YOU ARE LEARNING:
Sex-Linked Disorders

Sex-Linked Disorders
Sex-linked disorders are related to a sex chromosome - either faulty genes on the sex chromosome, or the absence of one or part of one. Examples include haemophilia and Turner syndrome.
What do you think it means if a disorder is sex-linked?

What are the sex chromosomes of male and female humans?

Sex-linked disorders are disorders that are due to mutations on the sex chromosomes. They are often inherited. Two examples of sex-linked disorders are haemophilia and Turner syndrome.
Haemophilia is a recessive disorder. What does that mean?

Haemophilia is a sex-linked trait on the X chromosome. Who can inherit it?

Let's see how haemophilia is inherited.
This Punnett square shows a female carrier of haemophilia crossed with an unaffected male. Remember, haemophilia is a recessive disorder on just the X chromosome.
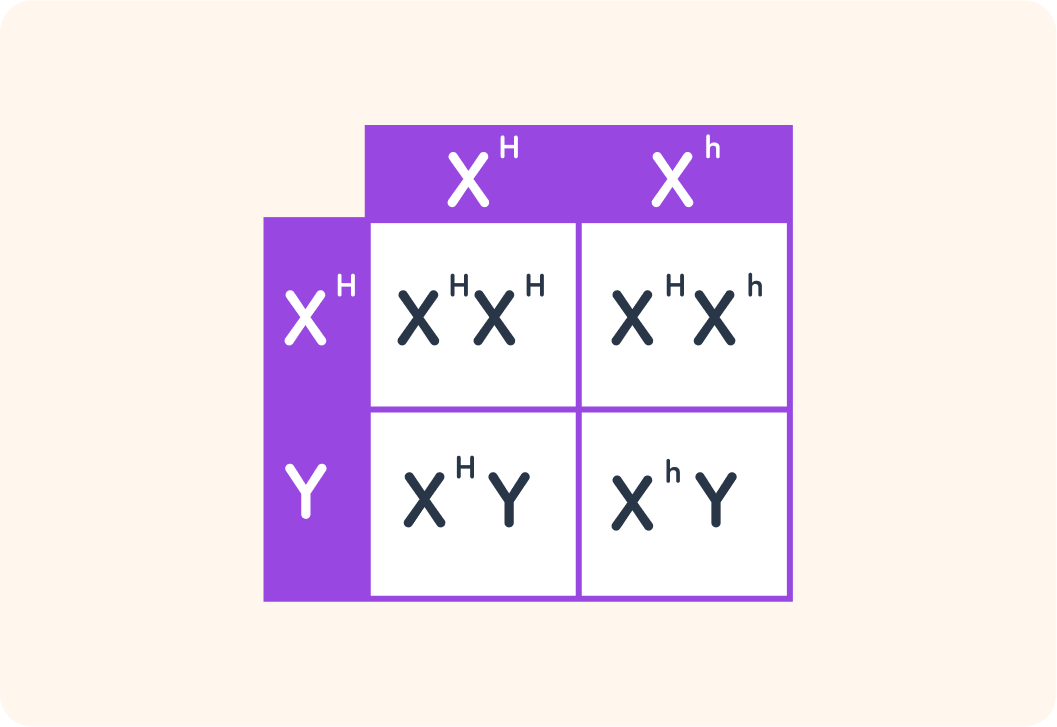
Are there any offspring affected with the disease? Answer yes or no.


Which box is the haemophiliac offspring in?
A) Top left B) Top right C) Bottom left D) Bottom right


What is the offspring in the top right box called?
A) Affected B) Semi-affected C) Carrier


Turner syndrome is a disorder where part or all of the X chromosome is missing. Do you think this will be more dangerous for a male or female embryo?

This is an example of a set of chromosomes of a person with Turner syndrome.
Usually in a female, there would be two X chromosomes, but here we just see one.
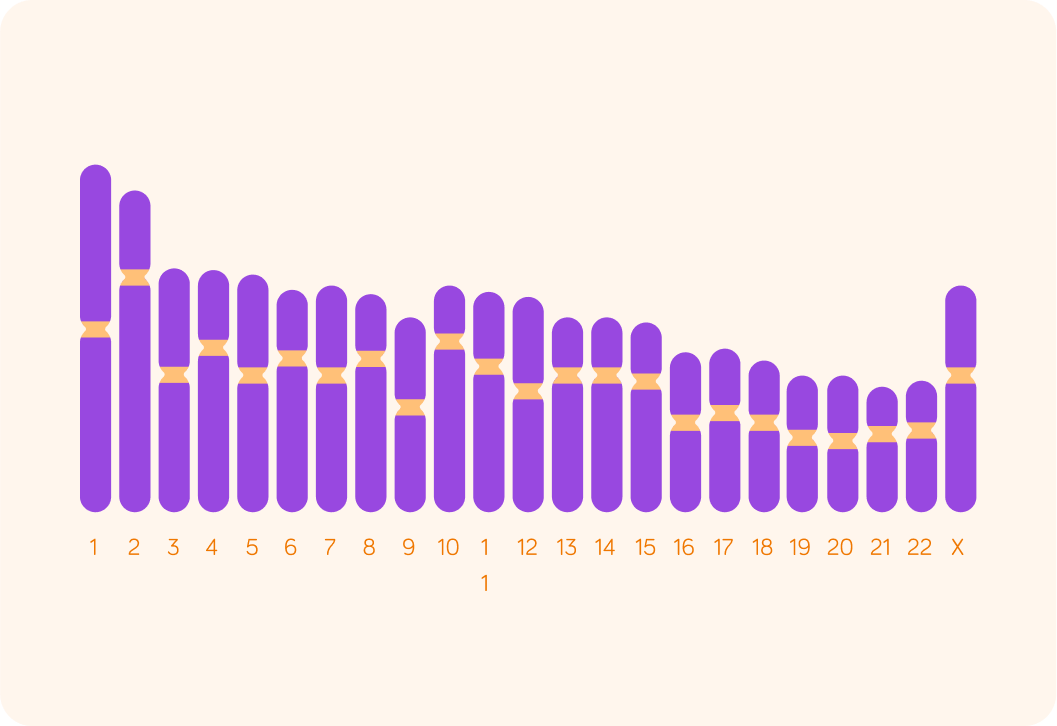
Turner syndrome is due to a chromosome abnormality. Do you think Turner syndrome is inherited?

Why is Turner syndrome only present in women?

