YOU ARE LEARNING:
The Menstrual Cycle
The Menstrual Cycle
Oestrogen is the main reproductive hormone in females. During puberty, the levels spike, triggering the menstrual cycle to begin. This cycle releases an egg from the ovaries every 28 days, a process known as ovulation.
During puberty, hormones cause secondary sexual characteristics to develop in men and women. These changes are driven by different hormones.
In men, the hormone that gets released during puberty is testosterone, which among other things initiates sperm production. What do you think is the main hormone in female puberty?

What do you think o****estrogen does?

The main reproductive hormone in women is oestrogen. It is the female equivalent of the male sex hormone testosterone.
Which organ do you think produces oestrogen?

So the ovaries are responsible for producing oestrogen. Females have two ovaries. Which label do the ovaries have? Answer A, B or C.

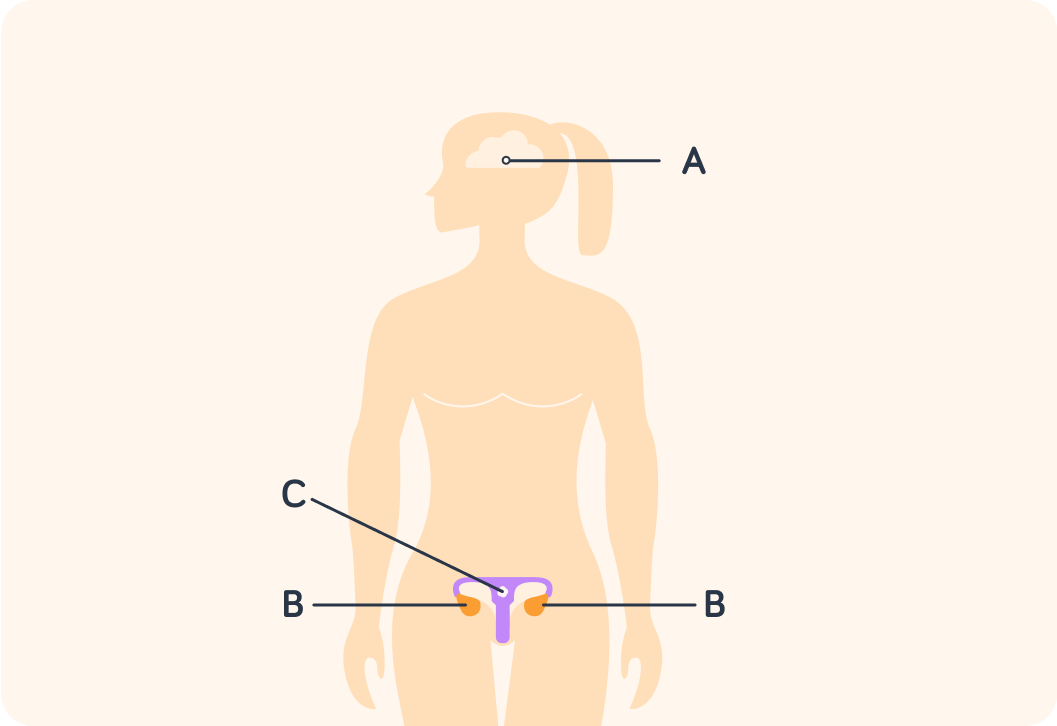
Every month after puberty, an egg travels from an ovary to the uterus, which has been prepped in case of a pregnancy. Where do you think the uterus is? Answer A, B or C.


Label A is for the pituitary gland
The pituitary gland is also very important for the female reproductive cycle. It is a small pea sized gland in the brain, and it is a sort of "master gland" which is in charge of a lot of hormone production other places in the body.

Oestrogen is produced in the ovaries. It causes visible changes, like breast development, but it also causes an egg to be released from the ovaries in a monthly cycle. What do we call that cycle?

The word menstruation comes from the latin word menses which means "month". So the menstrual cycle is a monthly cycle. The uterus lining is prepared for pregnancy. If a pregnancy doesn’t occur, the body sheds the uterus lining along with the unfertilised egg. The cycle has four stages and is controlled by four hormones.
Stage 1 (days 1-4): This is when menstruation starts. What do you notice about the lining of the uterus?
A) It is breaking down B) It is getting thicker C) It doesn't change
Answer A, B or C.

