YOU ARE LEARNING:
Straight Line Graphs 2

Straight Line Graphs 2
We can find the equation of a straight line by finding the gradient and the y-intercept.
The gradient tells us a couple of things about a line - what are they?

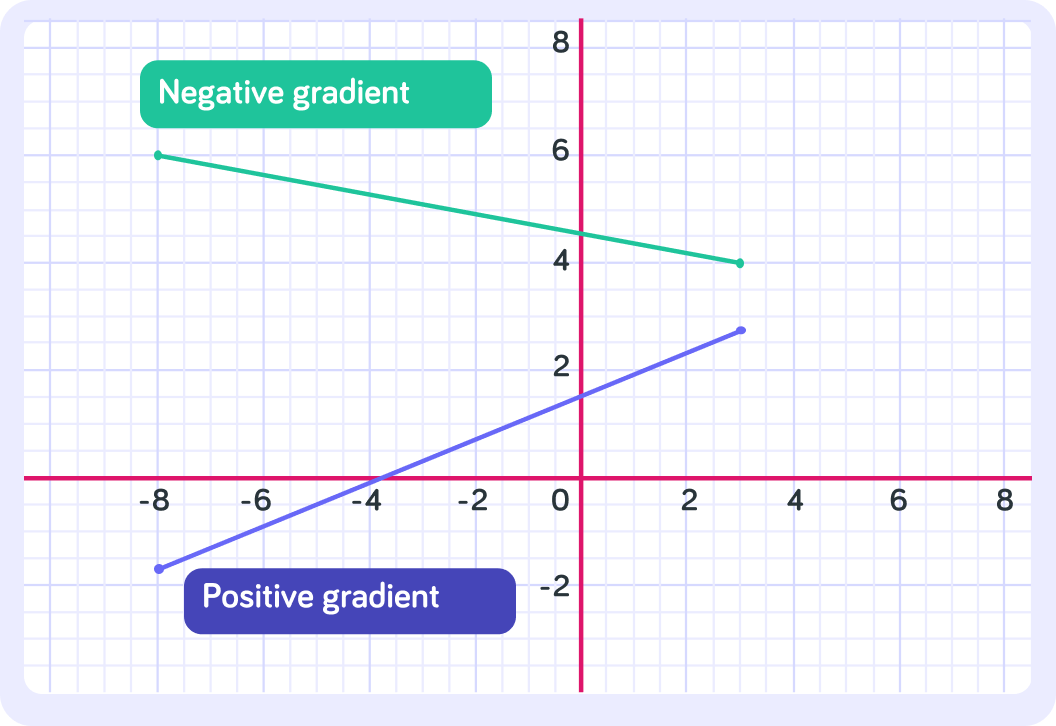
The direction of the slope is determined by the sign of the gradient.
A positive gradient rises from left to right. A negative gradient descends from left to right.
We can calculate the gradient of a straight line if we know two points on that line.
This is the line that passes through the points (2,8) and (0,2).
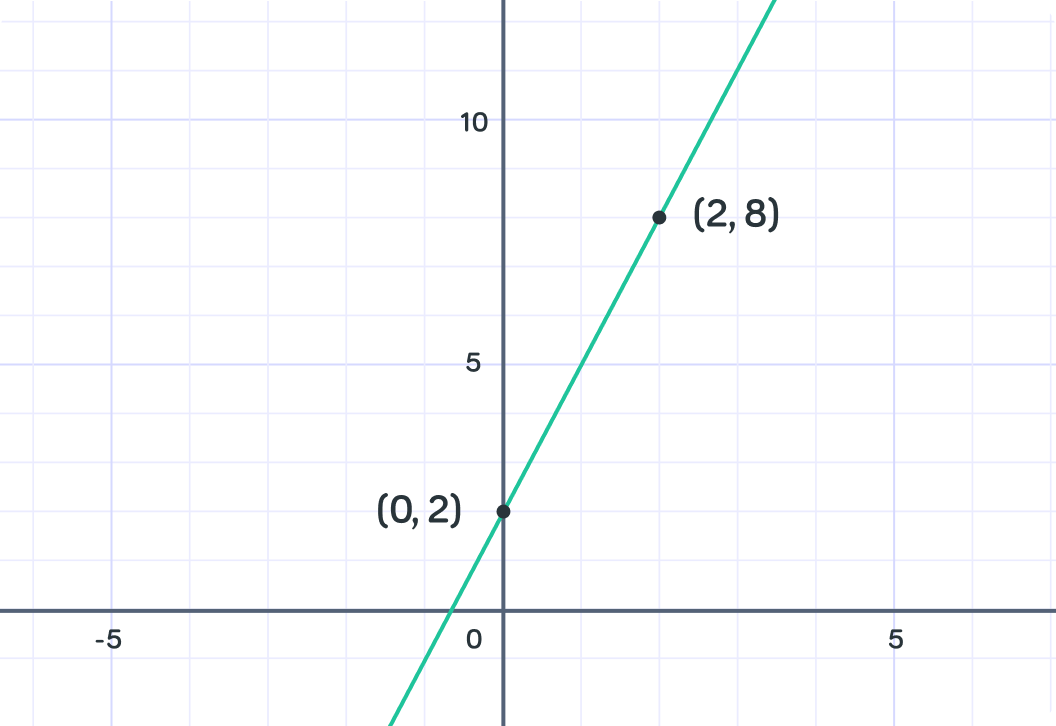
We need to find the difference in the y coordinates and divide by the difference in the x coordinates.
This is also known as runrise.

