YOU ARE LEARNING:
Other Uses of Radiation

Other Uses of Radiation
Gamma radiation is used for sterilising food and equipment and beta radiation can be used for gauging thickness and detecting leaks.
Radiation has many uses!
Earlier lessons have given some common examples
Cancer treatment Medical tracers and PET scans Smoke alarms
This lesson quickly introduces another 4 uses
Sterilisation of medical equipment Sterilisation of food Gauging thickness Detecting leaks
Radiation used to sterilise medical equipment
First of all, what does it mean to sterilise something?

So sterilisation means to remove all bacteria
Gamma radiation can help do this, so that medical equipment doesn't bring bacteria into the body during surgery for example.
Gamma radiation can be used to sterilise medical equipment because it _________ all living cells and microorganisms, like bacteria.

Why does gamma radiation kill living cell?

Gamma radiation is better than for example boiling equipment to sterilise it. Why do you think that is?

So gamma radiation doesn't require high temperatures
This means it can be used to sterilise equipment that would otherwise melt, for example plastic syringes like this one.
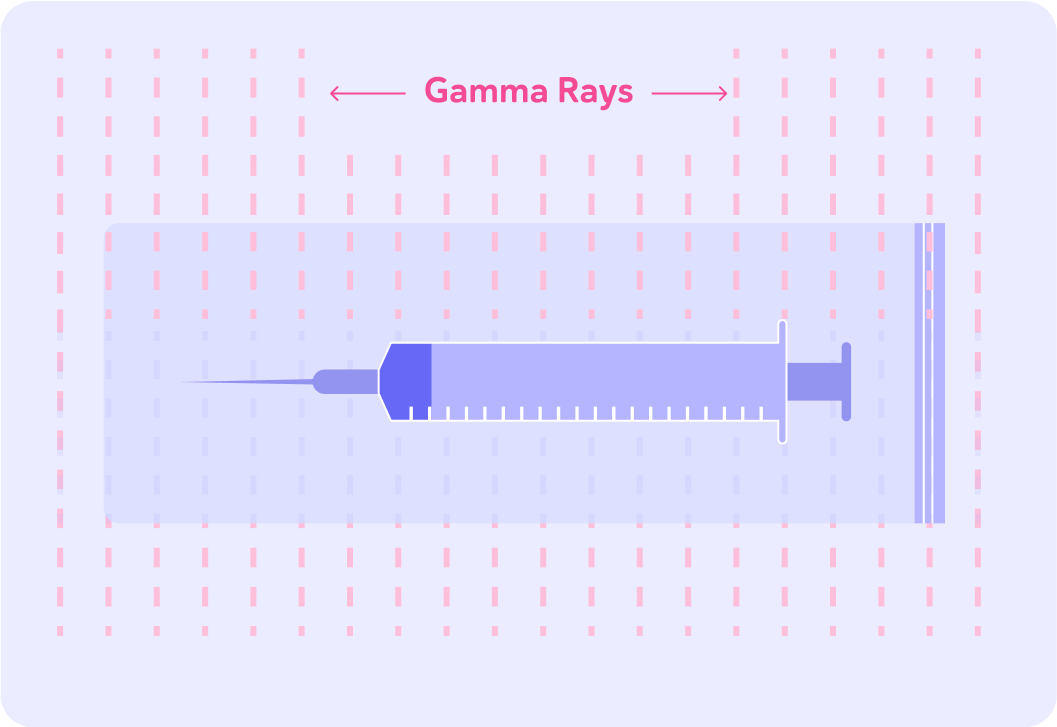
The syringe is sealed before it is sterilised with gamma radiation. Why do you think that is?
A) So that the gamma radiation does not destroy it B) So that it cannot become dirty again C) So that the doctor doesn't injure himself


But how does gamma radiation get into the packaging?
A) It doesn't, it only sterilises the outside of the package. B) It dissolves the sealing on the package. C) It goes straight through because it is highly penetrating.


It's important that medical equipment is sealed in packaging before it's sterilised
Gamma radiation is the most penetrating kind of ionising radiation, so it goes straight through the packaging and sterilises the syringe inside. This ensures that the syringe stays sterilised until it's going to be used.

Radiation used to sterilise food
Gamma irradiation can also be used to preserve foods, like vegetables and fresh fruit
This means they will be safe to eat even though they haven't been heated up.
What do you think gamma radiation destroys when food gets irradiated? Pick all the options you think are correct.

