YOU ARE LEARNING:
What Are Enzymes?

What Are Enzymes?
Enzymes, as biological catalysts, speed up chemical reactions in living organisms
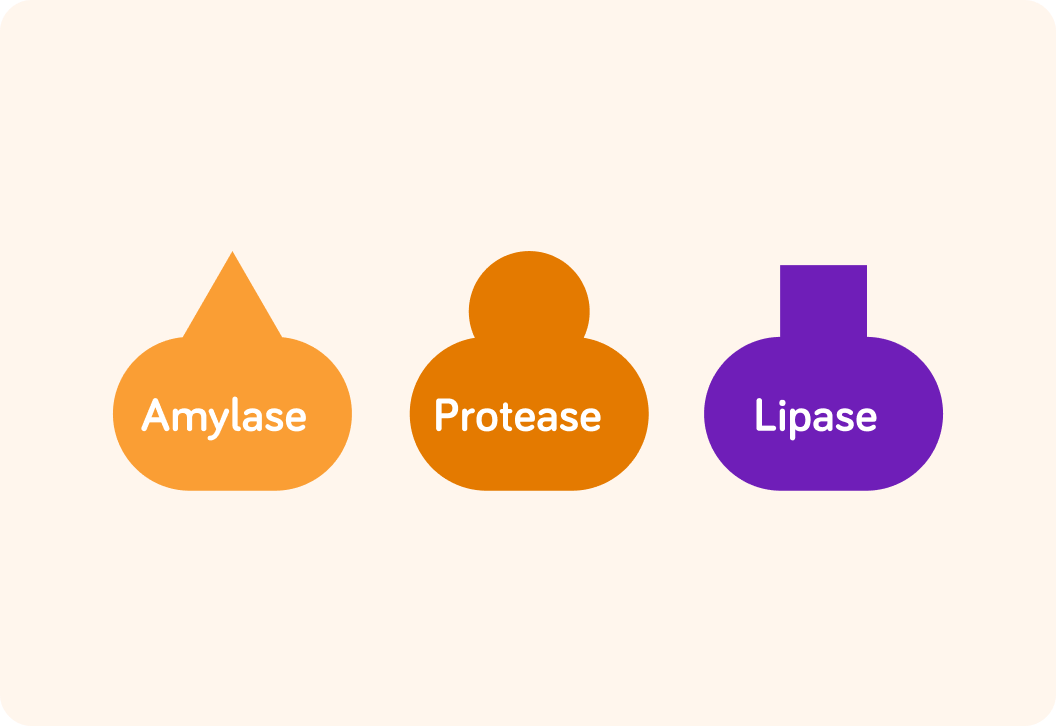
These are all example of enzymes
Enzymes are types of proteins.
You can think of enzymes kind of like the body's "party-starters". What do you think that means?
A) Enzymes stop reactions B) Enzymes slow down reactions C) Enzymes speed up reactions


So enzymes are proteins that speed up chemical reactions in the body
We also call them biological catalysts.

Amylase is an enzyme. Where in the body do you find amylase?
A) In the mouth B) In the stomach C) In the brain