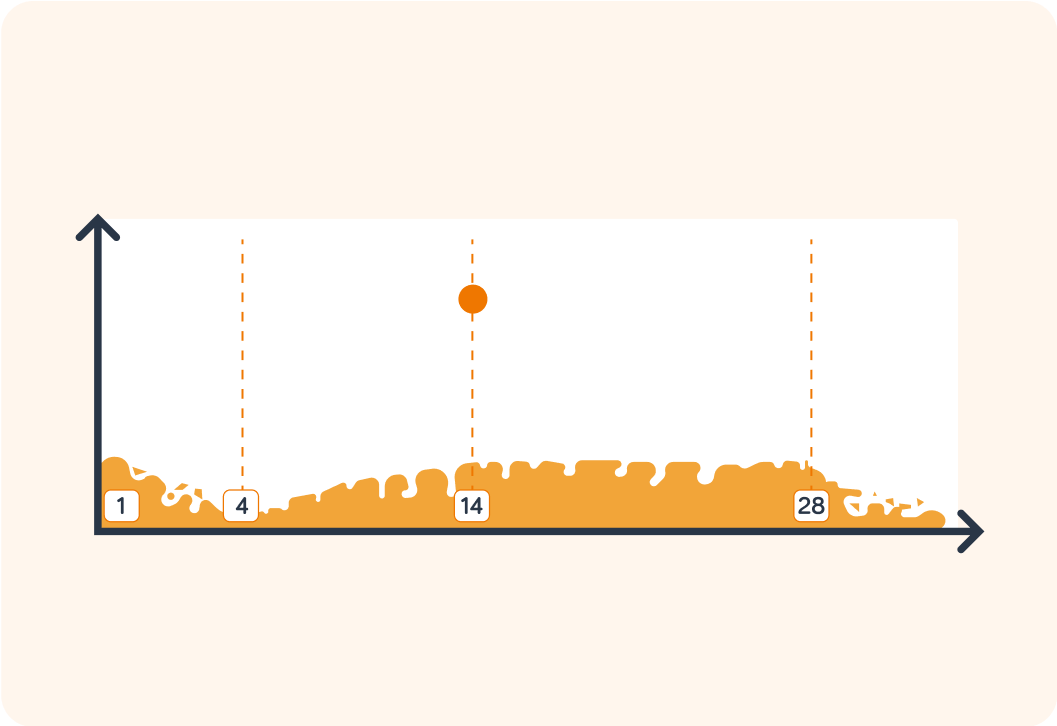
Stage 2 (days 4-14): The uterus lining takes about 10 days to build back up again, into a thick layer of blood vessels. Why do you think this occurs?
A) To produce hormones. B) To send blood to the ovaries. C) To get ready to receive a fertilised egg.
Answer A, B or C.


Stage 3 (day 14): This stage is called ovulation. This is where an egg is released. From which organ is an egg released and to where does it travel?
A) Uterus to the ovary B) Ovary to the uterus C) Placenta to the uterus
Answer A, B or C.


Stage 4 (days 14-28): During this time, the wall is preserved in case an egg gets fertilised and needs to implant on the wall to begin to grow.
If no egg is fertilised or implants, the uterus lining starts to break down again, and the cycle resumes from stage 1.

What stage takes 10 days to complete?
A) Stage 1 B) Stage 2 C) Stage 3 D) Stage 4
Answer A, B, C or D.


