YOU ARE LEARNING:
Reflexes
Reflexes
Reflexes are immediate and automatic response to stimuli that cause harm to the body.
Imagine you're holding a little furry hamster, and it decides to attack and bite you!
Without thinking, you'd pull your hand away sharpish!
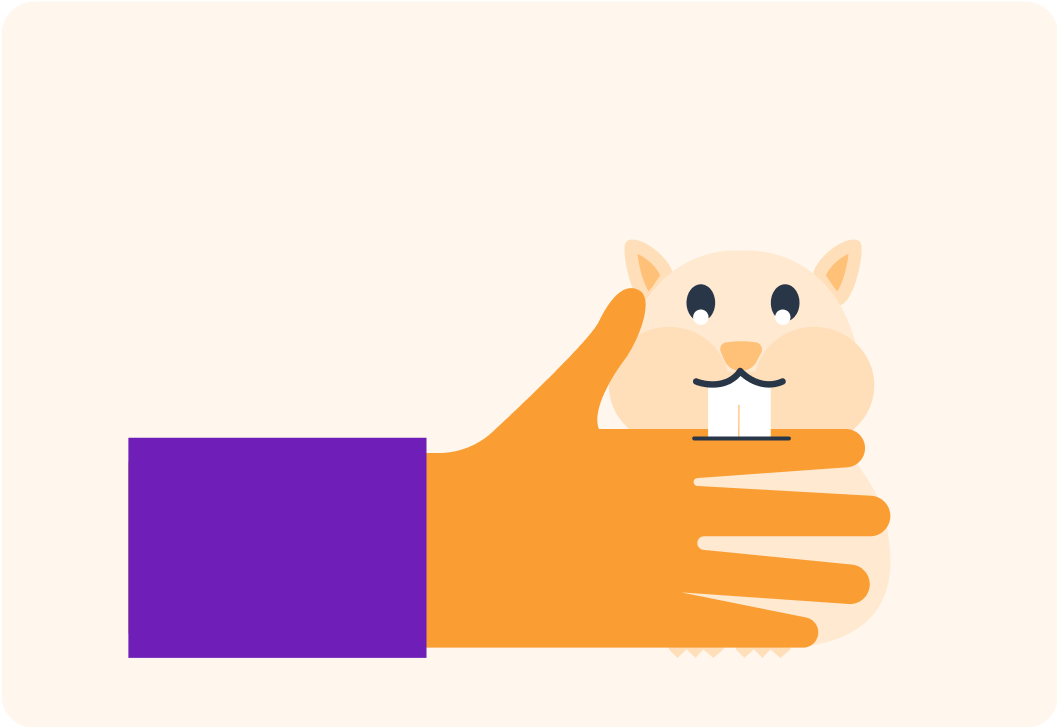

What type of reaction do you think this is?
A) Accidental B) Controlled C) Reflex


A reflex reaction is an automatic reaction your body carries out to prevent a stimulus causing damage.
Another type of reflex reaction is your eye response to bright light. If someone shines a light in your eye, your pupil contracts to limit the light entering the eye, to prevent damage.

Reflex reactions are automatic. Do you think they involve the conscious part of the brain?

Reflexes don't involve the conscious part of your brain. The reason for this is that they should be rapid enough to reduce the risk of the body being damaged by the stimulus. This reduced pathway from receptor to effector is called a reflex arc.
The main difference in the reflex arc compared to normal responses is the relay neurone. Where are the relay neurones located?

When a hamster bites your finger, the signals don't actually go all the way to the conscious part of the central nervous system. It only makes it to the relay neurones in the spinal cord that are closest to the finger. Then the signal goes straight back down the motor neurone from there to the effector. So you can think of reflex arcs as a kind of short-cut for signals.
If the action is automatic, why does the impulse have to go to the central nervous system at all?

This picture summarises everything so far
Reflex arcs are faster than usual responses because the signal travels a shorter distance than in conscious reactions.

Through which structure does a message from the sensory neurone reach the relay neurone?
A) Effector B) Synapse C) Bridge


Do electrical impulses cross a synapse? Answer yes or no.


What is the chemical called that crosses a synapse?


Why are reflex arcs faster than normal responses?
A) The CNS isn't used in the reflex arc. B) The effector organ can decide itself what action to take. C) The electrical impulse doesn't have to travel all the way to the brain.


What is missing in block C?


What is missing in block E?


What is missing in block F?


The time it takes for reflexes to happen can be measured.
Reaction times can be measured by catching a ruler as described below.
One person should sit with their arm resting on a table, their hand extending off the edge.
This will ensure their arm doesn't move during the test.
Another person should place a ruler vertically in between their thumb and forefinger.
They should ensure the zero end of the ruler is down towards the thumb.
Then they let go of the ruler. Do you think they should tell the person when they are going to let go? Answer yes or no.

The person will then have to try and catch the ruler before it falls through their fingers. If person A catches the rules after 24 cm and person B catches the rules after 8 cm, then who has the fastest reaction time? Answer A or B.

This test should be repeated several times. Why is this?
A) So the person can choose their best results to use for analysing. B) So the person can practice their catching technique. C) So an average can be calculated to give a good representation of reaction time.

The different reaction times can then be added together for that person, and divided by the number of attempts they had.
This will give them an average reaction time under those circumstances.
Which factors do you think might affect reaction times?

You can select multiple answers
Imagine that person had a caffeinated drink. That would impact their reaction time. We would be able to see that if we repeated the experiment 10 minutes or so after consumption of the drink.
Here is a graph with the results from the two different experimental conditions.
The blue shows the first experiment before caffeine was taken, the red shows the reaction times after a caffeinated drink was taken.

What effect has caffeine generally had on this person's reaction times?
A) Slower B) No effect C) Faster


What general change do you notice between each catch attempt?
A) The person gets slower and slower. B) The person gets faster and faster.


Which is the fastest reaction time overall?
A) Before caffeine, 1st catch attempt B) After caffeine, 3rd catch attempt C) Before caffeine, 3rd catch attempt


What distance had the ruler travelled on the slowest reaction time overall?
A) Around 20 cm. B) Around 14 cm. C) Around 25 cm.


What distance had the ruler travelled on the slowest reaction time in the caffeinated trial?
A) Around 14 cm. B) Around 18 cm. C) Around 20 cm.


