YOU ARE LEARNING:
Ray Diagrams of Refraction

Ray Diagrams of Refraction
Drawing ray diagrams for refraction allow us to see clearly the angles of incidence and refraction. We can also locate where virtual images are formed.
What is light refraction?

What features of a wave are affected by refraction?

You can select multiple answers
This lesson will focus on drawing ray diagrams for refraction. When a light ray hits a surface, what is the angle it makes with the normal called?

In this diagram we can see a light ray travelling from air into glass, and then from glass to air again. The angle of refraction is measured between the refracted ray and the ... ?

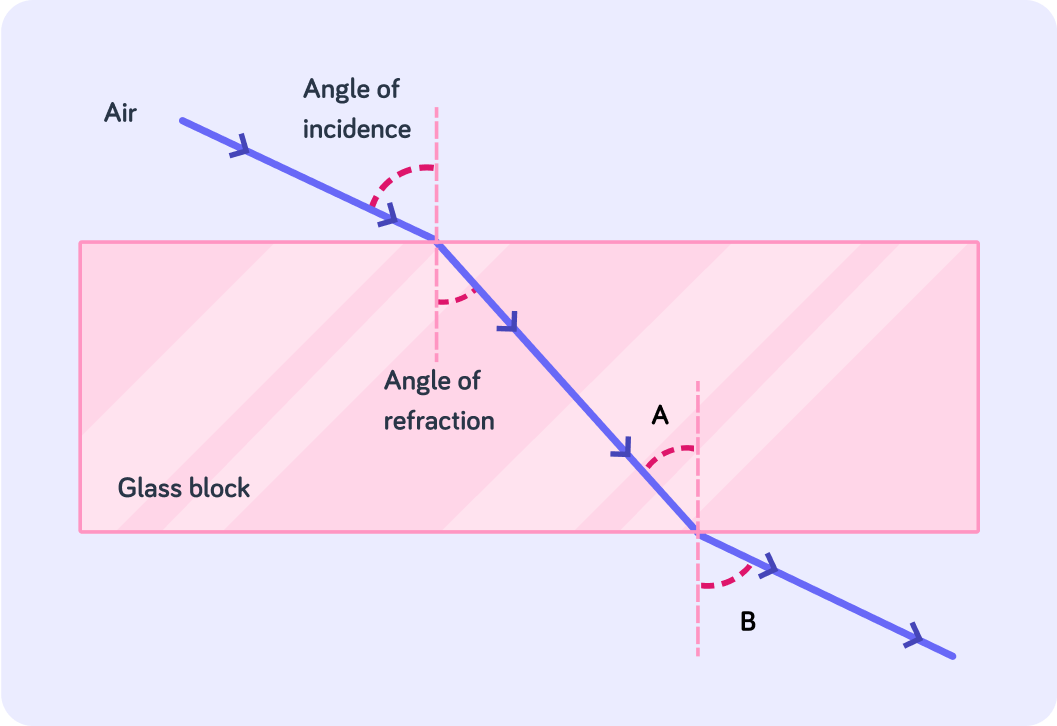
The light gets refracted a second time when it goes from the glass block to air. Which angle is the angle of incidence? Answer A or B.


Does the angle of incidence equal the angle of refraction?

Do you remember how going from less dense to a more dense medium affects the speed of light?

Does the light ray's speed increase or decrease?

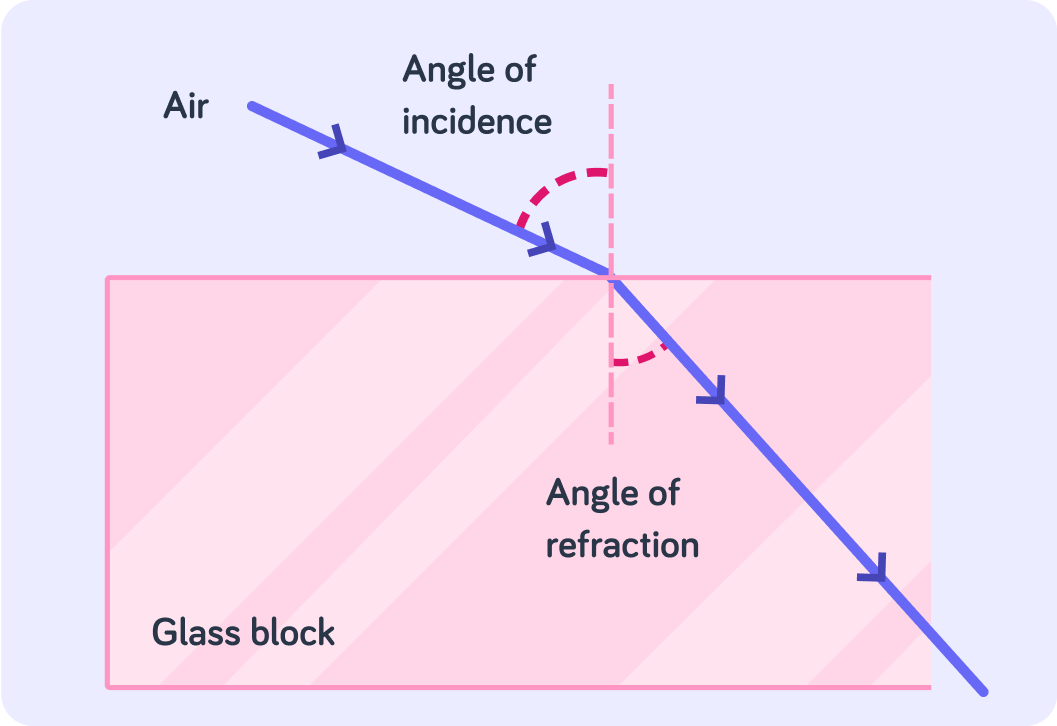
Does the refracted ray move towards or away from the normal?


