YOU ARE LEARNING:
Stem Cells in Therapy
Stem Cells in Therapy
Stem cell therapy may be able to treat conditions by replacing diseased cells.
Many essential functions in the body rely on the actions of specialist cells. If these fail, a person can get ill.
Cells in the pancreas produce insulin to control blood sugar levels. If those cells don't work properly, the person will get ill. Do you know what we call that condition?

Type I diabetes and paralysis from conditions such as multiple sclerosis result from the failure of specialist cells.
If it were possible to replace these damaged pancreas cells with functioning cells, it might be possible to cure type I diabetes. What sort of cells are capable of changing to form new specialist pancreas cells in the body?

Paralysis, caused by nerve damage in an accident for example, is another condition that is hard to treat, because adult nerve cells do not re-grow once damaged. So to re-grow these damaged nerve cells, we would need a cell capable of forming all types of adult cells. Which of these would that be?

Why is it not possible to simply take stem cells from an embryo and inject them into the patient with type 1 diabetes, multiple sclerosis or paralysis for example, so they can make new working cells?

Therapeutic cloning is an attempt to use stem cells in a way that they will not be rejected by the patient's immune system.
The technique uses therapeutic cloning. This means it uses cloning to treat illnesses. It is still in development. It is not in regular clinical use in the UK yet.
What is a clone?
A) A new cell produced by division B) A copy of an organism C) A genetic copy of a cell or an organism


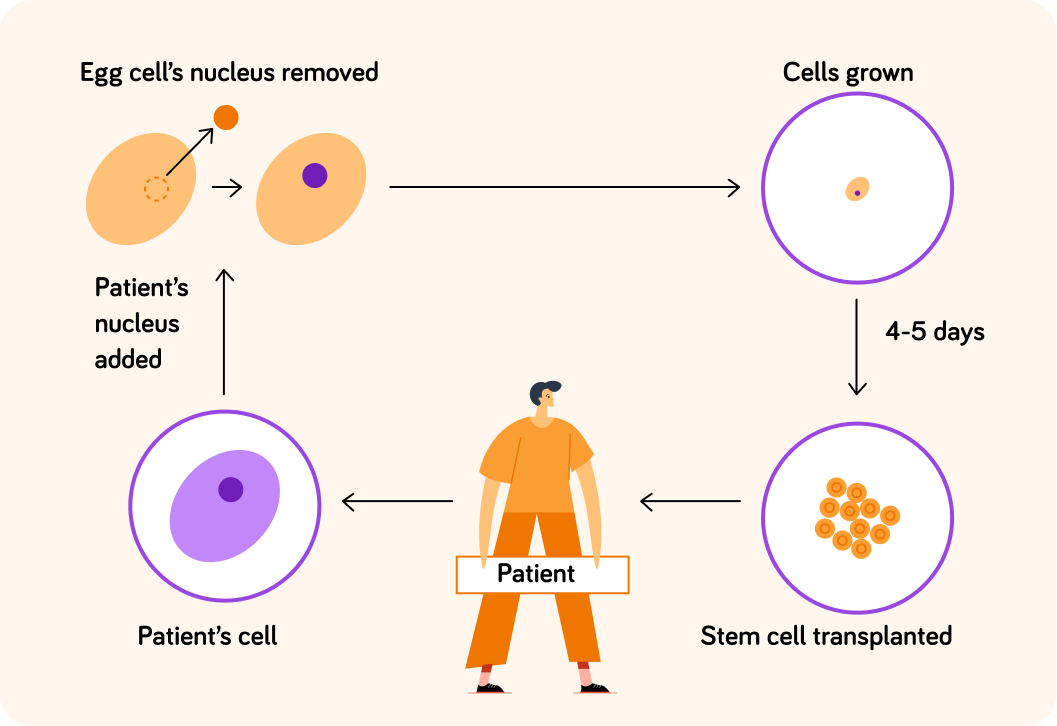
We remove an egg cell from a donor. Then we replace the nucleus with the nucleus from one of the patient's own cells. Why do you think we need to replace the nucleus?
A) We need the cell to contain the patient's genome. B) We need to convert the cell into a stem cell.


The cell is now a clone of the patient's cells. It now divides and grows into a ball of stem cells over the next 4-5 days. It is then transplanted into the patient. Are these stem cells embryonic or adult stem cells?


So with therapeutic cloning, the new embryonic stem cells can differentiate to replace the specialist cells that have failed or been damaged. Why are they less likely to be rejected than embryonic stem cells from another source?

Now, remember that therapeutic cloning is still in development. It is not in regular clinical use in the UK yet. However, we have been transplanting bone marrow stem cells for many years. What type of stem cells can be collected from a person's bone marrow?

Stem cells from bone marrow transplants are used to treat leukaemia (blood cancer). The cells must be taken from a donor with the same tissue type (similar to blood groups) to reduce the risk of rejection. What type of cells do you think bone marrow stem cells can differentiate into?

Treatment of leukaemia with adult stem cells is well established in most countries. Treating diabetes etc. with embryonic stems cells is not. Partly, this is due to the fact that in some of these treatments, the embryo is killed. So which of these options do you think is the reason that it is not more widely used?

You can select multiple answers
Stem cell therapies could bring great advances in treatments, but there will always be ethical considerations with these treatments. We will cover ethical concerns in more detail in a later lesson.
