YOU ARE LEARNING:
Mitosis

Mitosis
Mitosis is a type of cell division that produces two identical cells to its parent cell.
This image shows what mitosis does. Which description do you think fits best?
A) One cell becomes two cells B) Two cells become one cell C) One cell marries another cell

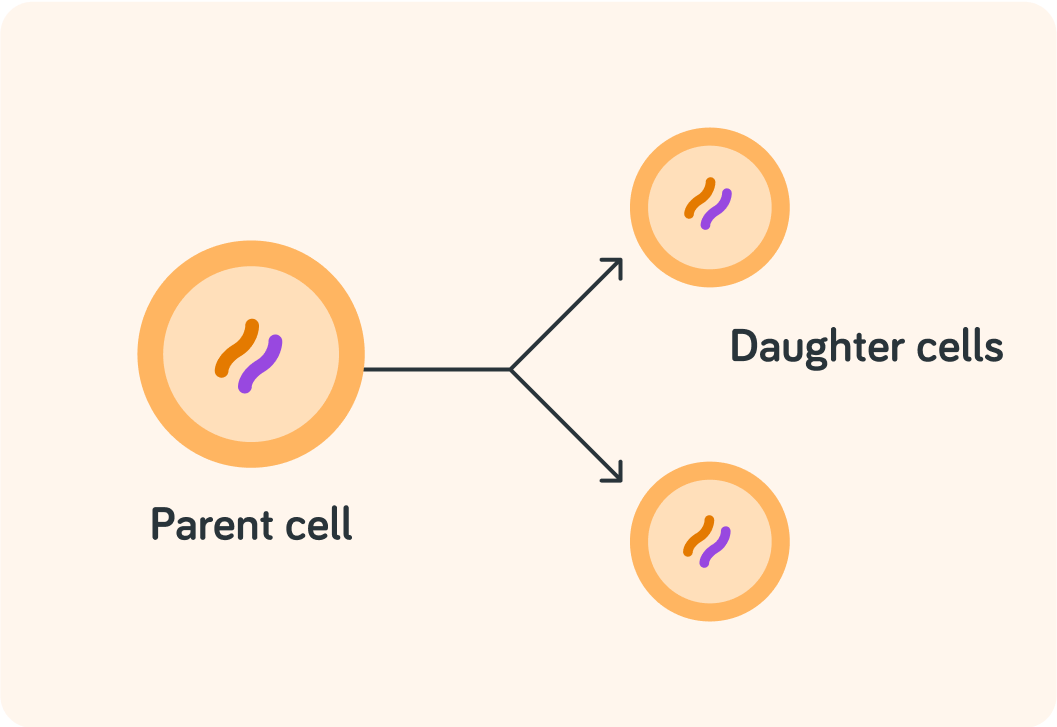
The parent cell splits into two daughter cells. Does that mean you end up with 2 cells or 3 cells in total?


During mitosis the parent cell splits itself
This means the original parent cells isn't there anymore. It has become the two daughter cells.

