YOU ARE LEARNING:
Cancer

Cancer
We will understand cancer in the context of cell division that is uncontrolled.
Cells in the body have to make identical copies of themselves for growth and repair by cell division. What is this type of cell division called?

Mitosis is responsible for producing new cells during development and replacing damaged and old cells throughout life. It is our genetics that control this process so that it only happens where and when it is needed.
What might happen if the genes controlling mitosis were damaged or disabled?

Cells that are replicating uncontrollably form a ball of cells. You might know already what we call such a ball of cells. We call it a ___________.

Tumours are different from the cells of the tissue around them. Are all tumour cancers?

Some tumours grow slowly and do not spread from the organ in which they develop. These are known as benign tumours. Have a look at the image. What do you think helps prevent these tumours from spreading?

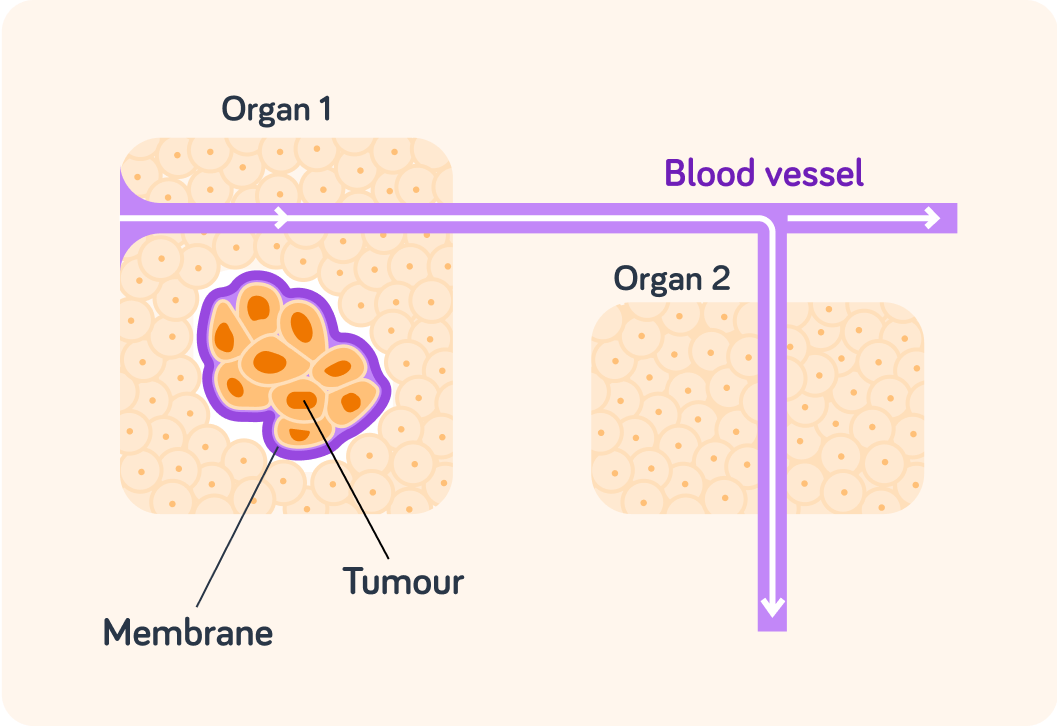
This membrane also makes it easier, in some cases, to surgically remove the tumour.
Benign tumours are less likely to reappear than cancerous tumours.

Although benign tumours are not cancerous, they are still a medical concern. Why might they cause a problem to the patient? Pick all the options you think are correct.

You can select multiple answers
Malignant (cancerous) tumours are also a ball of cells that are dividing uncontrollably. However, in this case there is no membrane to hold the cells in place.
These tumours produce chemicals that encourage the local blood vessels to grow towards and around them.
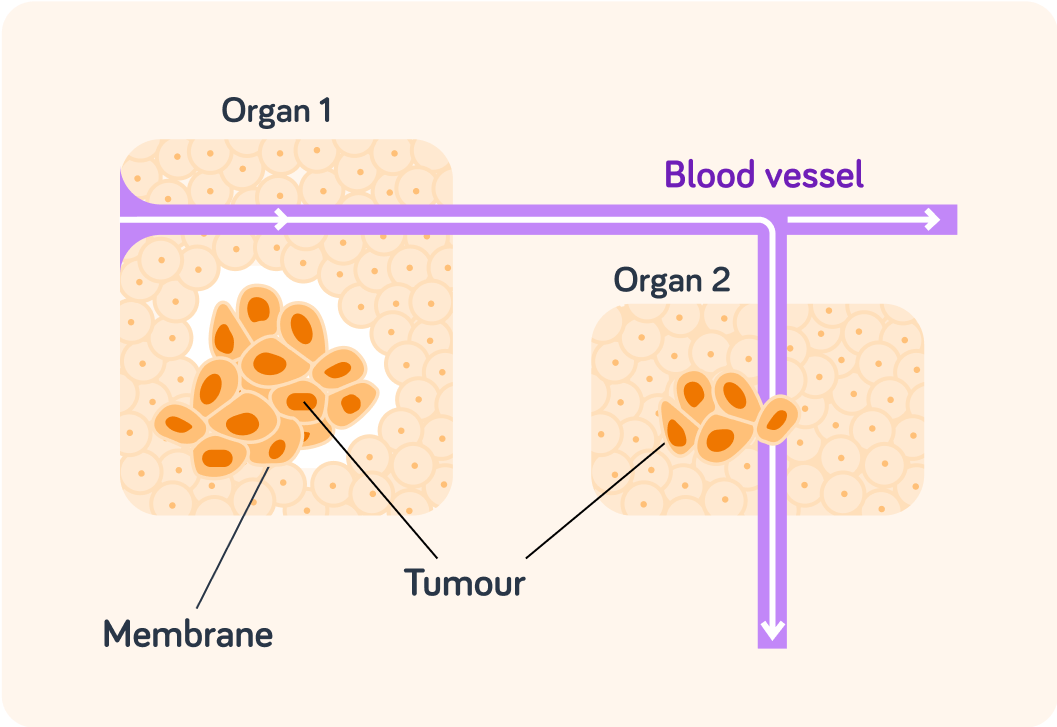
What do these new blood vessels allow the cancer cells to do that the benign ones couldn't?
A) Move from one part of the body to another. B) Develop a membrane. C) Grow slowly.


The blood flow allows loose cancer cells to flow around the body to form new cancers.
This is how cancer spreads.

The rich blood supply to the malignant tumour will have one other effect on the tumour. It means that the tumour will grow and develop ____________.

Benign tumour: Slow growth rate, enclosed in a membrane, no additional blood supply, can't spread. Malignant tumour: Fast growth rate, no membrane, additional blood supply, can spread.
Are cancers contagious?

Cancer results from changes in the cell that make it divide uncontrollably. Certain factors increase the risk of developing certain cancers. What is meant here by the word risk?

Pick all the statement that are true about the risks of developing cancers.

You can select multiple answers
Summary
Sunbathing...
exposes the body to high energy UV radiation and can cause skin cancers.
HPV - Human papilloma virus...
can increases the risk of genital cancers in both women and men. That's why all school children in the UK now get offered a vaccine to protect them.
A healthy diet...
reduces the overall risks for all cancers.
True or false? Although many life style factors (diet, smoking etc.) affect the risk of developing cancer, some cancers are affected by genetics. Some cancers run in families.

