YOU ARE LEARNING:
Gaseous Exchange

Gaseous Exchange
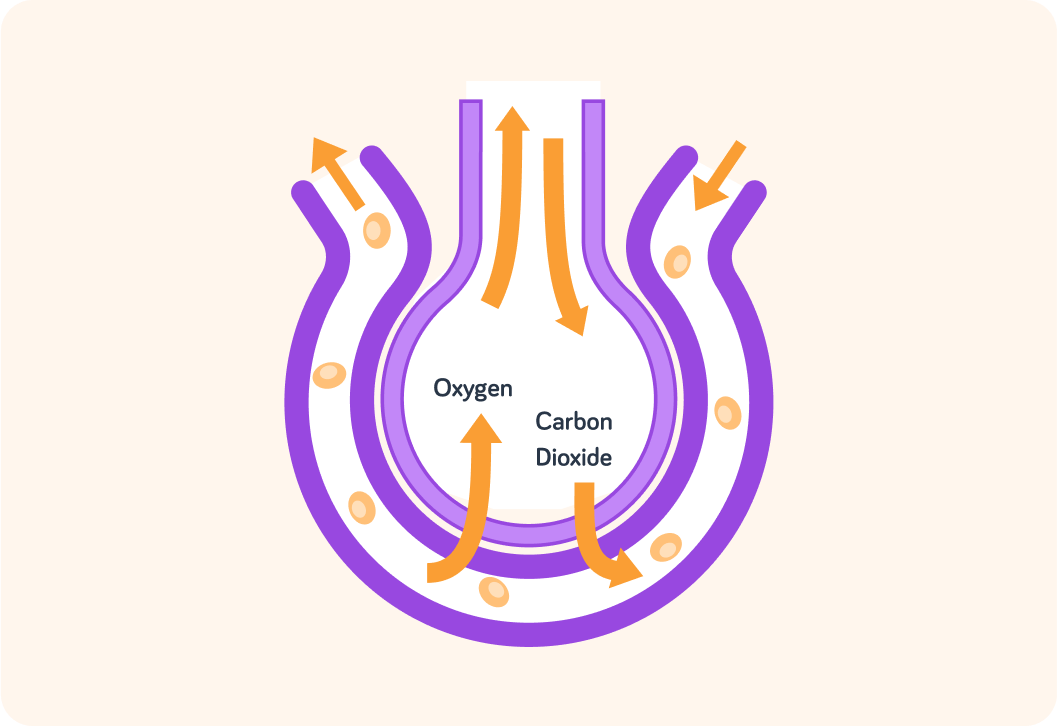
The alveoli are adapted for important gas exchange via diffusion between air in the lungs and blood in capillaries.
Do you remember what the composition of inhaled and exhaled air is? Choose the right values from the options provided.

You can select multiple answers
Why is there more oxygen in the air we breathe in than in the air we breathe out, and why is it the other way around for carbon dioxide? Pick the most correct option.

Where do you think gaseous exchange takes place? Pick all the options you think are correct.

You can select multiple answers
Gaseous exchange in the lungs takes place in the alveoli
The surface that gases move across should be very thin (a single layer of cells, usually), be moist, have a large surface area and it should have a good transport system that carries gases to and from the exchange surface.
Air enters the alveolus
We breathe in air with a high O2 concentration and low CO2 concentration. Some of the O2 and CO2 dissolves in the water, lining the inside of the alveoli.

Where do you think the O2 concentration is higher?
A) In the blood in the capillary on the outside of the alveoli B) In the water, lining the inside of the alveoli


The movement of oxygen
O2 moved from the higher concentration in the water that lines the alveoli to the lower concentration in the blood in the capillary on the outside of the alveoli.

What do we call the process where particles and substances move from higher to lower concentration, like the O2 that moves from the water lining to the blood in the alveoli?


The movement of carbon dioxide.
CO2 is a waste product of cellular respiration. The blood carries it from the cells to the capillaries around the alveoli. It diffuses in the opposite direction to O2 because the concentration of CO2 in the blood is higher **** than the concentration in the water lining the alveoli.

Select all the characteristics needed for an effective gas exchange surface.

You can select multiple answers
When the concentration of particles in one area is higher than the concentration in another area, it is known as a ....

The alveoli have adapted to make the rate of diffusion of O2 and CO2 as effective as possible.
A large surface area
The more space there is for molecules to move from one place to another, the quicker they can move.
A short diffusion distance
The walls of the alveoli and surrounding capillaries are each only one cell thick. Molecules can diffuse quicker if they don't have too far to move.
A steep concentration gradient
A concentration gradient is when there's a difference between two concentrations. If this difference is large, substances will diffuse faster.
We use the word _______ to refer to the amount of substance in a defined space.

Would you say the relationship between distance and the rate of diffusion is directly or inversely proportional?

Fick's law of diffusion states that rateofdiffusion∝thicknessofmembranesurfacearea×concentrationdifference
What do you think would happen to the rate of diffusion if the thickness of a membrane doubled?