You can select multiple answers
So sterilising food means the food will stay fresh for longer
It kills microorganisms like fungi and bacteria, which would otherwise make the food start to decay. It also inhibits germination and premature ripening in fruits and vegetables.
When food gets irradiated, does it become radioactive? Answer yes or no.

So sterilising food helps to prolong its shelf life
The food itself does not become radioactive!
Radiation can also be used to find leaks in underground pipelines, like the one in this image.
Here, an underground industrial pipeline with water going through it has a crack in the middle of the pipe and water is leaking out.
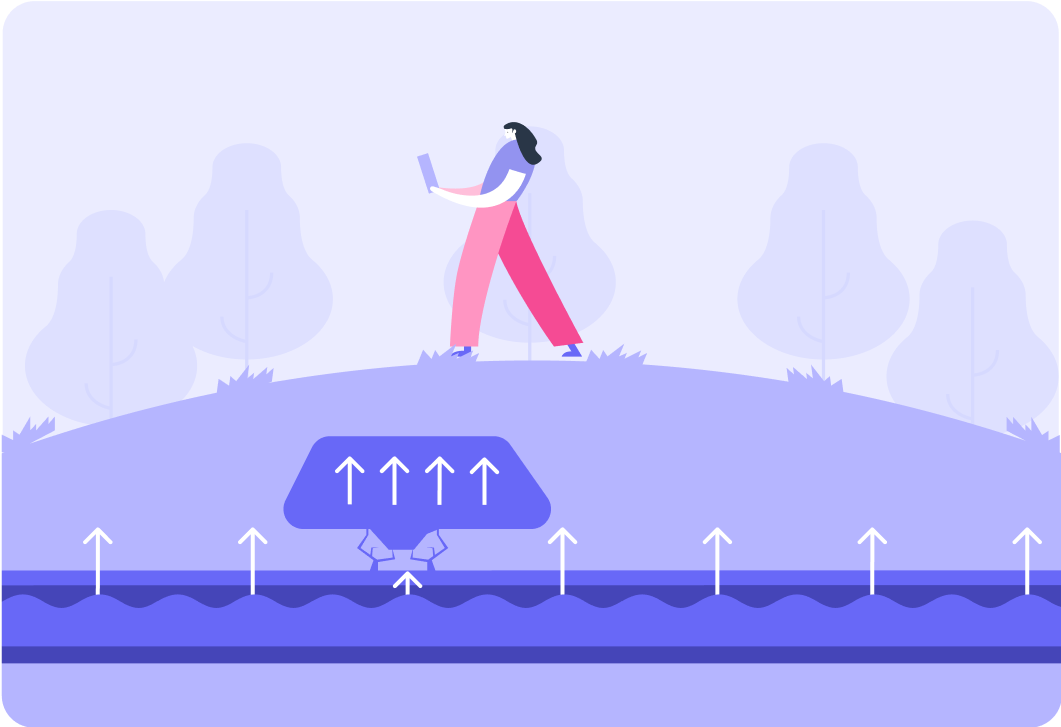

A radioactive tracer, like sodium-24, is sent through the pipe
As it decays, it emits radiation which can be detected from the surface above the pipe by the person holding the Geiger-Muller tube and counter.

Where will the Geiger-Muller tube detect the most radiation?
A) Directly above the leak B) Furthest away from the leak


The count rate on the GM tube will increase directly above where the pipe is leaking
A larger amount of water and sodium-24 will collect there, so the person will know that this is where the leak is.

Can you use alpha radiation to detect leaks in underground pipes? Answer yes or no.


You would use beta radiation or gamma radiation, depending on where the pipe is
If the pipe is buried under many layers of rock or concrete, you have to use gamma radiation because beta radiation wouldn't reach the surface.
If the pipe is in the sea or buried in only a thin layer of soil, beta radiation is better because gamma radiation would penetrate everywhere - not just where the leak is.

Should you use tracers with long or short half-lives as industrial tracers?
A) Long B) Short


It's important to use a radioisotope with a half-life of just a few hours or days
For example, sodium-24 has a half-life of about 15 hours. That means that the danger to living organisms near the pipe is minimal.

