YOU ARE LEARNING:
How Do Transformers Work?
How Do Transformers Work?
Transformers work by inputting a voltage through a primary coil which is connected to a secondary coil via an iron core, which outputs a new voltage.
What does a transformer change?

There are two coils on a transformer. The first coil is called the primary coil, so the other coil is called the...

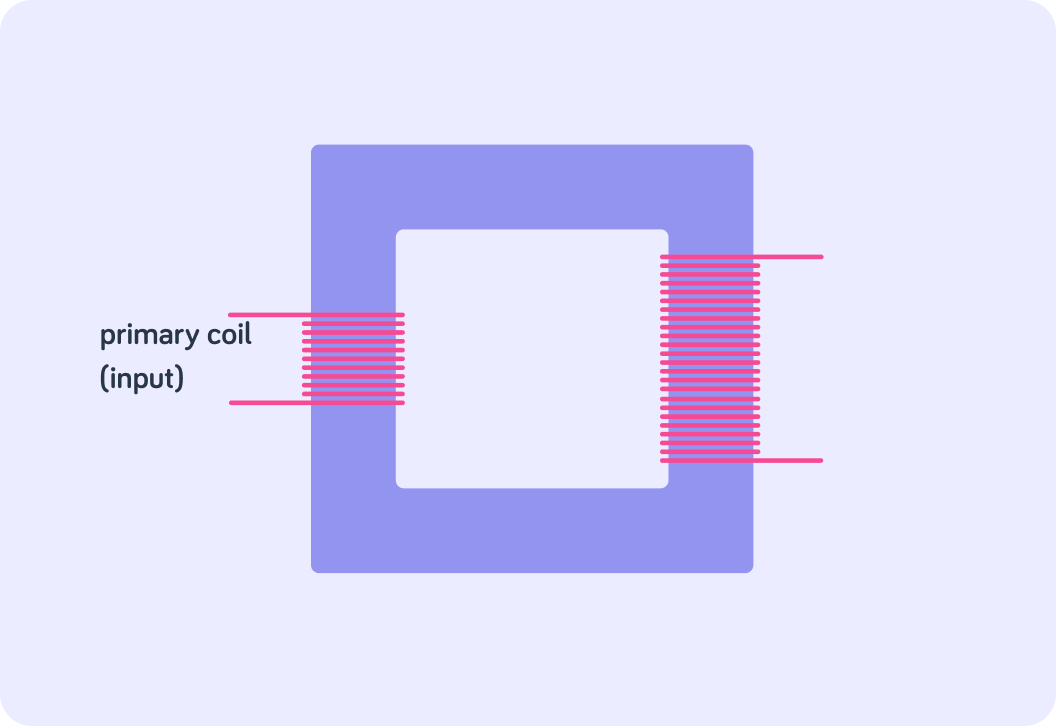
You can see the core that links the two coils. What do you think it's made of?

