YOU ARE LEARNING:
What Are Stem Cells?
What Are Stem Cells?
Stem cells have the ability to transform from undifferentiated to specialised cells.
True or false? Organisms have many different types of cells.

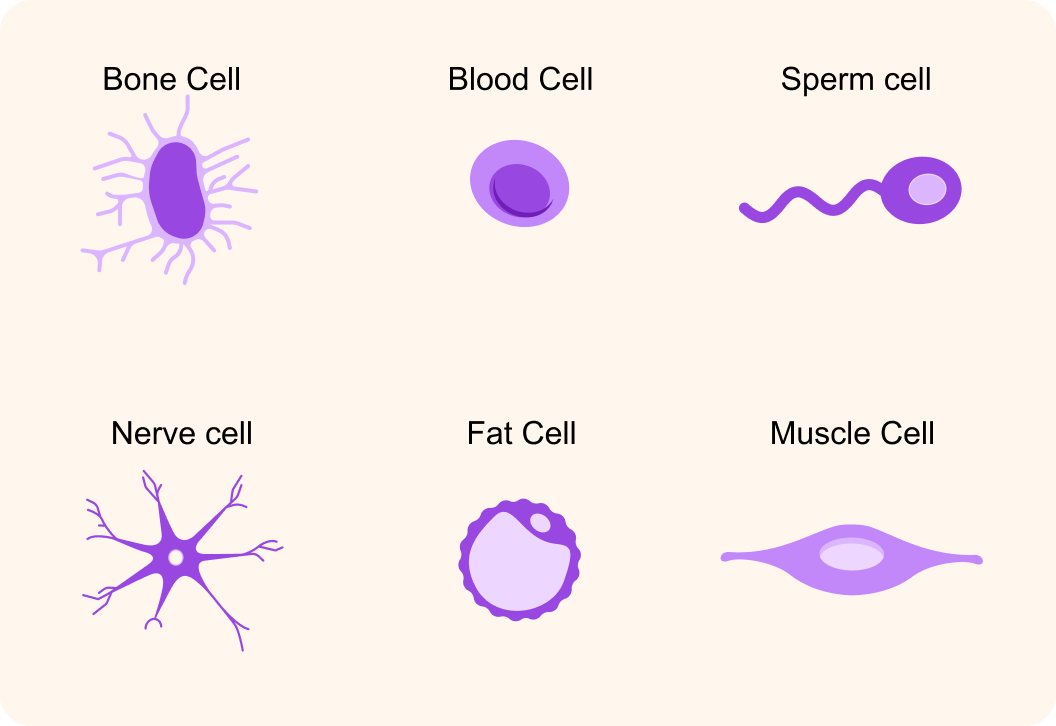
True or false? Skin cells, lung cells, brain cells etc. are highly specialised cells.


So your body consists of highly specialised cells
But at the very beginning, there was only one egg cell and one sperm cell. How did those two cells become all of these very different types of cells?

True or false? When an egg cell and a sperm cell meet, they immediately become one of each of all the specialised cells the body needs.


True or false? When a specialised cell divides, for example a skin cell, it can become any one of the other types of specialised cells.


