YOU ARE LEARNING:
Meiosis

Meiosis
Meiosis is a type of cell division where new cells are made with half the number of chromosomes as the original. This is important in gamete (egg and sperm) production.
In order for an organism to reproduce by sexual reproduction and pass on their genes to their offspring, they need to combine their genes with a member of the opposite sex. To do this, they need to produce sex cells, or gametes, through a process called meiosis.
Meiosis is the process that makes sure that the amount of genetic DNA, stored in chromosomes, is halved. Why does it need to be halved?

What is the name of these cells that have half the number of chromosomes as the parent organism?

Gamete cells can be referred to as haploid due to their number of chromosomes. These cells have half the number of chromosomes as a parent cell, which is referred to as diploid. Haploid means half.
The process of meiosis only takes place in certain organs in our body. Where do you think this is?

So, meiosis produces gametes, which have half the number of chromosomes as the parent organism. They can then join with a gamete of the opposite sex, to produce a zygote. In humans, the gametes would be an egg and sperm. You can remember it like this: Meiosis produces egg and sperm (in humans).
This shows meiosis, occurring in either the testes or ovaries.
The different colours show the different copies of chromosomes that make up a pair, e.g. purple from your mother and orange from your father. This diagram of meiosis only shows 2 chromosome pairs involved, but in reality there would be 23 pairs.
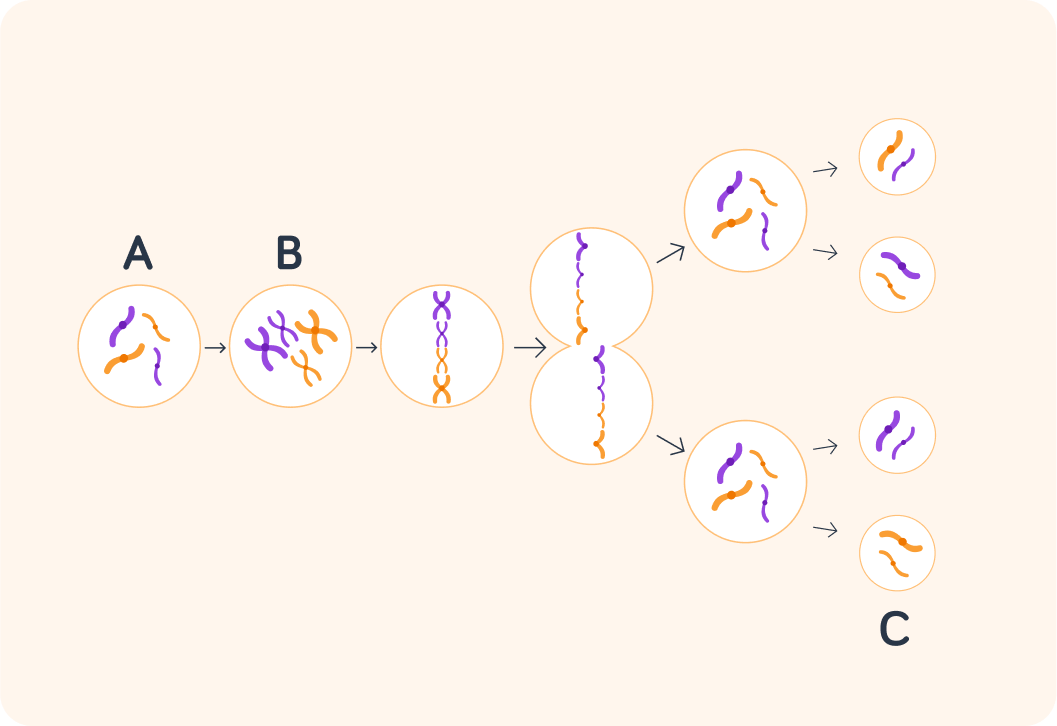
Which do you think is the parental cell? A, B or C?


What happens to the number of chromosomes in stage B?
A) It halves. B) It doubles. C) It stays the same.


After the chromosomes produce a copy of themselves, they line up in the middle of the chromosome, and each chromosome pair gets pulled apart.
This produces two cells with the same number of chromosomes as the original cell.

Then what happens to the cells?
A) They divide again. B) Their double their chromosomes. C) They divide their chromosomes.


This halves the number of chromosomes, so the final cells have half the number of the original cell. What are these cells called?


What do you notice about the gametes?
A) They are the same as each other. B) They have a different number of chromosomes to each other. C) They have a different combination of chromosomes to each other.


Pick the correct option. Notice that the options state the total number of chromosomes.

So one diploid parent cell creates four haploid cells. So a diploid parent cell has 23 paired chromosomes and...

We have just seen an example of meiosis with just two chromosomes. Now, imagine if we looked at meiosis with 23 pairs of chromosomes, combining in different ways. What do you think can be said about gametes?

Which of these statements about gametes are true? Pick all the options you think are correct.

You can select multiple answers
To sum up meiosis
Chromosomes in parental cells produce an exact copy of themselves.
The chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell, each side ready to be pulled apart into separate cells.
Once in separate cells, these cells divide again straight away.
No further chromosome duplication takes place.
Gametes are formed with single chromosomes, waiting to pair up with other single chromosomes in a gamete from the opposite sex.
This produces a child with 23 pairs of chromosomes, with each chromosome in a pair being a copy from each parent.