Both daughter cells turn out identical to the original parent cell
The parent cell doesn't simply split itself down the middle. If it did that, then each daughter cell would be only "half" a parent cell. So there are multiple steps to mitosis.
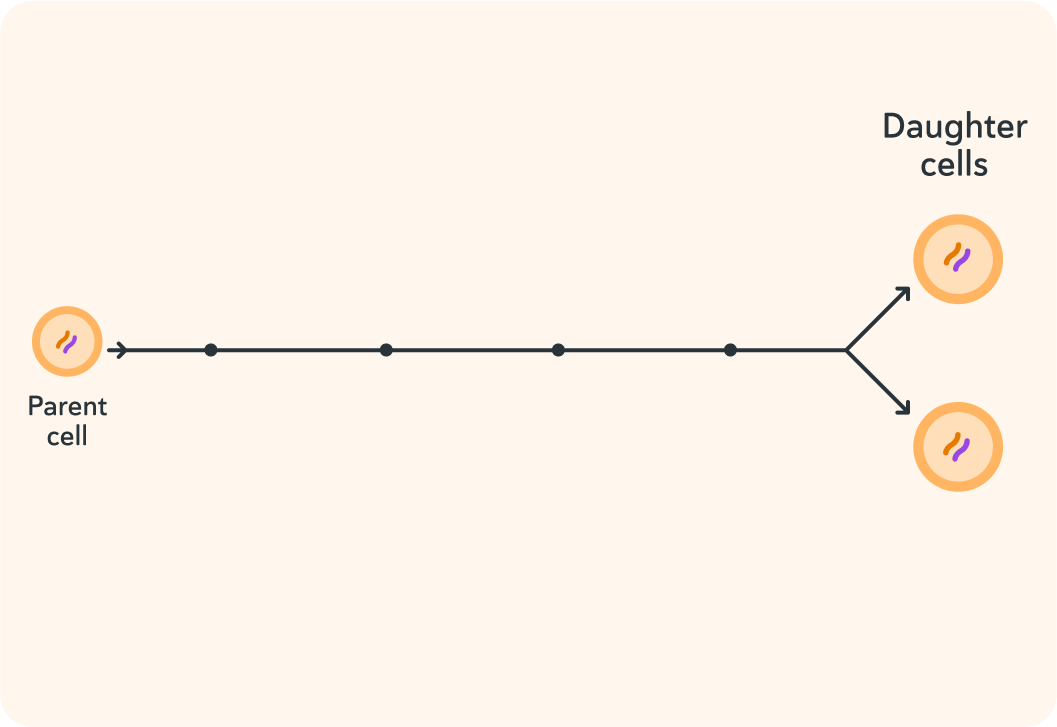
But first! Why do you think a cell might multiply into identical daughter cells? Pick 2 options.