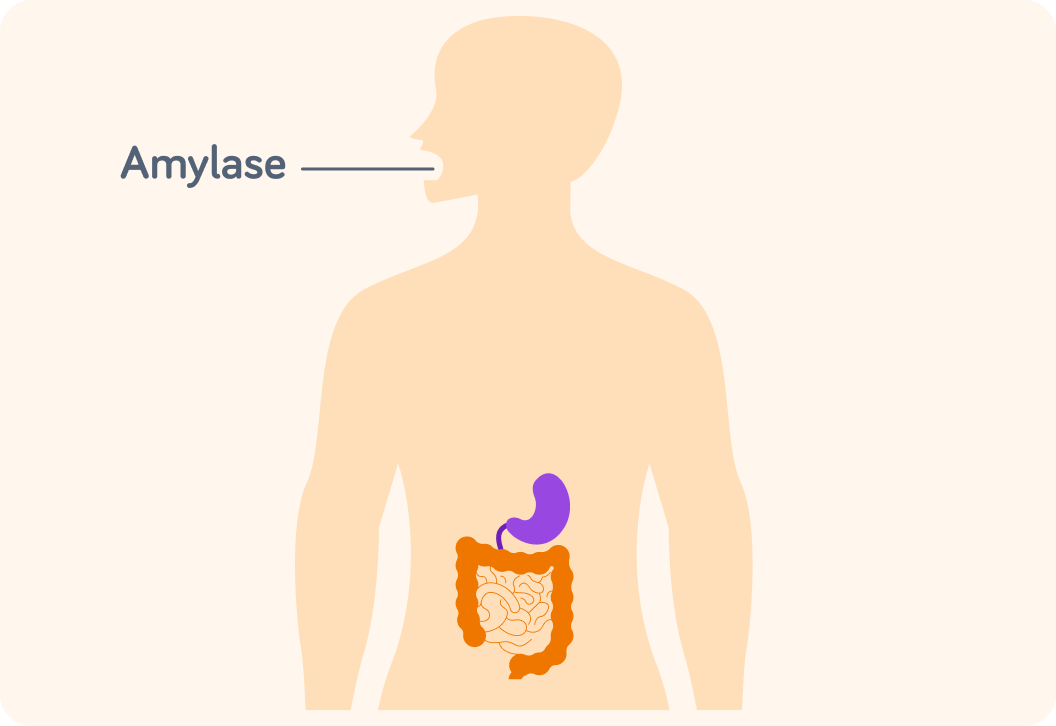
Amylase is an enzyme found in saliva in the mouth. What is saliva?
A) Tooth fillings B) Taste buds C) Spit


Amylase is part of the system that helps break down the food you eat. What is that system called?
A) The respiratory system B) The circulatory system C) The digestive system


What do you think amylase does as part of the digestive system?
A) Breaks down complex compounds B) Builds up complex compounds


So amylase is an enzyme in the mouth's saliva
It is part of the digestive system where it breaks down starch sugars (for example maltose).

Protease is also an enzyme. Where in the body do you find protease?
A) In the mouth B) In the stomach C) In the brain

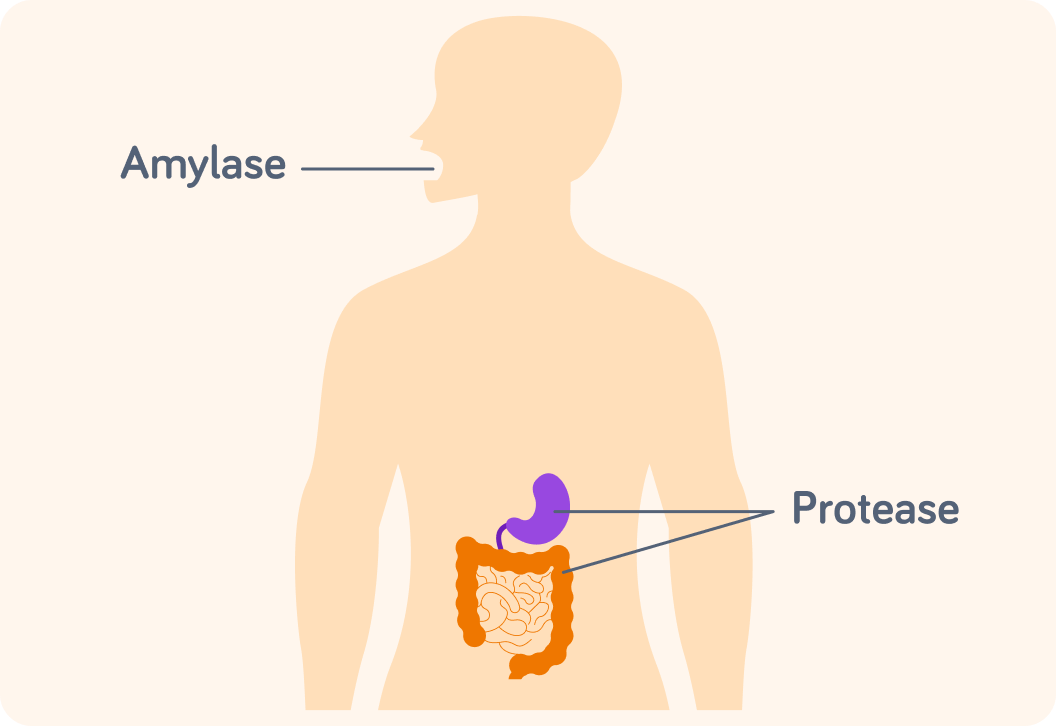
Like amylase, protease is part of the body's ______________ system.


