YOU ARE LEARNING:
Mendel

Mendel
Gregor Mendel carried out pea plant breeding experiments in the mid-19th century. He discovered certain characteristics were inherited as unchanged 'units' which we now call genes.
What do we mean by the term genetic inheritance?

One of the first people to study genetic inheritance was the Austrian monk, Gregor Mendel. He did his work about 170 years ago, so in the _________________.

Mendel studied pea plants. Pea plants reproduce by crossing two parents, so by ____________ reproduction.

In the mid-1800s, science didn't know about DNA or genes or chromosomes yet, so Mendel studied mainly traits that he could observe in the phenotype of the pea plants. What does that mean?

So Mendel only studied traits of the pea plants that he could see on the outside. What kind of traits might that have been? Pick all the options you think are correct.

You can select multiple answers
To recap
Gregor Mendel was an Austrian monk who studied genetic inheritance around the mid-1800s
He was one of the first scientists to study genetics.
Mendel studied pea plants
Back then, science didn't know about DNA, chromosomes and genes, so Mendel studied the pea plants' phenotypes.
The phenotype is what an individual actually looks like
For example if you are tall or short.
This is a "family" of pea plants
Mendel wanted to find out why some turned out tall and some turned out short, so he would cross different pea plants and see what their offspring looked like.
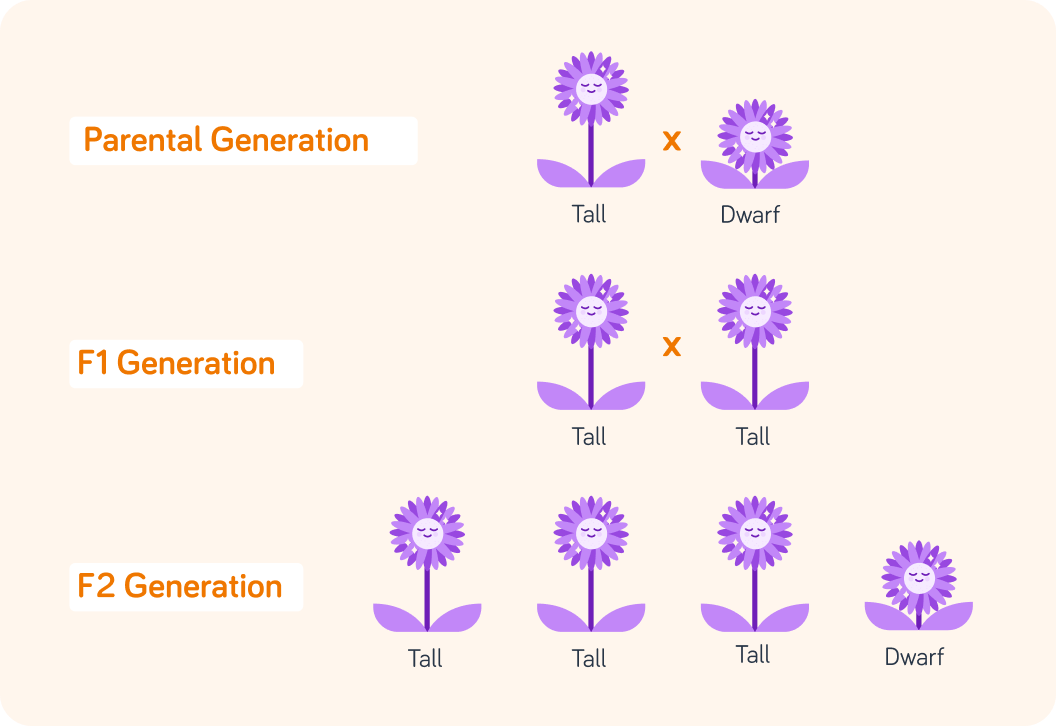
What do we call the offspring from the first set of parents?


If we cross the two individuals in the F1 generation, what do we call the new generation?