Here is the same diagram of the uterus lining as before.
But here we also see the hormones that are responsible for changes in the uterus lining and egg cycle. There are four of them: FSH, oestrogen, LH and progesterone
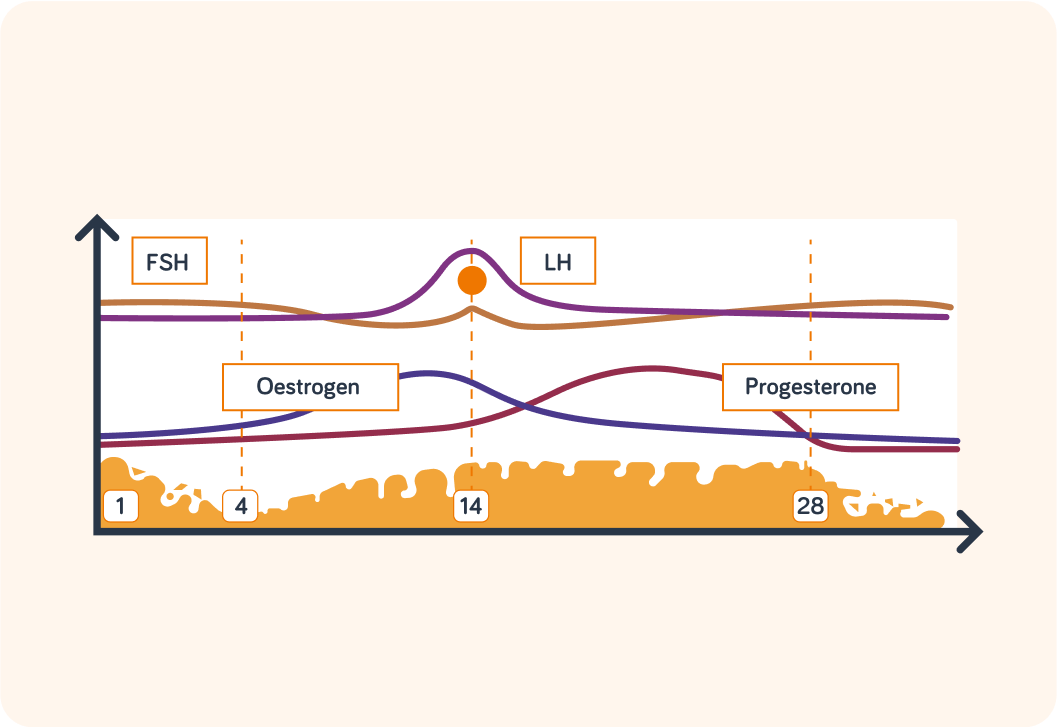
The first hormone is FSH (Follicle-Stimulating Hormone). FSH is produced in a gland in the brain. Which one?
A) Ovary gland B) Pituitary gland C) Pineal gland


FSH causes an egg to mature in one of the ovaries. The structure the egg is in is called a follicle. What stage do you think FSH works in?


Next is the hormone oestrogen. Where is that produced?
A) Ovaries B) Pituitary gland C) Uterus
Answer A, B or C.


Oestrogen is active in stage 2 (days 4-14). What does it do?
A) Causes the lining of the uterus to break down. B) Causes the lining of the uterus to thicken. C) Causes an egg to be released from the follicle.
Answer A, B or C.


Next is the hormone LH (Luteinising Hormone). It is released from the same place as FSH. Where is that?
A) The pineal gland B) The pituitary gland C) The ovaries
Answer A, B or C.


LH is responsible for encouraging the release of a mature egg from the ovary at day 14. What is this process called?


Lastly, progesterone is produced by the remains of the follicle after the egg has left. In what reproductive organ is the follicle that produces progesterone?


High levels of progesterone maintain the thick uterus lining. What do you think happens if the levels of progesterone falls?
A) The lining breaks down. B) The lining thickness stays the same. C) Oestrogen will cause levels of progesterone to increase again.


Back to stage 1.
If no egg is implanted in the uterus lining, the levels of progesterone fall and the uterus lining breaks down. And so the cycle starts again.

Where are both FSH and LH produced?

Where are both oestrogen and progesterone produced?

So, a good way to remember where each hormone is produced, is that oestrogen and progesterone are produced by the ovaries, while the two acronyms FSH and LH are produced by the pituitary gland.
It's a lot to take in! Luckily, there is also a good trick to remember the order that different hormones are active in in the cycle.
FSH is first...
and it’s alphabetically first too.
Then we have oestrogen...
which is the first of the two full hormone names (not the acronyms), and it is alphabetically before the other hormone that is not an acronym (progesterone). O comes before P in the alphabet.
The comes LH...
which is the second of the two acronyms.
Finally comes progesterone...
which is the second of the two full name hormones (not acronyms).
So it goes acronym, full name, acronym, full name...
where the acronym and the full name that are alphabetically before the other acronym of full name comes first: FSH, oestrogen, LH, progesterone.
