YOU ARE LEARNING:
Influencing Enzyme Activity

Influencing Enzyme Activity
Temperature, pH and substrate concentration can all affect the level of enzyme activity.
When someone is unwell, the medical staff often check a patient's body temperature. What is the ideal body temperature?

The graph shows how temperature affects the rate of reaction of a typical enzyme. At what temperature is the rate of reaction at its highest?

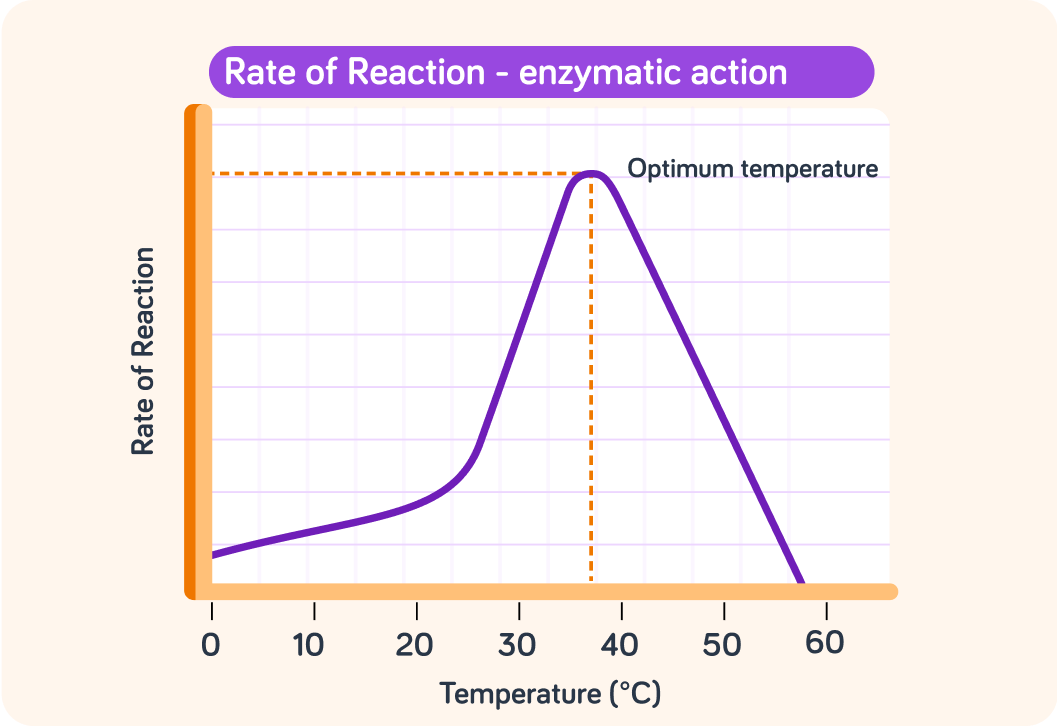
This is the reason that our body temperature is 37oC
At this temperature, our enzymes are working at their optimum rate.

What happens to the rate of reaction as the temperature changes away from 37oC?
A) Stops B) Increases C) Decreases


The reason for the change in the rate of the reaction below 37oC is the same as it is for any chemical reaction. It's due to the change in the motion of the particles, but which type of energy is decreasing as the temperature decreases?

Above 37oC the additional kinetic energy does not increase the rate of the reaction in an enzymatic reaction, as it does in other chemical reactions, because the additional heat energy has an effect on the enzyme.
The most important physical attribute of an enzyme that allows it to perform its function is the ________ of the active site.

As the temperature increases above 37oC the enzymes denature. This means they change. Which of these changes is the reason why the enzymes start to work less effectively and eventually fail altogether?