You can select multiple answers
Recap
During mitosis one parent cell becomes two identical daughter cells
There are multiple steps to mitosis to make sure that you don't just end up with two half parent cells.
Mitosis is essential for an organism to grow
For example, there are more cells in an adult body than in a child body. Those extra cells got there from mitosis.
Mitosis is essential for an organism to repair itself
For example, if you cut yourself, you have to produce more skin cells to close the wound.
Mitosis also allows some organisms to reproduce asexually
This means that they don't need a female and a male to produce offspring. Roughly speaking, they just produce clones of themselves single-handedly.
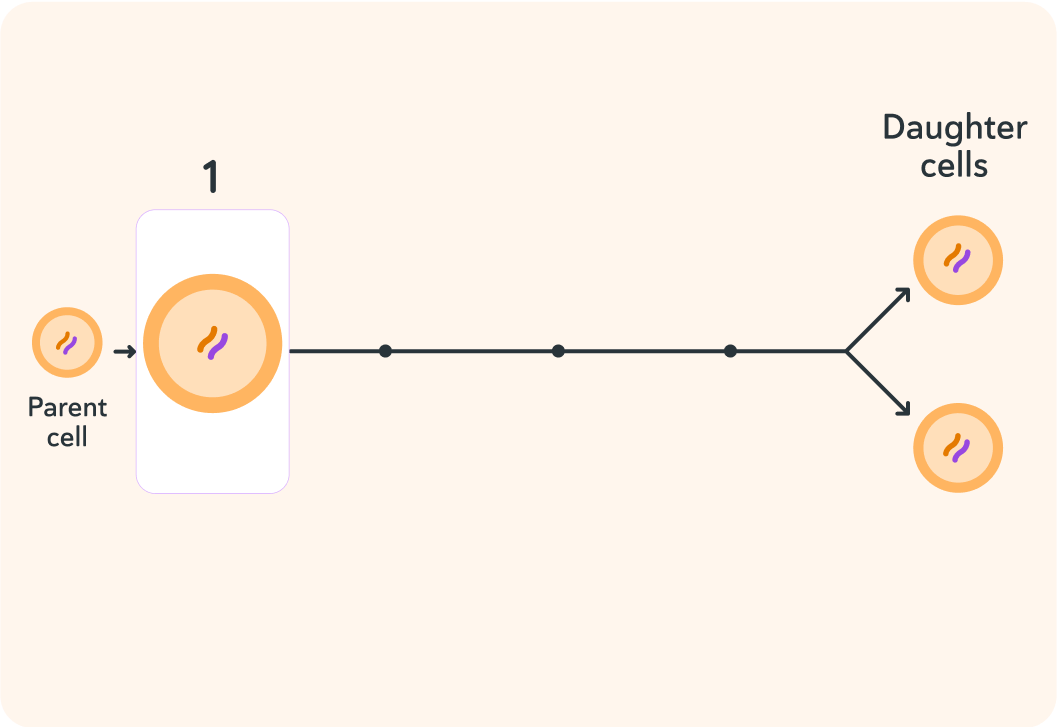
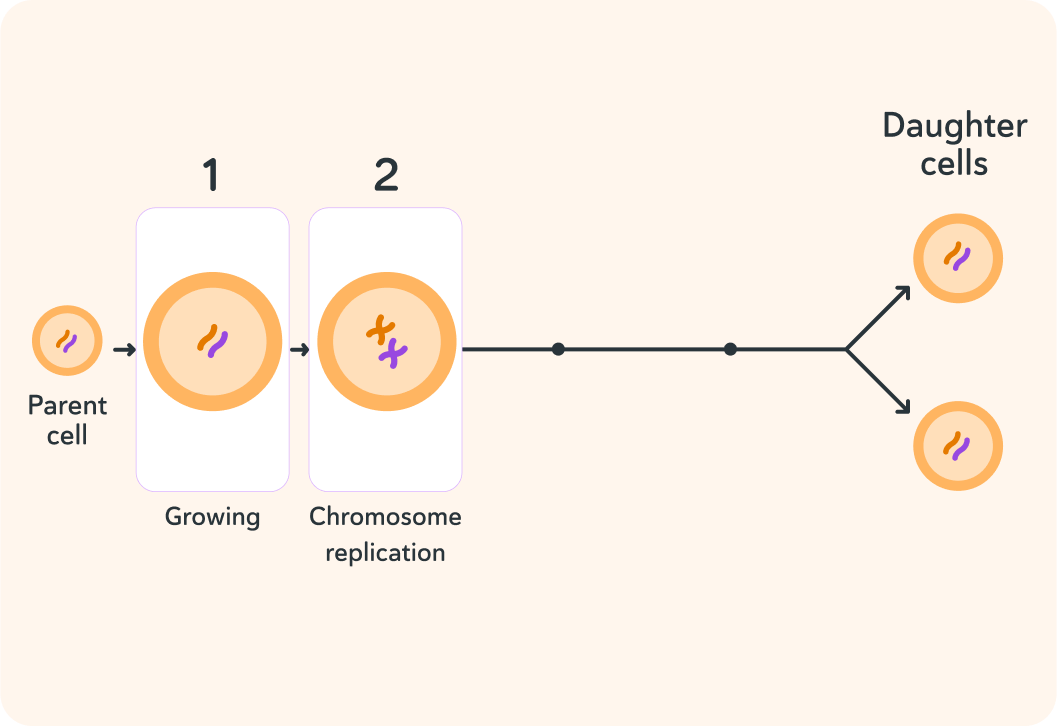
This shows the first step in mitosis. In this stage, the parent cell __________.
A) shrinks B) grows C) blows up

What happens inside the parent cell in the second step?
A) Internal structures are replicated B) The whole cell is replicated C) The cell splits in two