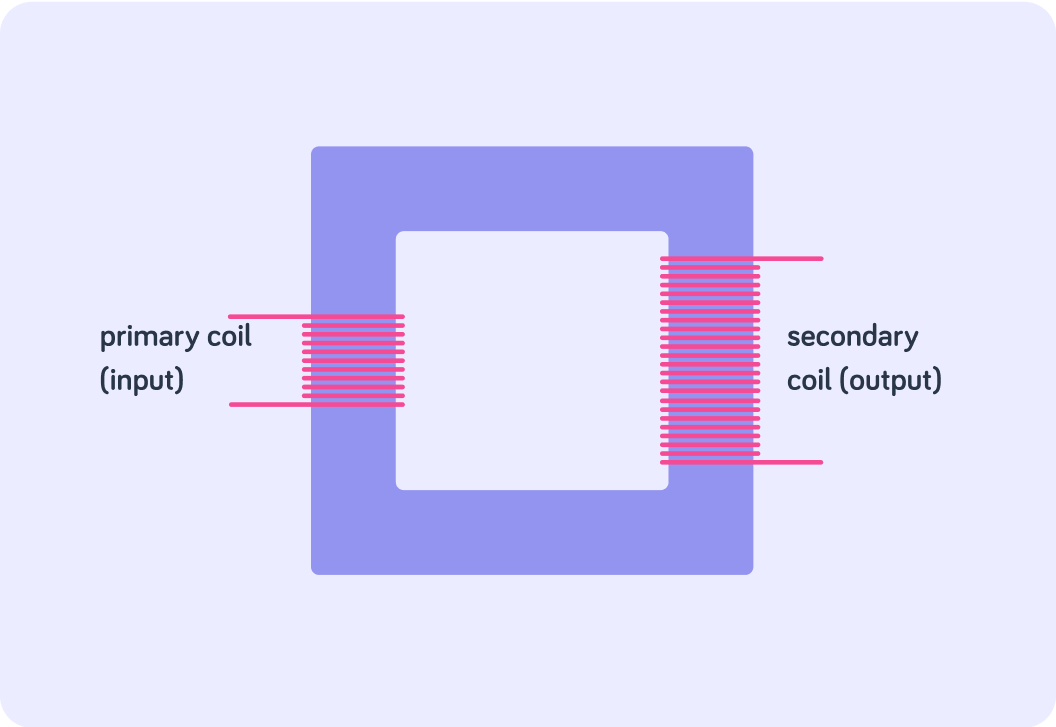
So here it is!
A transformer consists of two coils (a primary and secondary coil) which are each connected to a magnetic iron core. We use iron because it is easily magnetised.
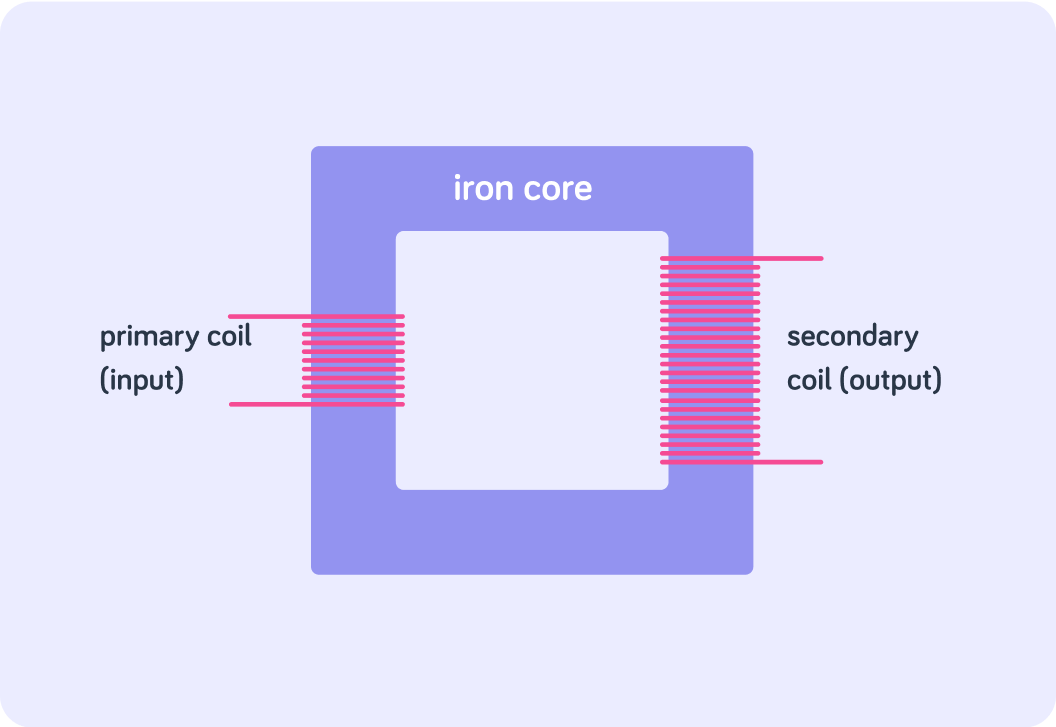
What type of current do transformers work with?

When electricity flows through the primary coil, the primary coil becomes...

When the primary coil has become an electromagnet, what does it produce?

The iron core transports this alternating magnetic field around to the secondary coil. What will this magnetic field induce in the secondary coil?

Are the number of turns in the primary and secondary coil of a transformer the same?


Will the electromagnetic field that is induced across the secondary coil be larger or smaller in this example?


This is how we are able to increase or decrease the voltage the current travels at.
If the secondary coil has more turns in it than the primary coil, the voltage induced in it will be larger than the voltage in the primary coil. If the secondary coil has less turns in it than the primary coil the voltage induced will be smaller.

Is iron classed as a soft or hard magnet?

Iron is a soft magnet. That means that it is easily magnetised and easily demagnetised. That is why we use iron cores in transformers. They are extremely good at transferring the magnetic field from the primary coil to the secondary coil to induce the current in the second coil.
