YOU ARE LEARNING:
Structure of the Cell Membrane
Structure of the Cell Membrane
We will now look more closely at the components of the cell membrane and what they do.
In this lesson we zoom in to take a look at the structure of the cell membrane.
Do you remember what the main component cell membranes is?

This is a zoomed-in picture of the cell membrane.
Arrow D points to a phospholipid, but as you can see there are other components too.
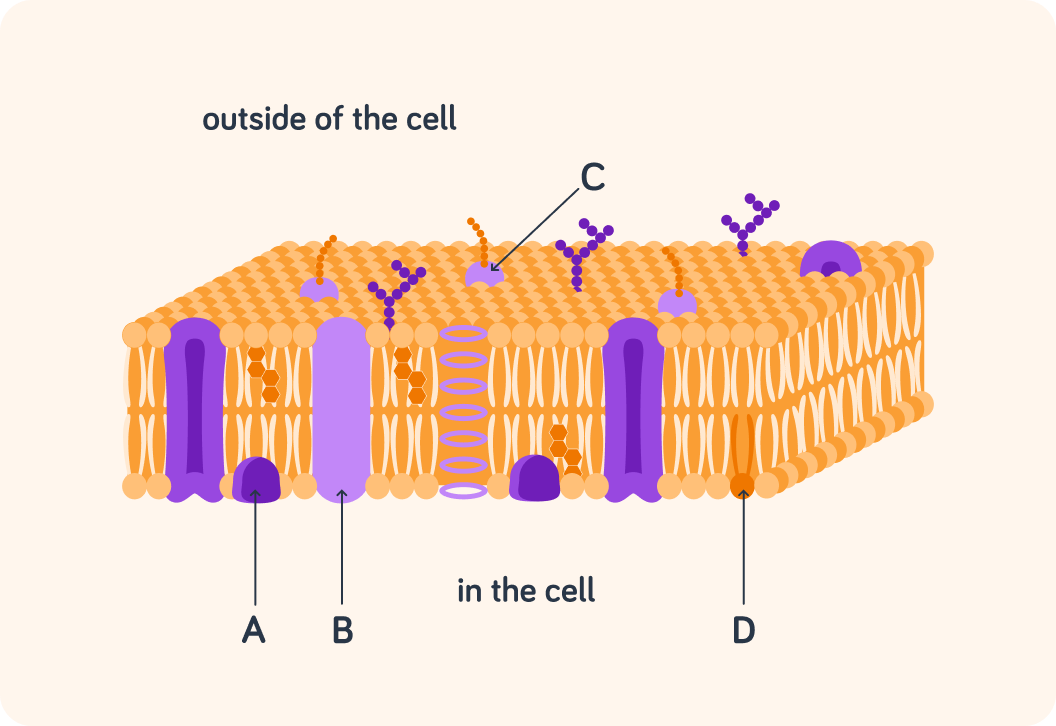
The plasma membrane contains many proteins (in purple). There are different types of proteins. One type are peripheral proteins (indicated with A). What is a peripheral protein?
A) A protein which goes through the cell membrane. B) A protein only on one side of the cell membrane. C) A protein which has a carbohydrate structure attached


Another type are transmembrane proteins (indicated with B). What is a transmembrane protein?
A) A protein which goes through the cell membrane. B) A protein only on one side of the cell membrane. C) A protein which has a carbohydrate structure attached.


The third type of proteins are glycoproteins (indicated with C). What is a glycoprotein?
A) A protein which goes through the cell membrane. B) A protein only on one side of the cell membrane. C) A protein which has a carbohydrate structure attached.


Which type of protein do you think regulates transport through the cell membrane?

What do you think is the function of glycoproteins?

Peripheral proteins have two functions. Which two?

You can select multiple answers
The cell membrane contains many proteins:
Transmembrane proteins function in transport. Glycoproteins have a function in cell identification so other cells can see if it is a skin cell or a heart cell for example. Peripheral proteins support the membrane structure and function as a receptor that can react to molecules outside the cell, for example if a hormone delivers a "message" to the cell.
Next to proteins, we find two other things in the membrane.
Take a look at this picture, where C is a phospholipid.
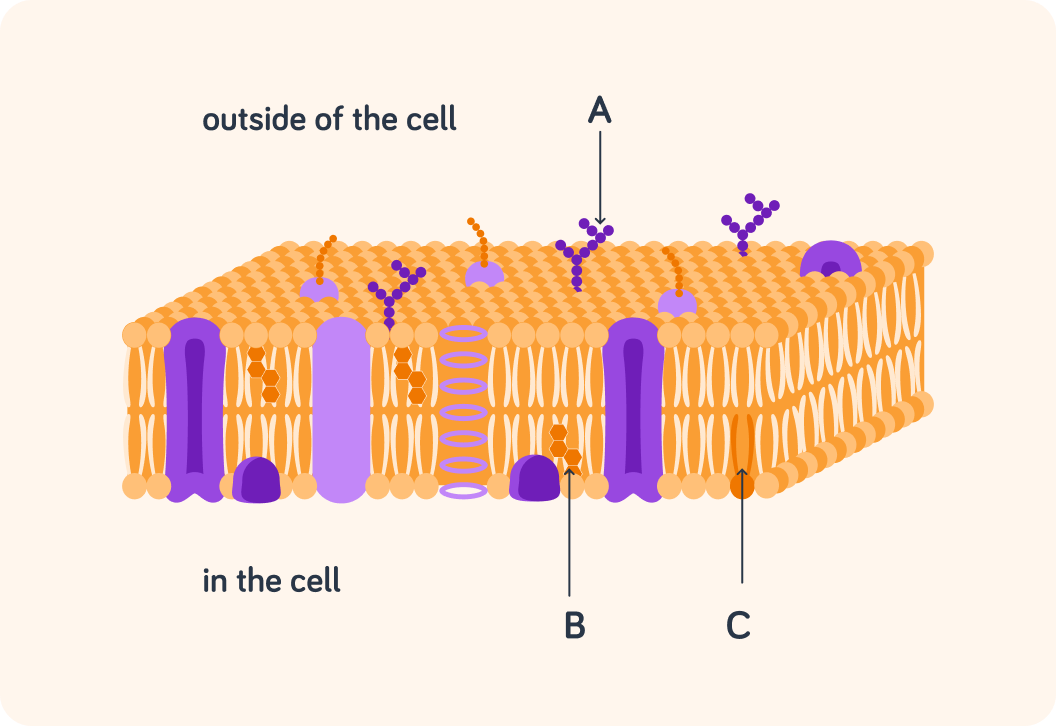
Glycolipids (indicated with A) are phospholipids with a carbohydrate group attached. What do you think glycolipids do?
A) Transport, like transmembrane proteins B) Support, like peripheral proteins C) Receptor, like peripheral proteins D) Identification, like glycoproteins.


Cholesterol (indicated with B) is located inside the membrane. What do you think it does?
A) Cell identification B) Transport C) Regulation of membrane fluidity


So cholesterol regulates membrane fluidity. What does that mean?

The cell membrane also contains glycolipids for cell identification and cholesterol, which regulates membrane fluidity, so that particles can move in and out of the cell.