Finally, beta radiation can be used to trace and gauge thickness
For example, this image shows how aluminium foil is made.
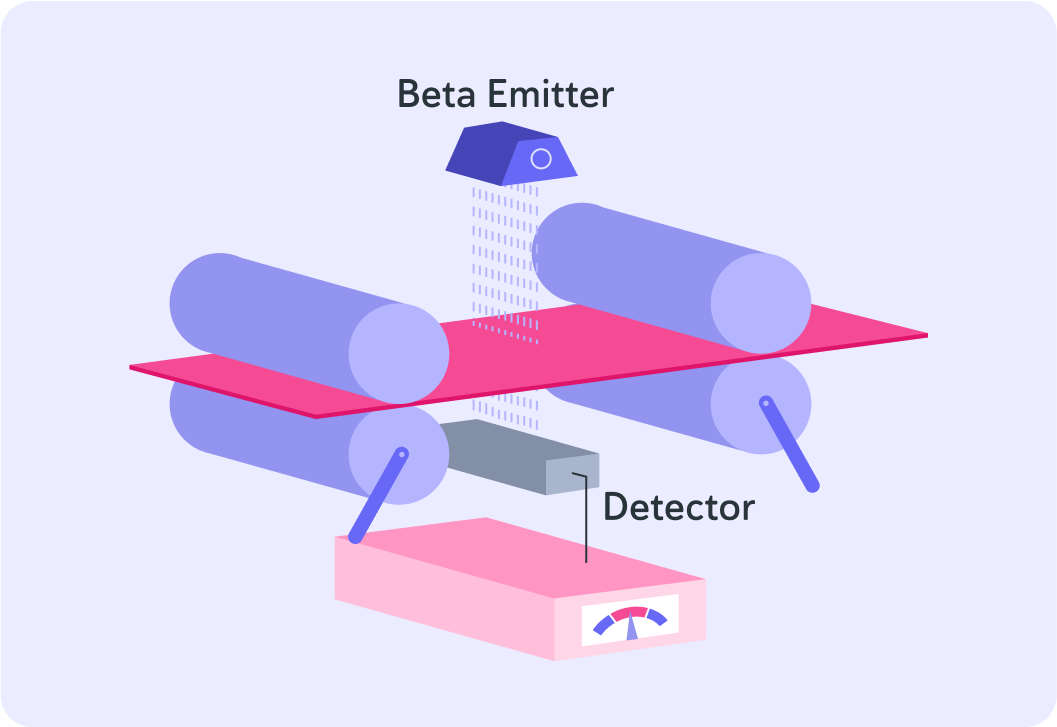
Beta radiation is passed through the foil and is detected on the other side. By measuring how much radiation has gone through, we can tell...
A) how magnetic the foil is. B) how thick the foil is. C) how smooth the foil is.


The thicker the foil is, the ______ beta radiation will be detected.
A) more B) less


The thicker the foil, the more beta radiation will be absorbed
This means that the thicker foil is, the less beta radiation will be detected on the other side.

If the detecter finds that there is too little beta radiation passing thorough it will send a signal to the rollers
The rollers then increase the force on the foil to make it thinner.

Why do you think beta radiation and not gamma radiation is used?
A) Gamma radiation would ionise the foil. B) Gamma radiation is too dangerous. C) Gamma radiation wouldn't be absorbed by the foil at all.


The radioisotopes that are used for thickness control actually tend to have longer half-lives
This is so that the factory will produce less waste as they will have to replace the radioisotopes less often.

Summary
Radiation is used for many purposes
Previous lessons explained the use of radioisotopes as medical tracers, to treat cancer and in smoke alarms.
This lesson looked at radioisotopes used for sterilising equipment, sterilising food, detecting leaks and gauging and controlling thickness.
It is important to know the properties of the radioisotope that is being used for different purposes
You should think about its half-life, its penetrating power and its ionising potential.
Why half-life matters
We use radioisotopes with short half-lives as medical and industrial tracers. This is to reduce the risk of irradiation to humans and the environment.
We use radioisotopes with longer half-lives for gauging thickness to reduce the amount of waste produced.
Why penetrating power matters
For sterilising equipment, we need radiation that can easily penetrate sealed packaging, so we use gamma radiation.
For detecting leaks we can use either gamma or beta radiation depending on how far down into the ground the pipes are.
For gauging thickness we need radiation with a penetrating power that is not too strong and not too weak, so beta radiation.
Why ionising potential matters
You don't want to use a type of radiation with an unnecessary amount of energy. Ionising radiation kills living cells, so it can cause damage to humans and the environment.