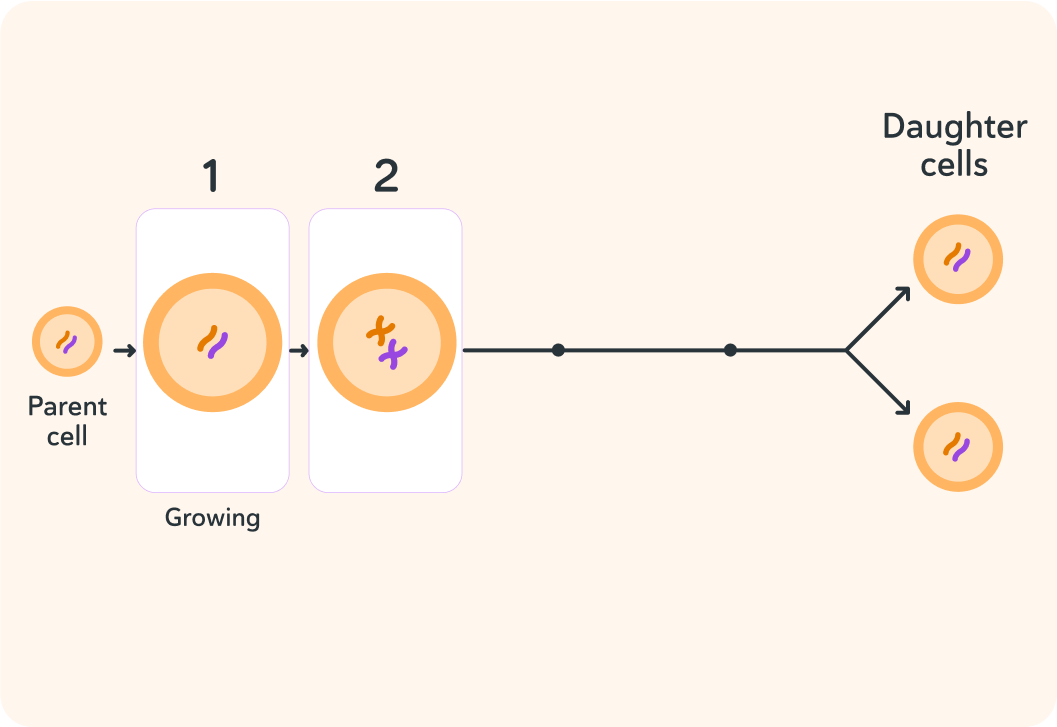
So the cell replicates its internal structures
Specifically, it's very important that it replicates its chromosomes (DNA) correctly, so it does that in a special way.
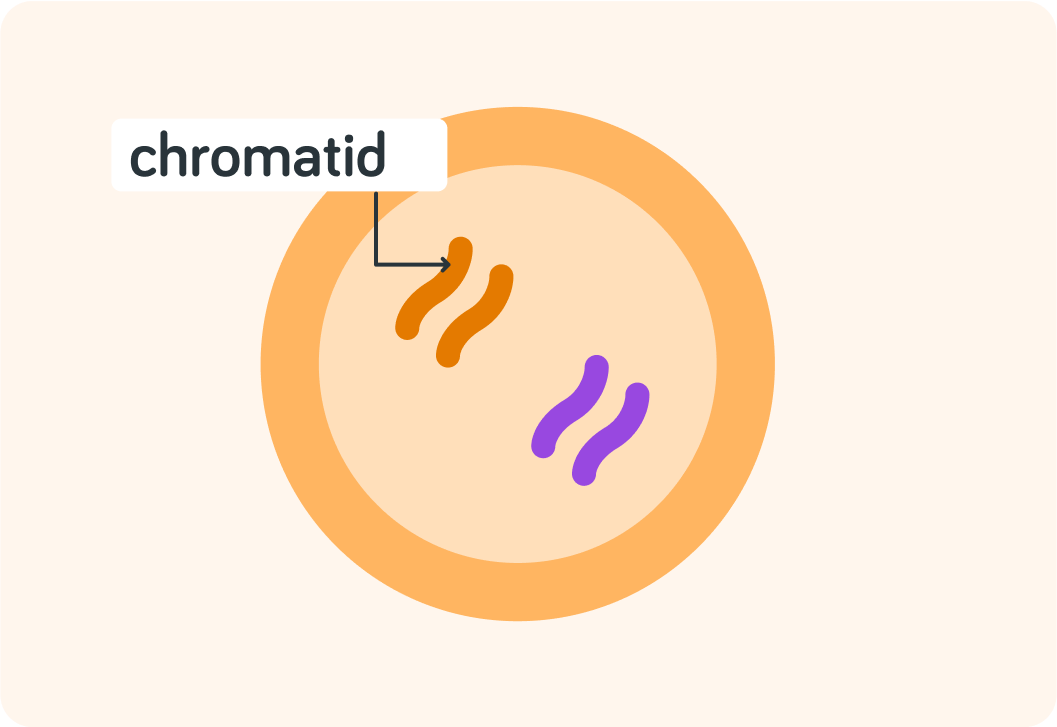
First each strand of DNA replicates itself
Each strand is called a chromatid.
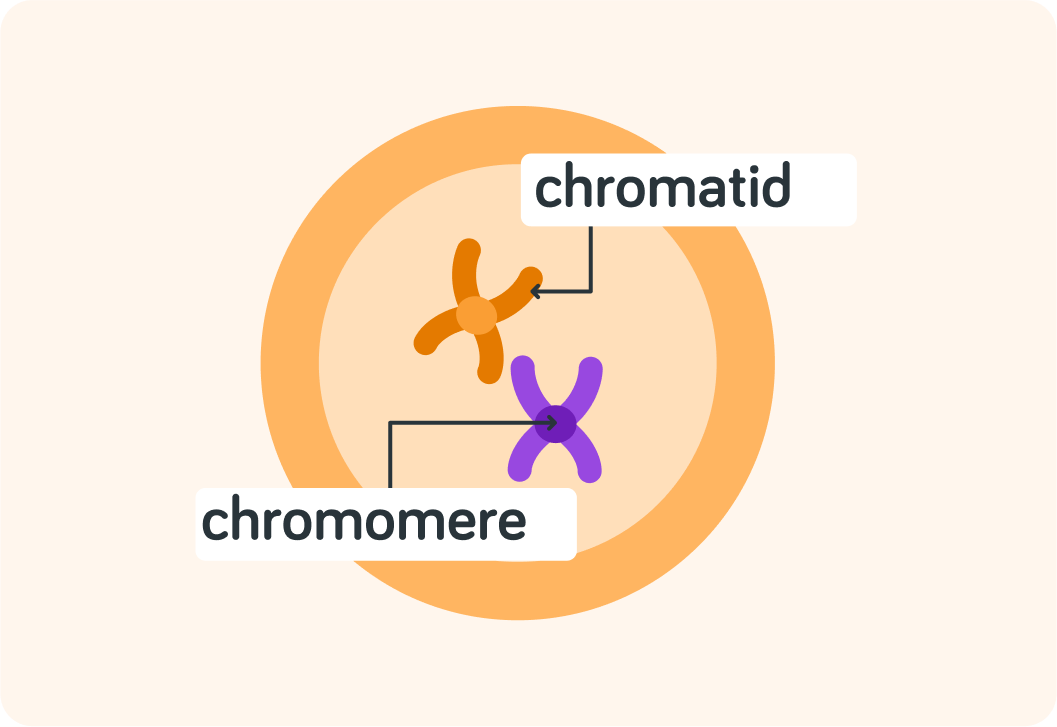
Next, the cell makes sure the chromotids stick together until the cell is ready to separate
