YOU ARE LEARNING:
Nuclear Chain Reactions

Nuclear Chain Reactions
Neutrons emitted from decaying isotopes during fission cause further fission in other isotopes, causing a chain reaction.
For nuclear fission to occur in a nuclear reactor, what must the uranium-235 nucleus first absorb?

We make nuclear reactors slow down the neutrons that we bombard nuclei with. Why do you think we do that? Pick 2 options.

You can select multiple answers
In any reaction, there are reactants and products. Name one of the two reactants in nuclear fission.

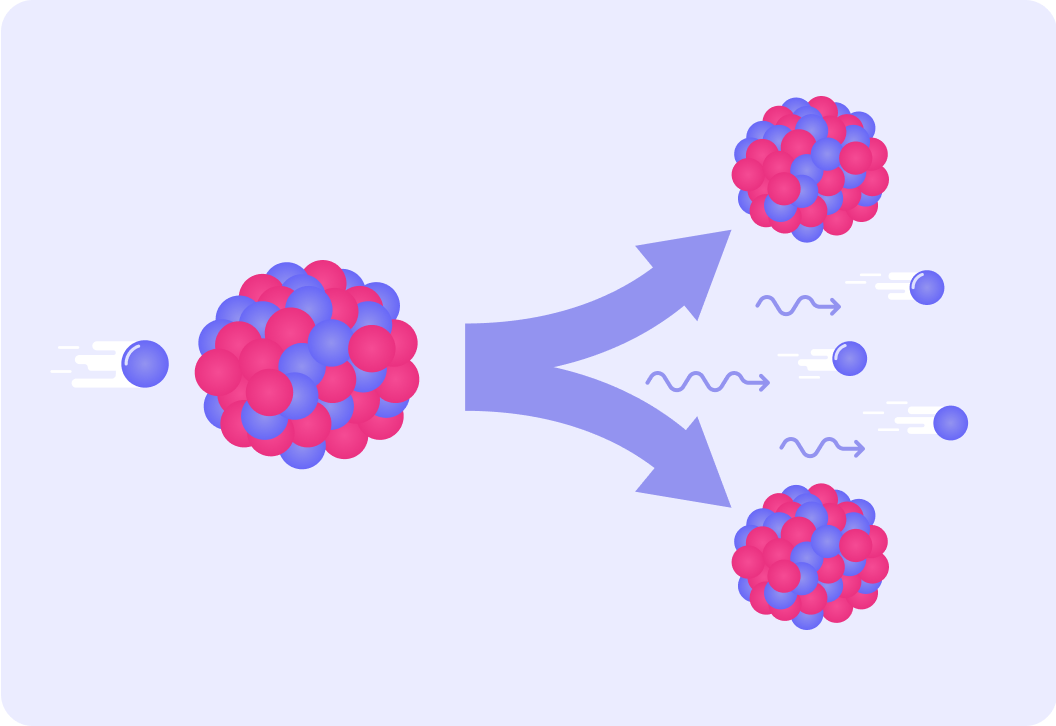
The two reactants in nuclear fission are...
uranium-235 nuclei and neutrons.

Radiation is also emitted during this process. It is represented in the diagram by the wavy arrows. What type of radiation is this?


The products of the reaction are two smaller nuclei, and three neutrons. The neutrons have a lot of kinetic energy, so will they be moving fast or slowly?


How likely are the fast-moving neutrons to hit another U-235 nucleus?
A) very likely B) not very likely
Answer A or B.


To release the most amount of energy in a nuclear reactor, conditions are controlled so that each fission event creates further fission events.
To achieve this, the fast moving neutron products of fission must first be slowed down, otherwise they go straight past the uranium nuclei.

The image shows the core of a nuclear reactor. Which of part of it do you think provides the uranium for fission?
A) Control rods B) Graphite moderator C) Fuel rods
Answer A, B or C.

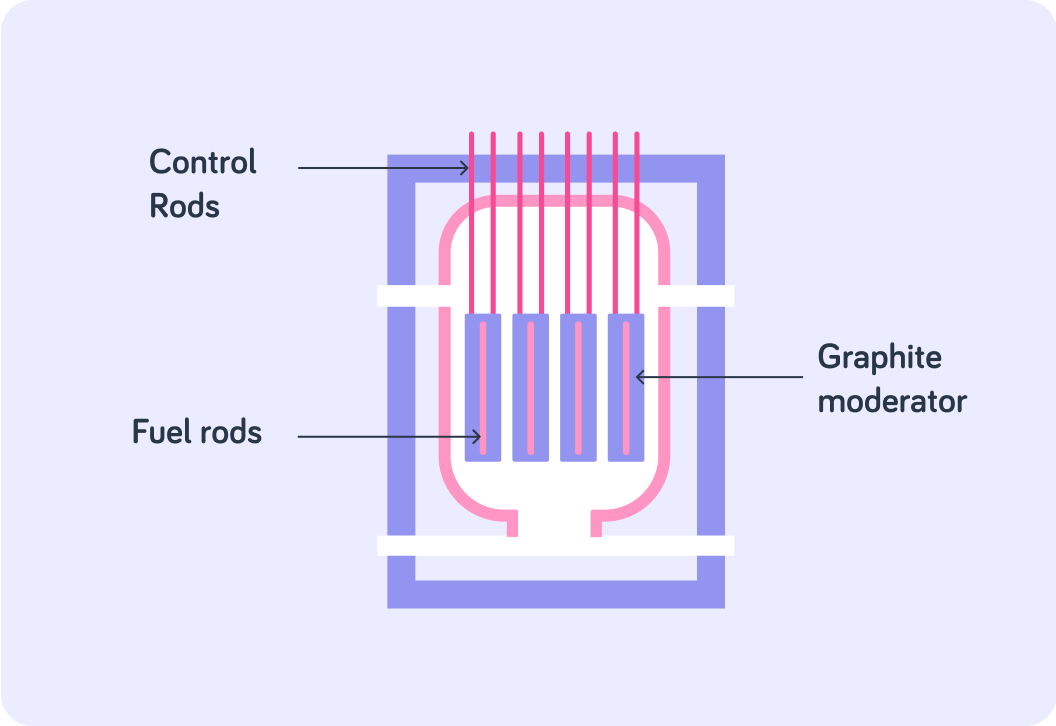
Which part of the reactor core do you think is responsible for slowing down neutrons so that they are more likely to be absorbed by the U-235 nuclei?
A) Control rods B) Graphite moderator C) Fuel rods
Answer A, B or C.