Denaturing results in a permanent change to the active site's shape. Denaturing is irreversible. That means that it cannot be undone.
This graph shows how an enzyme reaction is affected by pH.
This enzyme is typical of many enzymes and has its optimum pH around neutral, pH 7.
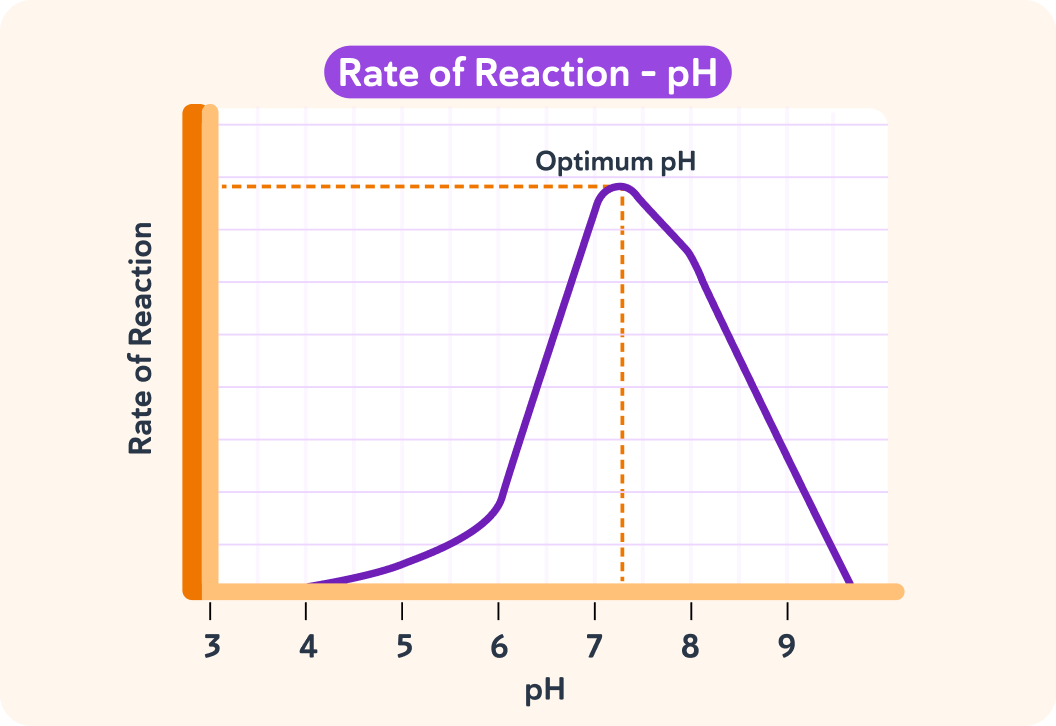
Some enzymes, pepsin for example, have an optimum rate of reaction in acidic conditions. If we changed conditions so that pepsin was not in pH7 conditions, it would _____________.


The rate of reaction drops on either side of the optimum pH.
This is because the enzyme natures and the shape of the active site changes as the pH alters.

In this example, the rate of the reaction is being affected by the concentration, (amount) of the substrate. At what concentration does the reaction reach its maximum rate? Answer to 2 decimal points.

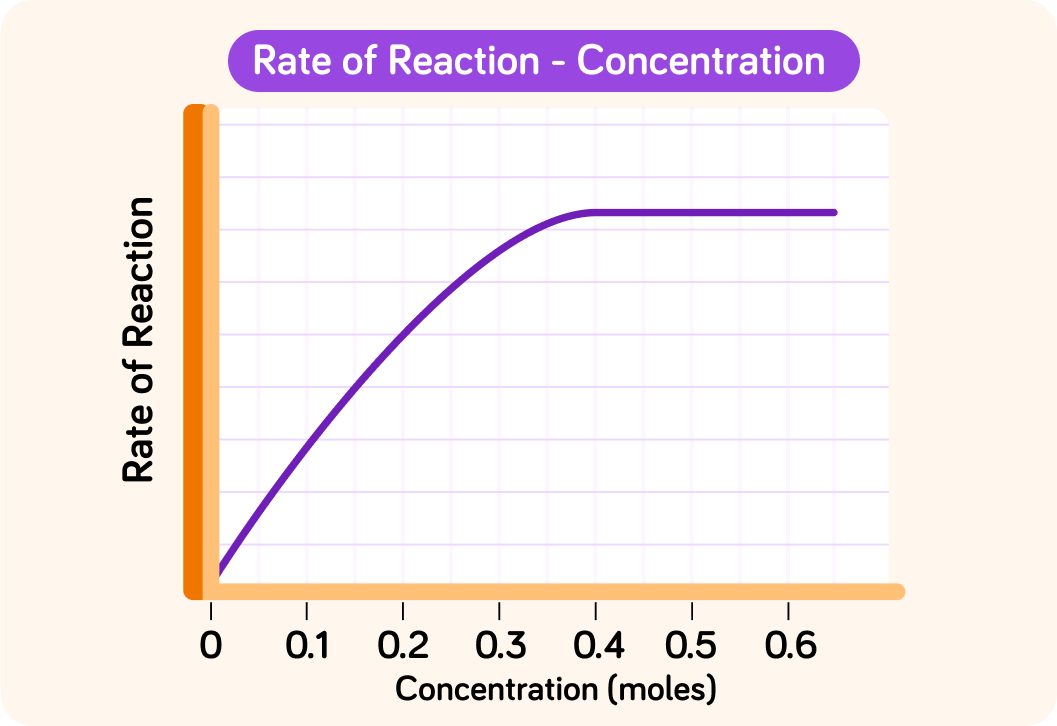
What happens to the rate of reaction as the concentration increases above this level?
A) Increases B) Decreases C) Remains constant


So initially...
the higher the concentration, the more substrate the enzymes have to work on, so the higher the rate.

At a certain concentration though, the enzymes are working as fast as they can. Adding more substrate has no effect, because the enzymes can not process them any faster. What would happen at this point if more enzymes were added to the reaction?
A) The rate would remain constant. B) The rate would increase.


At the maximum rate, an enzymatic reaction is limited by certain factors. We call them limiting factors. To increase the rate of a reaction, we must change the limiting factors to allow the rate to increase. Which of these are potential limiting factors? Pick all the options you think are correct.

You can select multiple answers
Enzymes are sensitive to changes in pH and temperature. Small changes slow down the reactions, but large changes denature the enzyme and stop the reactions. This can cause illness and death, for example by hyperthermia.