It does that with a chromomere, which is like a little "knot" of DNA that acts like glue.
The next thing that happens is that the chromosomes will split apart
They do this before the whole cell splits into two daughter cells
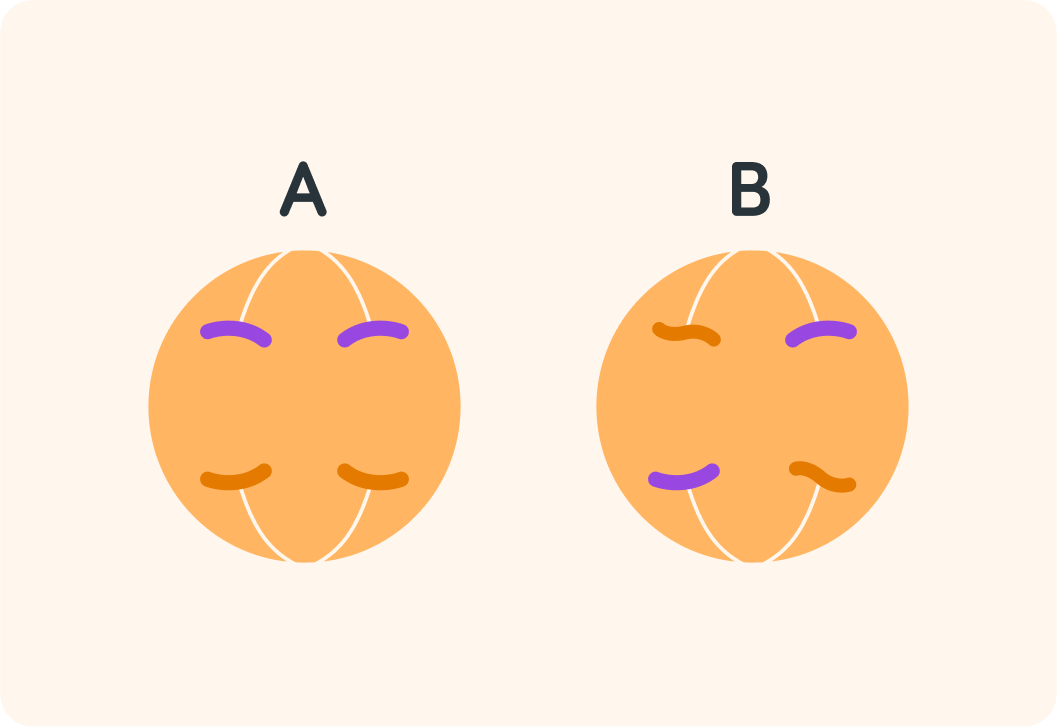
Each daughter cell has to be identical after the parent cell has split, so which option do you think correctly shows how the chromosomes split? Answer A or B.


