YOU ARE LEARNING:
Reducing Unwanted Energy Transfers

Reducing Unwanted Energy Transfers
In everyday engineering, there are design features that tackle the problem of unwanted energy transfers.
The diagram shows how heat is lost in a house.
The different arrows show the different amounts of heat lost in different areas of the house.
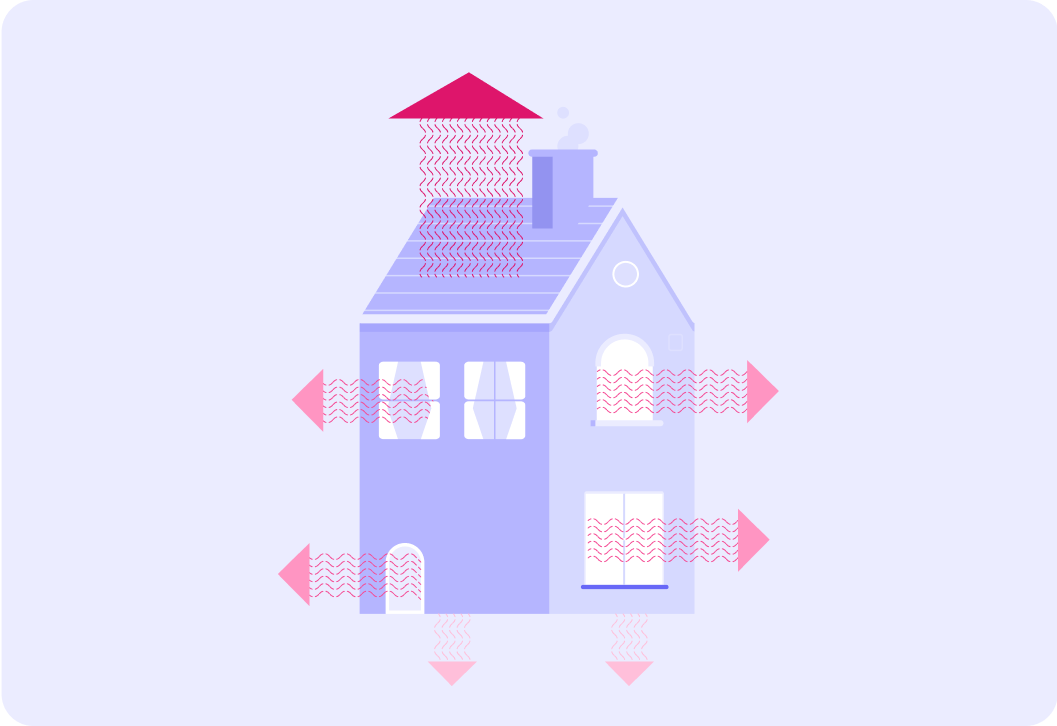
Where is the most heat lost in a home


Why is heat lost through the roof of a house?

Which of the following methods would prevent heat escaping from the roof of a house?

What it is exactly that loft insulation helps to prevent?

The roof is not the only place where heat is escaping. Where else do houses lose a lot of heat?


How does double glazing prevent unwanted energy transfers?

Homes lose a lot of energy through heat escaping from the house.
We have many methods of reducing this unwanted energy transfer including, loft and wall insulation, double glazing and draught excluders on doors.
What do we call the force produced when two objects rub together?

True or false? When the cogs on gears rub together, there is an unwanted energy transfer produced, as friction between the gears causes heat to be released.

Which of the following are methods of reducing unwanted energy transfers caused by friction?

The cogs in gears get hot because of the friction that occurs when the cogs rub together. This is an unwanted energy transfer, because the gears getting hot does not help us towards moving forwards (or backwards), which is really what we want the gears to help us do.
We can reduce that friction and that loss of heat energy by lubricating the cogs, for example with oil.