Mendel found out that the traits of the pea plants must consist of two parts
He called these parts "hereditary units", but today we call them alleles. For example, a plant can carry two alleles for being tall, two alleles for being short, or one of each.

Mendel realised that one of the alleles could "override" the other one. Which one do you think that was?
A) The allele for being short B) The allele for being tall


So the allele for being tall could "override" the allele for being short. If a pea plant's genotype had both an allele for being tall and an allele for being short, then pea plant would ultimately turn out ________.
A) short B) tall


How did Mendel work this out from his pea plants?
He saw that some traits (for example being short) could skip a generation, so somehow those trait must be "hidden" in the generation in the middle. Otherwise, they couldn't reappear in F2 generations.

This is another way of showing a cross between two parents
Both parents have an allele for being tall (T) and an allele for being short (t). The middle of the diagram shows the four different genotypes the parents' alleles can combine into.
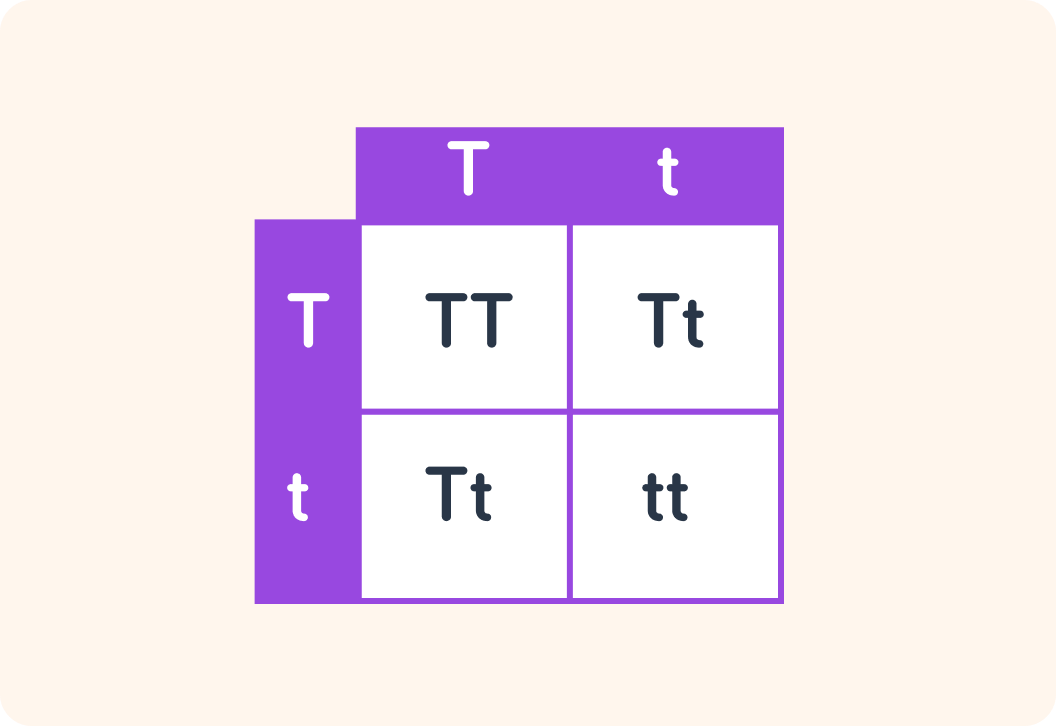
If these parents got 4 offspring, one of each of the possibilities in this diagram, how many of the offspring would be tall?


How many of the offspring would be short?


Mendel referred to "hereditary units", not to "alleles" as we call them today
He worked out that some of these "hereditary units" must be dominant (like T), and some must be recessive (like t).

Summary
Genetic inheritance...
is about which traits get passed onto offspring when two parents cross and why.
Gregory Mendel...
was one of the first scientists to study genetics, already in the mid-1800s.
Mendel worked out...
that a trait must be determined by "hereditary units" (today we call them "alleles") that could be either dominant or recessive.
He realised this because...
he saw some traits in his pea plants that would skip a generation.
