YOU ARE LEARNING:
Thyroxine

Thyroxine
Metabolic rate is controlled by the hormone thyroxine as a negative feedback system.
Thyroxine is a hormone that controls the body's metabolic rate. Which gland do you think secretes it?

Metabolic rate is a measure of how quickly the body's cell chemistry is working. The higher the concentration of thyroxine, the quicker this respiration happens. What is it respiration produces that is vital to life?

ATP is an energy rich compound that is used by cells for many vital functions. Without this energy, the body wouldn't function, and it wouldn't be able to grow and develop properly.
What might happen to a child if they do not have enough thyroxine in their body for a long period of time?

What symptoms might adults feel if they had low thyroxine levels?

The correct levels of thyroxine in the blood are vital to the proper function of the cells. If it drops below the optimum level, the body reacts to increase the levels back to normal. What type of feedback cycle is this an example of?

Thyroxine is secreted from the thyroid gland in the neck. However, it is not able to detect levels of thyroxine in the blood. The thyroid is controlled by the body's master gland, the pituitary gland at the base of the brain.
When the levels of thyroxine in the blood drop, this is detected by the hypothalamus in the brain.
The hypothalamus releases a hormone called TRH: Thyrotropin Releasing Hormone.
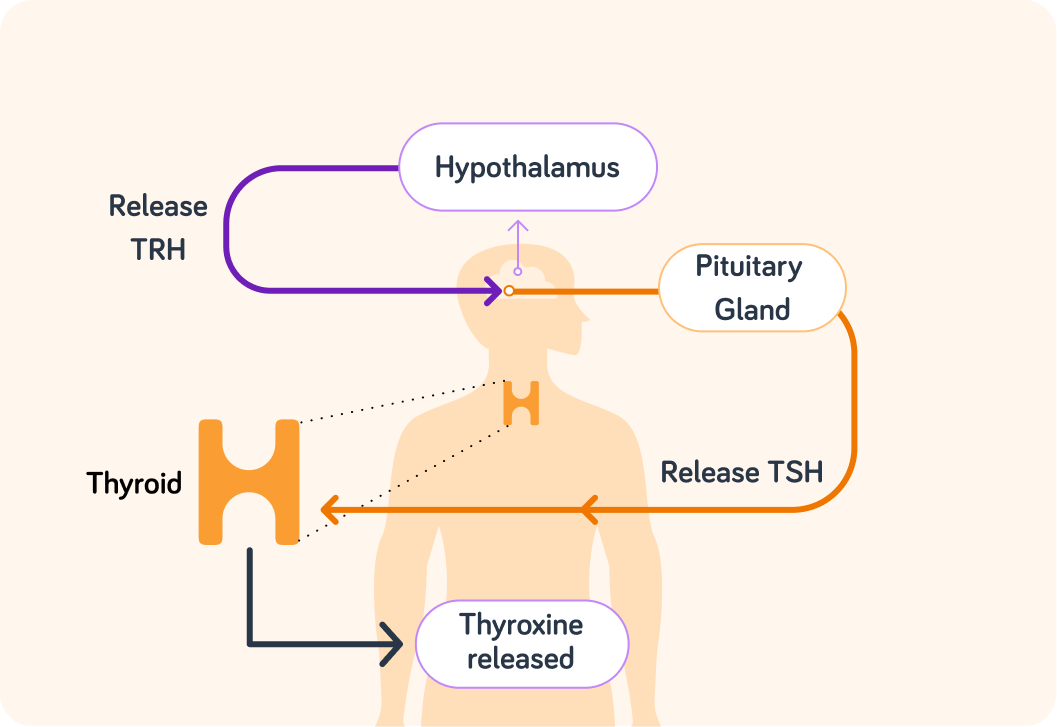
Look at the diagram. What is the target organ of TRH?


The pituitary gland responds to the TRH by secreting TSH: Tyroxine Stimulating Hormone. What effect do you think TSH has?


The thyroid makes more thyroxine.
The levels in the blood return to normal, and the thyroxine inhibits (stops) the release of TRH from the hypothalamus.

So to recap!
Low thyroxine is detected by the hypothalamus which secretes TRH. TRH reaches the pituitary which secretes TSH. TSH reaches the thyroid which secretes thyroxine. Thyroxine levels return to normal, so the hypothalamus stops TRH production.