Here we can see how a light ray slows down and bends towards the normal.
This happens when it goes from a less dense to a more dense medium.

In this case, does the light ray's speed increase or decrease?

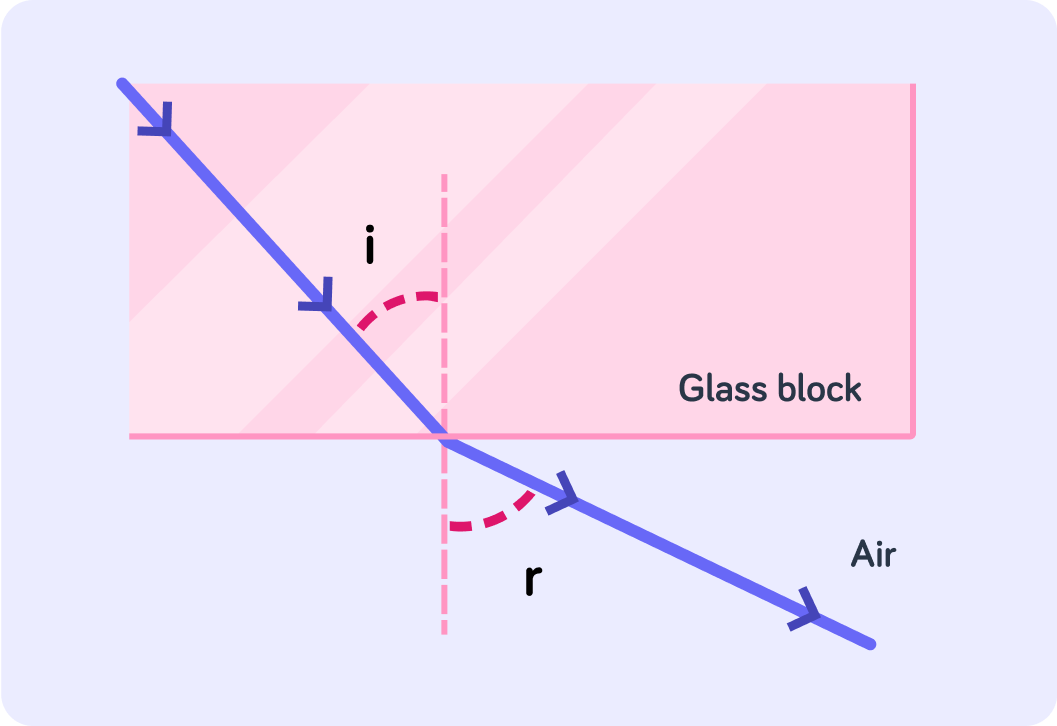
Does the refracted ray move towards or away from the normal?


Here we can see how a light ray speed up and bend away from the normal.
This happens when it goes from a denser to a less dense medium.

A way to remember how light bends when it is refracted, is by using F.A.S.T.
Faster speed bends Away from the normal. Slower speed bend Towards the normal.

If you look into a fish bowl, does the fish appear to be its actual size?

In this diagram you can see where a virtual image is formed.
Just like with reflected images, you find the location of the image by tracing the refracted ray backwards.
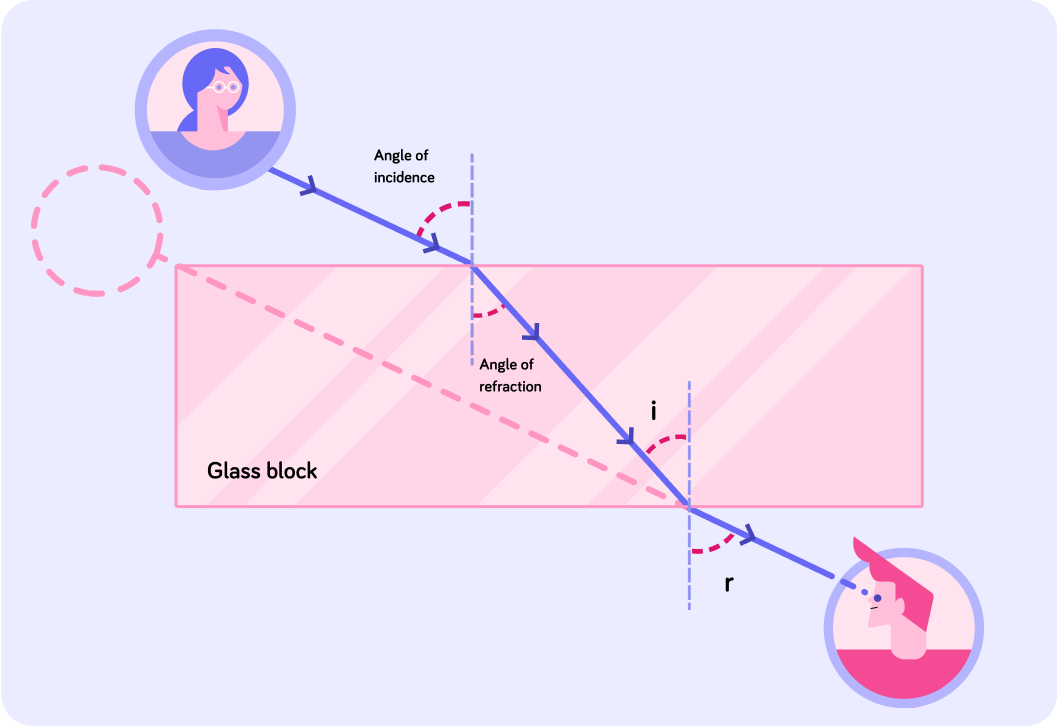
Here is an example of how refraction can make things appear differently.
You can try this out yourself with a glass of water!

