YOU ARE LEARNING:
The Human Genome Project

The Human Genome Project
The Human Genome Project was an international scientific research project which succeeded at sequencing all DNA base pairs in the human genome. It began in 1990 and was completed in 2003.
The Human Genome Project was an international collaboration by scientists, led by Francis Collins, studying the sequence of base pairs in human DNA. What do you think was one of the main goals of the Human Genome Project?

Take a guess at how many base pairs there are in our genome.

So that's 3 billion A, T, G, C bases repeating in a long chains making up our chromosomes! The main goal of the Human Genome Project was to produce a complete, ordered sequence of the 3 billion DNA base pairs that make up the human genome. Not a small task at all.
How many genes do you think make up this 3 billion base pair sequence?

The project began in 1990 and ended in 2003. So it took 13 years! The result of the project, our sequenced genome, was made publicly available. This means that anyone can go online and download sequences of the human genome.
Here is an image of the human genome.
We have 22 pairs of chromosomes and the sex chromosomes. Every gene in these chromosomes was 'mapped' in the Human Genome Project. This means they worked out where the different genes were located.
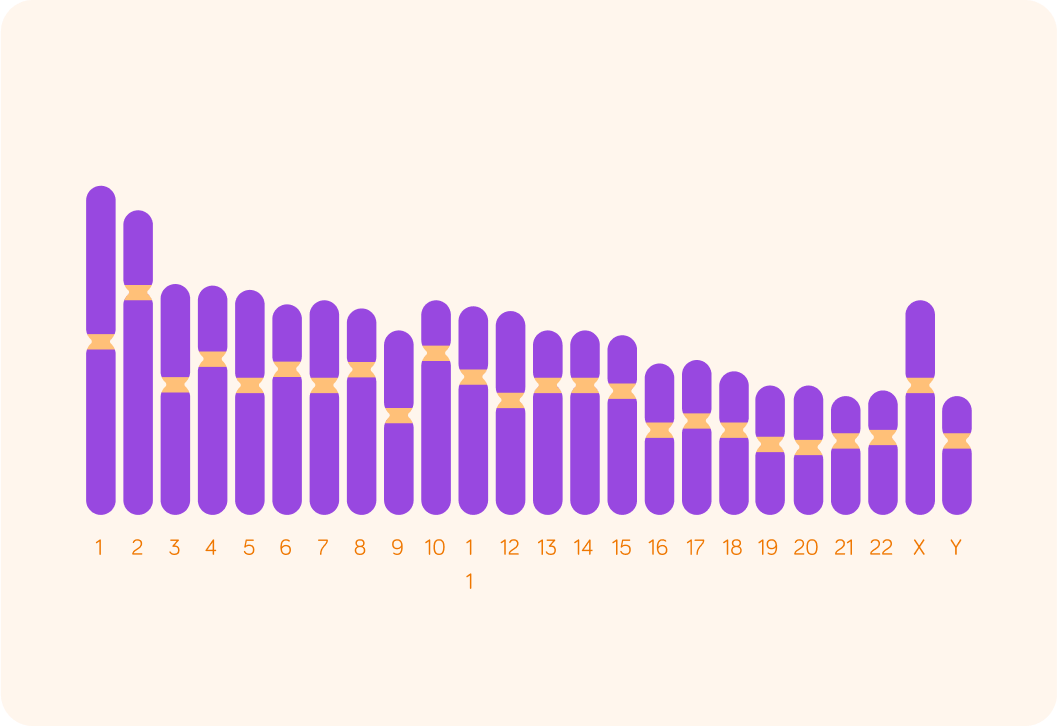
You can see this is a male, because the sex chromosomes are XY.
A female would have two copies of the X chromosome to make XX.

Why do you think it is useful to have such a "map" of the human genome? Pick all the options you think are correct.

You can select multiple answers
By the way, during the project, the team of scientists also sequenced the genome of brewers' yeast, the roundworm and the fruit fly.
How do you think the Human Genome Project has helped medicine? Pick all the options you think are correct.

You can select multiple answers
To sum up the findings of the Human Genome Project...
Mapping
We know which genes are kept on which chromosomes, what their base sequence is and what they code for.
Medicine
We are able to develop treatments for certain genetic disorders better, and to detect those who may carry or suffer from a genetic disease by looking at their DNA.
Human ancestry
We are better able to understand human origins, evolution and ancient migration patterns. Other species' DNA can also be studied for the same reasons.