In fact, all the different specialised cells in the body came from stem cells
Stem cells are "non-specialised" or "undifferentiated" cells, but they are actually very very special in their own way!
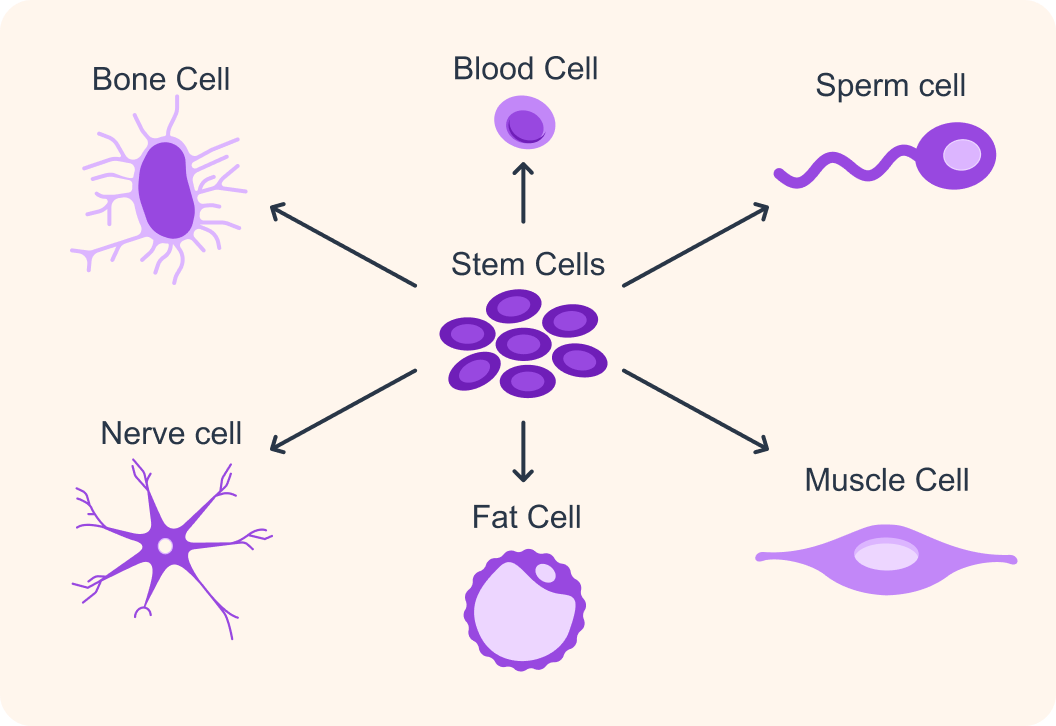
So what is it that stem cells can do that specialised cells can't do?

There are actually two types of stem cells.
The first type is the one we find in the womb, right after fertilisation. What do you think that type is called?

The second type of stem cells can be found in adults. What do you think that type is called?

One type of stem cells can differentiate into all kinds of specialised cells. The other type can only differentiate into some. Which type do you think can become all types of specialised cells?

When do we talk about "adult" stem cells, do you think?

Recap
All the different types of specialised cells in the body originally came from one type of cell - stem cells.

Embryonic stem cells
These are the stem cells we find in the womb, right after fertilisation. They can differentiate into all kinds of specialised cells and into other stem cells.

Adult stem cells
These are the cells we find in an organism when it is no longer an embryo. They can differentiate into some - not all - kinds of specialised cells.

So which adult stem cells can differentiate into what kind of cells?
This image shows an example.
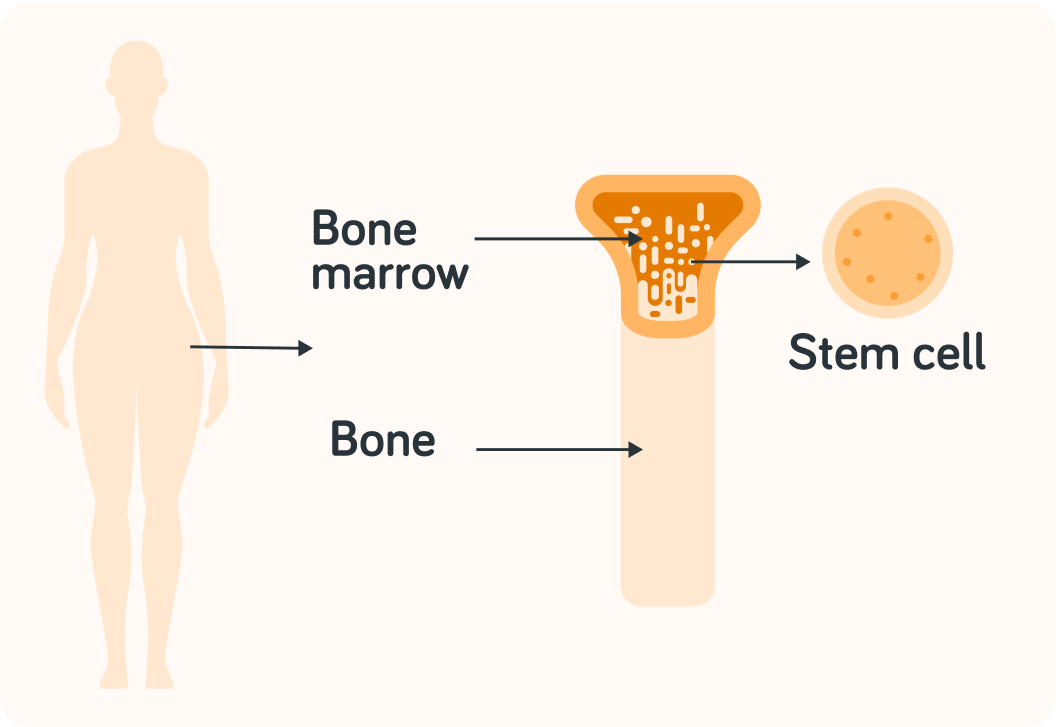
What do you think you call this type of adult stem cell?
A) Brain stem cells B) Bone marrow stem cells C) Skin stem cells