The chromosomes split so that part of both chromosomes move to either side of the cell
If the chromosomes didn't split like this, each daughter cell wouldn't turn out identical to each other or to the original parent cell.
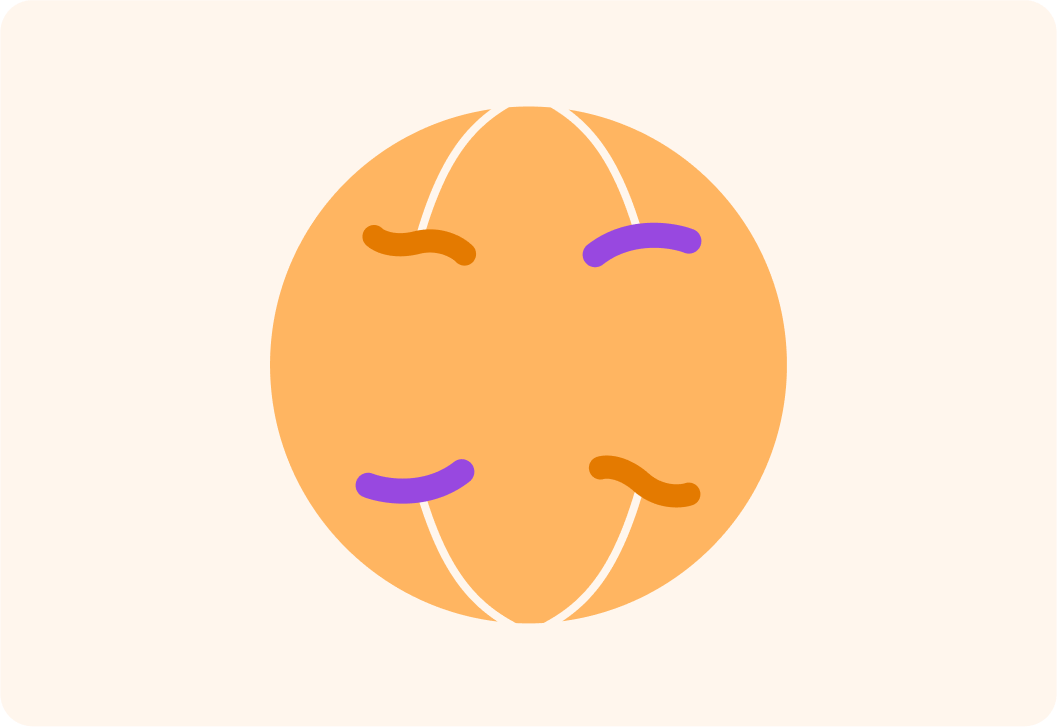
Finally, what is the fourth and last step of mitosis called?

