YOU ARE LEARNING:
Types of Neurones
Types of Neurones
Neurones are the agents that carry electrical impulses to communicate and it is what makes up the nervous system.
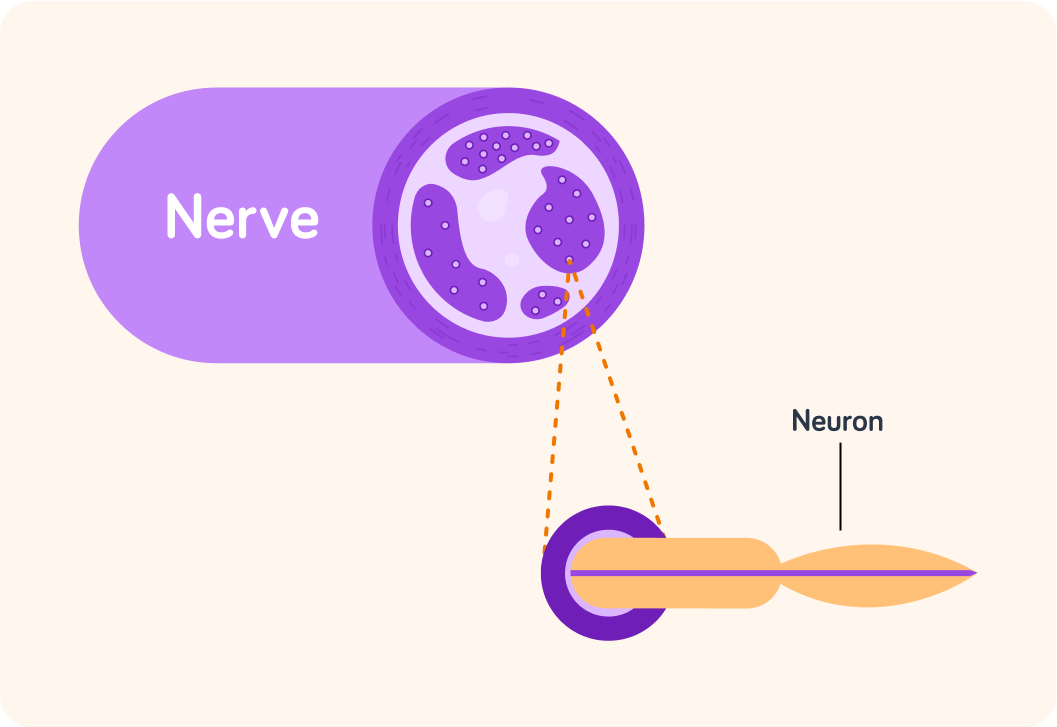
Nerve cells are also known as "neurones"
They are the cells responsible for carrying electrical messages (impulses) when stimulated. Many neurones make up a nerve.
To recap, what is the nervous system called that includes the brain and spinal cord?

Which part of the nervous system refers to the nerves outside of the brain and spinal cord?

There are three types of neurones.
The first type of neurone is sensory receptors. They are cells which receive stimuli and send the environmental information through neurones to the central nervous system. What do you think these neurones are called?

The second type of neurone is responsible for receiving information from the sensory neurone and passing it onto the third type of neurone. Its name relates to its function. What do you think this is?

The third type of neurone is the "motor neurone".
This neurone sends information about an action to be taken to an effector.
If relay neurones take information from a sensory neurone and pass it onto a motor neurone, where do you think the relay neurone might be located?