Have a good look at the name "protease". What do you think it breaks down?
A) Sugars B) Fats C) Proteins


So protease is an enzyme in the stomach
Like amylase, it is part of the digestive system. It breaks down proteins.

Lipase is yet another enzyme in the body's digestive system. What do you think lipase breaks down?

Enzymes have specific shapes that means they can react with specific things. Is amylase able to connect to proteins? Answer yes or no.

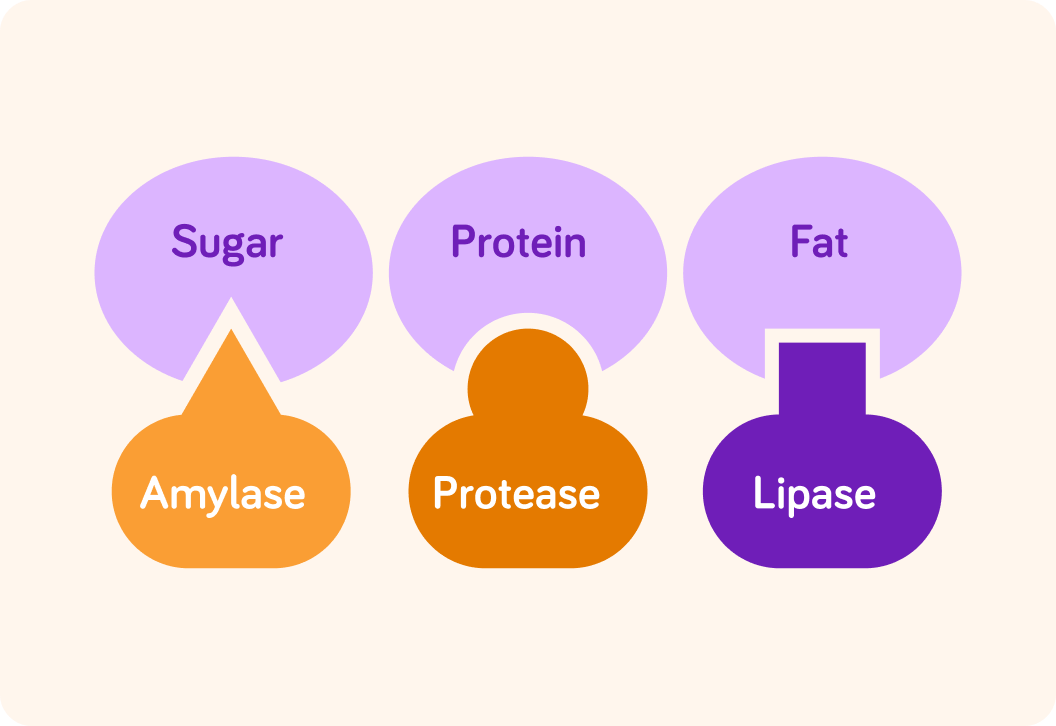
Amylase breaks down sugars, protease breaks down proteins, and lipase breaks down fats, so it seems like a given enzyme can do...
A) only one thing. B) many different things.


Enzymes are specialised to perform one function
They have specific shapes which means they will only fit with specific molecules.
For example, amylase only fits with certain sugars, protease with proteins and lipase with fats.

Now, chlorophyll is an enzyme in __________.
A) animals B) plants C) bacteria


What is the process called where plants use sunlight to turn carbon dioxide in the air into oxygen? It begins with a "p".


Chlorophyll is an en enzyme in plants' leaf structure
It is the enzyme that allows plants to be able to perform photosynthesis faster.

True or false? Humans also have the enzyme chlorophyll.


During photosynthesis, carbon dioxide disappears, but chlorophyll doesn't. So enzymes are __________ by the chemical reactions they take part in.
A) unchanged B) dissolved


Chlorophyll in unchanged during photosynthesis
Indeed, all enzymes remain unchanged during the chemical reactions they take part in. The chemical reactions do not break down the enzymes.

Summary! Enzymes are types of proteins
They are biological catalysts, which means they speed up reactions in organisms, like during digestion or photosynthesis.

Enzymes are highly specialised
They have specific shapes which means they perform very specific functions. For example, protease breaks down proteins and lipase breaks down fats.

The chemical reactions they take part in does not break down the enzymes
Enzymes remain unchanged.

By the way, many enzyme names end in -ase
For example amylase, protease and lipase.