What happens during cytokinesis?
A) The parent cell finally splits B) The parent cell dies C) The daughter cells become one


While the parent cell splits, the cell membrane makes sure the chromosomes are stuck safely to the edges
If the chromosomes were floating around in the middle of the cell, they might end up in the wrong cell!

Summary! Cells perform mitosis for different purposes
For growth, for repair or for asexual reproduction (if the organism can do that).

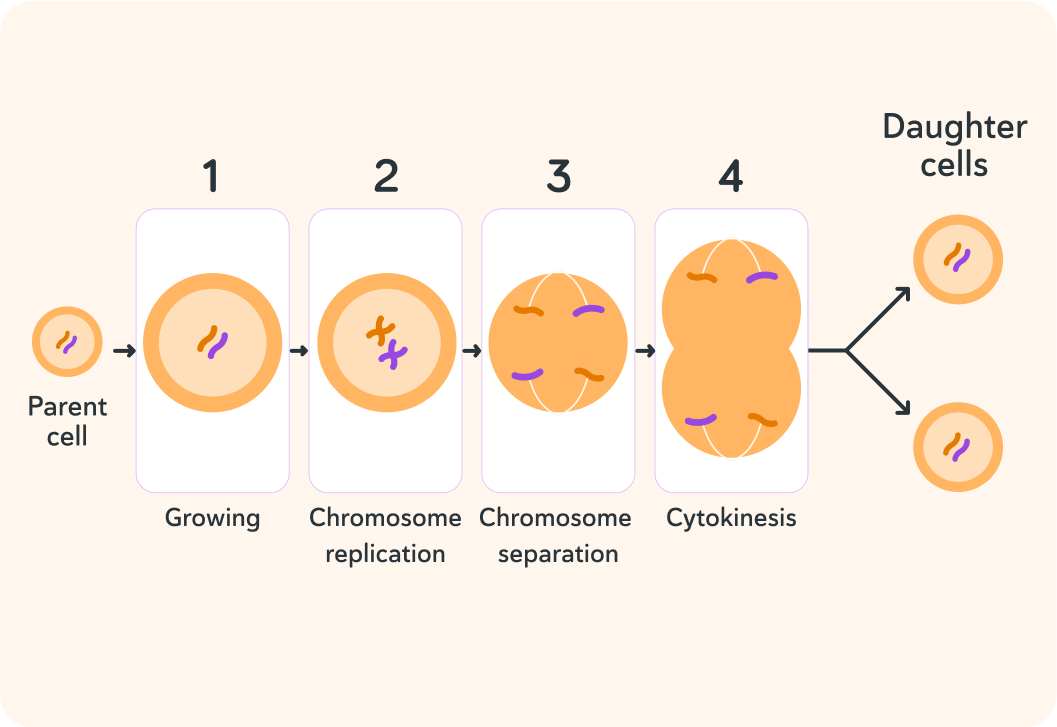
During mitosis, one parent cell splits into two daughter cells
Each daughter cell is identical to each other and to the original parent cell, so the parent cell doesn't simply split itself into two halves.

Step 1: Growing
The parent cell grows bigger.

Step 2: Chromosome replication
If the cell didn't replicate its chromosomes, each daughter cell would end up with only half the amount of chromosomes and they wouldn't function!

Step 3: Chromosome separation
The chromosomes then split evenly to either side of the parent cell.

Step 4: Cytokinesis
The cell membrane holds the chromosomes in place while the parent cell splits itself and becomes the two daughter cells.

By the way!
There should also be for example mitochondria and ribosomes in both daughter cells.
However, cells can make more mitochondria or ribosomes if they need to, so the most important thing for the parent cell is to make sure that the splitting of chromosomes happens correctly.