This is an image of a motor neurone.
The three neurone types share many features, but differ in others. We are going to focus on the features that all neurones share.
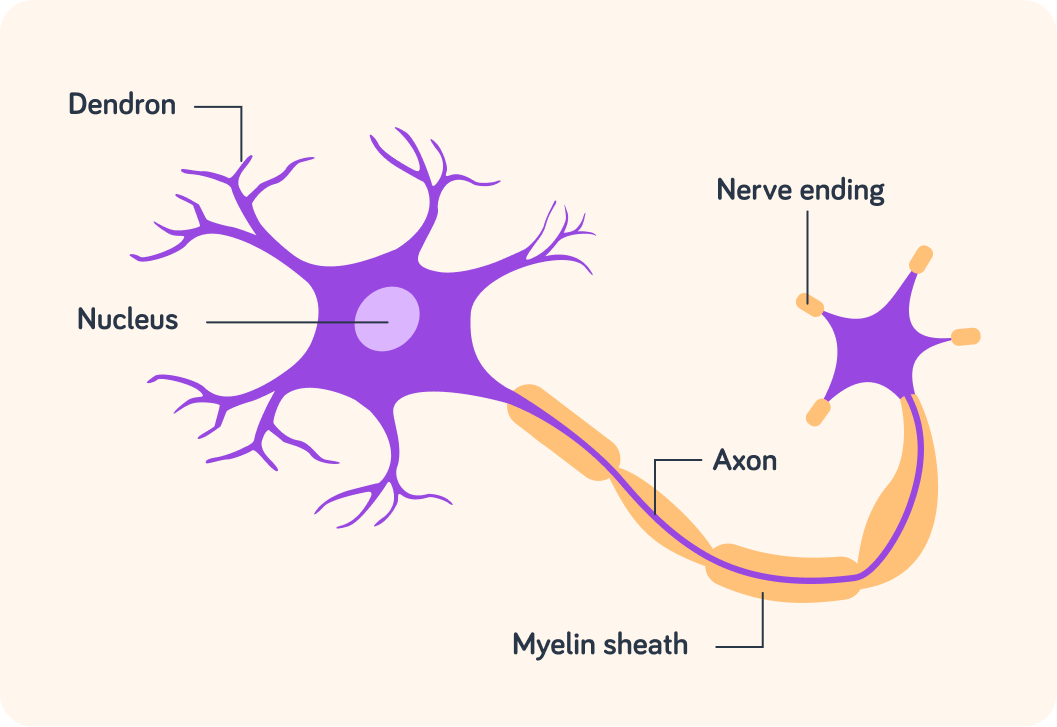
The dendrons are tiny branches coming off one end of the neurone. What do you think the function of dendrons are?
A) To implant the neurone in the surrounding tissue. B) To receive signals from other neurones and pass them down the neurone. C) To physically connect to many other neurones.


The axon is the long fibre of the neurone. What do you think its function is?
A) To carry electrical impulse messages along the neurone. B) To connect the receptor to the brain. C) To connect the stimulus to the brain.


The axon is surrounded by a fatty myelin sheath.
Like how a house's insulation stops heat escaping, the myelin sheath stops electrical impulses from escaping the neurone. This allows the electrical impulses to transmit efficiently.

Which way do you think the electrical impulse travels along the neurone, A or B?


What is structure A?

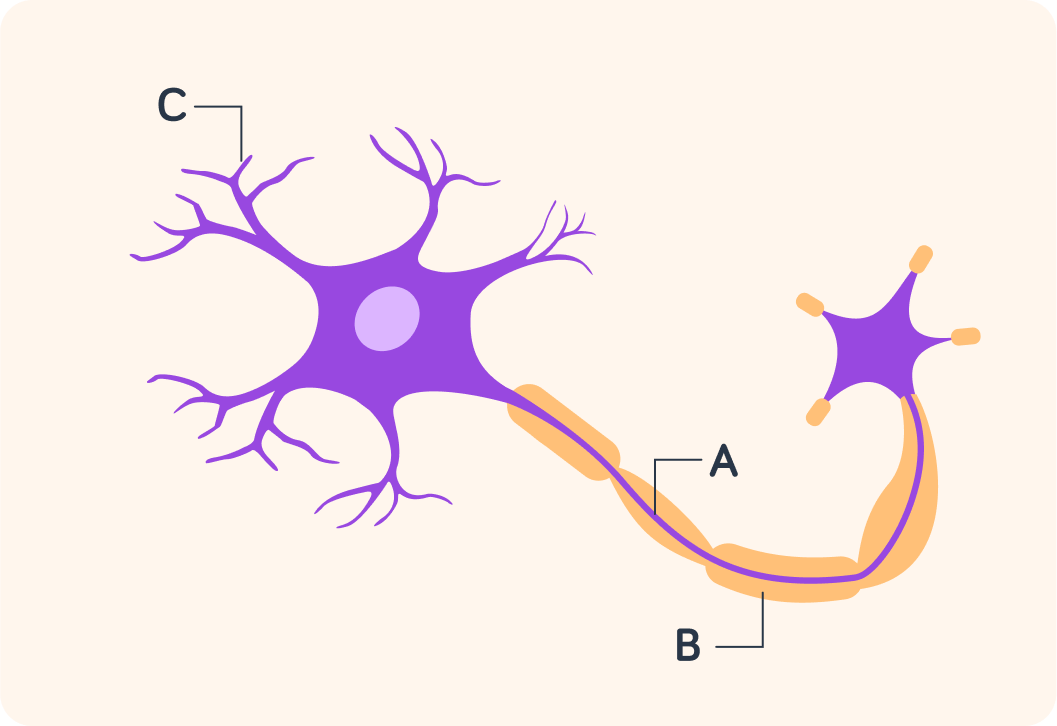
What is structure C?


What is structure B?


Which is the correct order for an impulse travelling through the nervous system?

To sum up
Sensory receptors...
respond to stimuli in the environment.
The receptors then send information via sensory neurones to the central nervous system.
This may be the brain or the spinal cord.
The central nervous system passes impulses to motor neurones...
which take information about the action to be taken, away from the central nervous system.
The action is ultimately taken by the effector.
This may be decreasing body temperature or moving your hand. Effectors include glands and muscles.