The moderator in a reactor is essential to slow down neutrons so that fission can occur.
Graphite moderators surround the fuel rods, so that all neutrons which reach the fuel rods have been slowed down. The image shows a graphite moderator, but some reactors use water as a moderator.

Imagine you line up a box of dominos. If you knock the first one over, the next one will get knocked over too and so on. That is an example of a chain reaction. What do you think we mean by a chain reaction in nuclear fission?

A nuclear chain reaction is when each fission event directly leads to more fission events. The neutrons which are released in one event strike further nuclei, which in turn release more neutrons so that the chain reaction continues.
Two neutrons from the first fission reaction cause two U-235 nuclei to split, releasing four more neutrons into the chain. How many neutrons will enter the chain after these four neutrons split four more uranium nuclei, if each of these releases two neutrons?

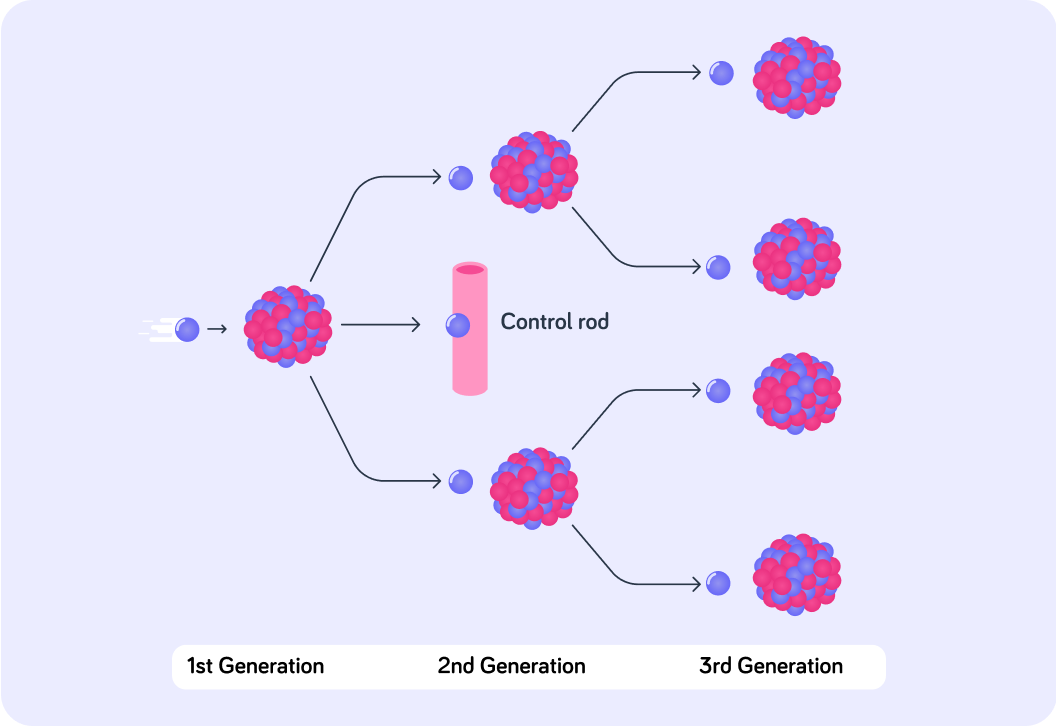
Each domino causes just one other domino to fall, but in a nuclear chain reaction each fission event leads to twice as many further reactions!
Sometimes, fission of U-235 releases more than two neutrons. In fact if you look closely at the second generation in the diagram, three neutrons have been released.

If every neutron caused another fission event, the rate of reaction would grow rapidly and uncontrollably in a very short period of time. This is dangerous! We use control rods to prevent this from happening. What do you think the control rods do?
A) Speed up neutrons B) Reflect neutrons C) Absorb neutrons
Answer A, B or C.


So a chain reaction allows fission reactions to continue and multiply, so that energy can be released efficiently and safely. The number of neutrons is controlled by control rods. What else do you think is important for controlling and sustaining the chain reaction?

Critical mass
If the mass of uranium available for fission is too large, we call that supercritical mass. This would cause a large number of neutrons to be released. The rate of fission in a chain reaction with a supercritical mass would...

What if we have too small a mass of uranium? Neutrons can then escape without colliding into any U-235 nuclei, causing the rate of reaction to decrease rapidly. What do you think we call it when the mass of uranium is too small?

So too much uranium mass is called supercritical mass and too little uranium mass is called subcritical mass. What is it called when we have just the right amount of uranium mass?

So to keep a chain reaction going, there must be enough uranium to prevent neutrons from escaping the chain reaction, but not so much that the chain reaction gets out of control.
We call this amount of mass for critical mass.
The chain reaction is controlled by using the critical mass of uranium. If the mass was subcritical, the chain reaction would not be sustained. On the other hand, with a supercritical mass the rate of reaction would increase too rapidly, causing temperature increases of thousands of degrees in a fraction of a second. This could cause a nuclear explosion!
