situations the glands need to be instructed to respond. What might be the sources of this control?

You can select multiple answers
The pituitary gland is the body's master gland. Where is it located?

The pituitary gland secretes several different hormones.
Some of these target other glands to control how much hormone they secret in turn.
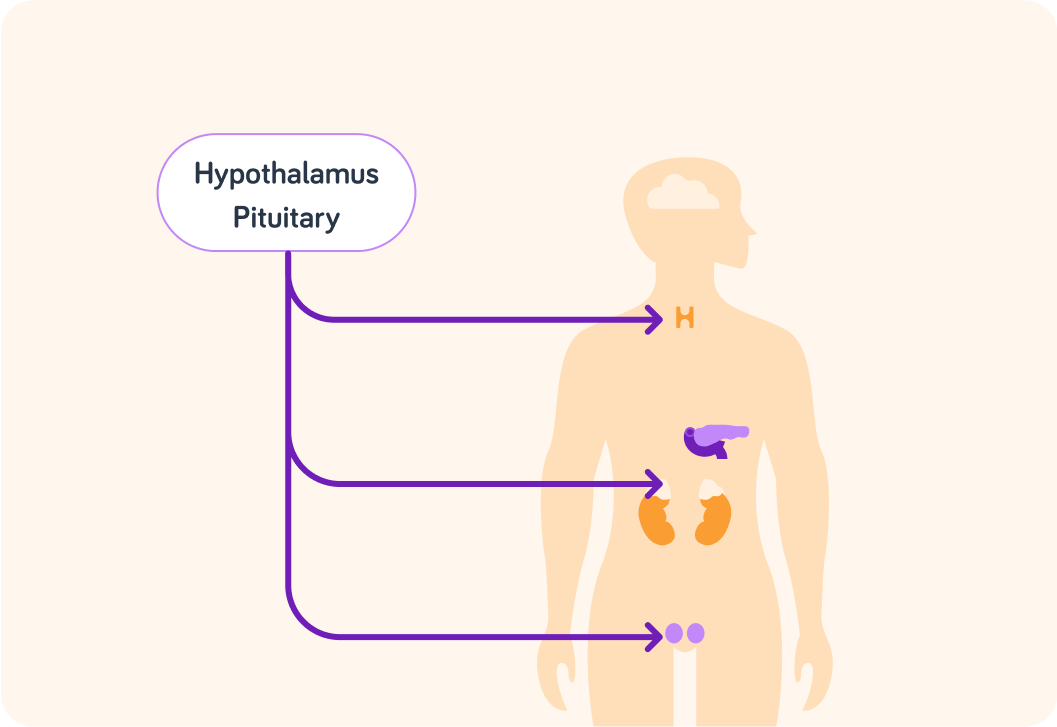
How do the hormones from the pituitary gland get to these other glands?

When a hormone from the pituitary gland reaches its target gland, what will it do to that gland?