True or false? Bone marrow stem cells can differentiate into brain cells.

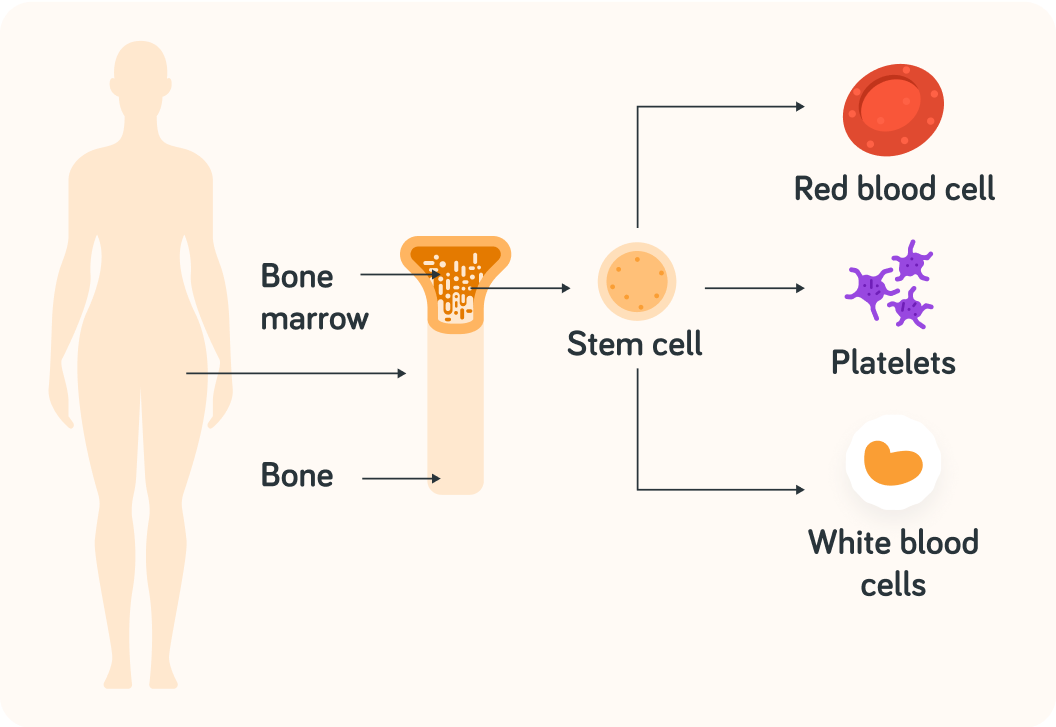
Bone marrow stem cells can only differentiate into ________________.
A) lung cells B) brain cells C) blood cells


Now, would embryonic stem cells be able to differentiate into for example brain cells? Answer yes or no.


So stem cells allow an organism to create different types of specialised cells with different specialised functions. Do humans, animals and plants all have stem cells?

Adult stem cells in plants can be found in seedlings, saplings and grown plants
You find them in the growing points on a plant because they are used for growth, so in the tips of roots and in the stems. We call those places meristems.
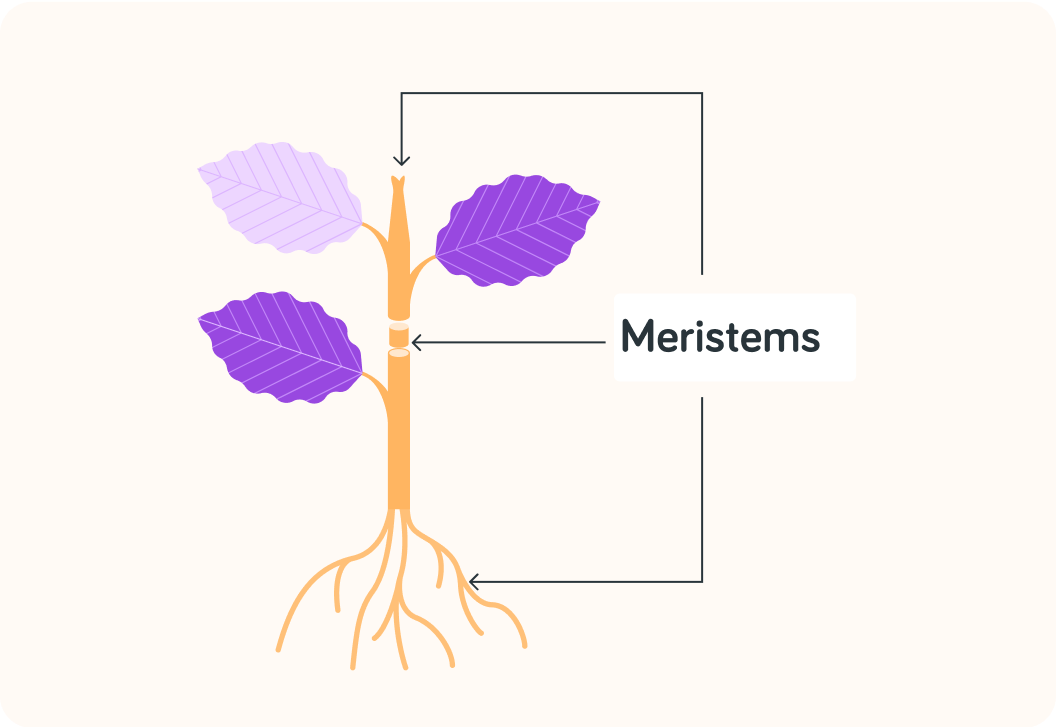
Can the adult stem cells in a plant differentiate into all types of specialised cells in the plant? Answer yes or no.


Just as in animals, adult stem cells in plants' meristems can only differentiate into some types of specialised cells
For example xylem cells, phloem cells and parenchyma cells.

If a stem cell doesn't differentiate, but divides like other cells, then what comes out of it?

When stem cells transform or change into specialised cells, you say they _____________ into specialised cells.

Summary! Stem cells are "non-specialised" or "undifferentiated" cells
They have no special features, like specialised cells.

But stem cells are in fact quite special
They can change their structure and differentiate into other types of cell. No specialised cells can do that!

There are two types of stem cells
Embryonic stem cells and adult stem cells.

Embryonic stem cells
These can differentiate into any kind of specialised cell or other stem cells.
If they simply divide themselves that just makes more embryonic stem cells.

Adult stem cells
These can differentiate into only some kinds of specialised cells. For example, bone marrow stem cells can differentiate into blood cells, but not into lung cells, brain cells etc.
If they simply divide themselves that just makes more of that kind of adult stem cells.