What is the difference between the y coordinates?


What is the difference in the x coordinates?


We know that m=26 so what is the gradient of this line?


It doesn't matter which point we use first but we must be consistent with the two coordinates.
We used 2−08−2=26=3 We could have used the points the other way round 0−22−6=−2−6=3.

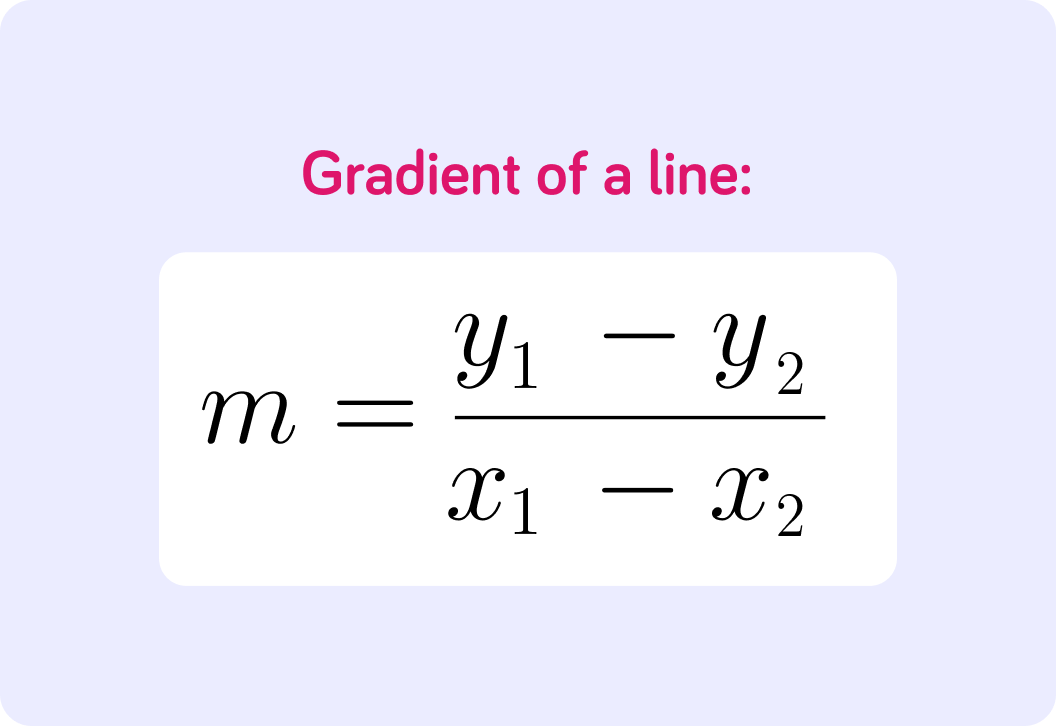
We can use the formula to find the gradient of the line.
The gradient of the line is normally shown as m.
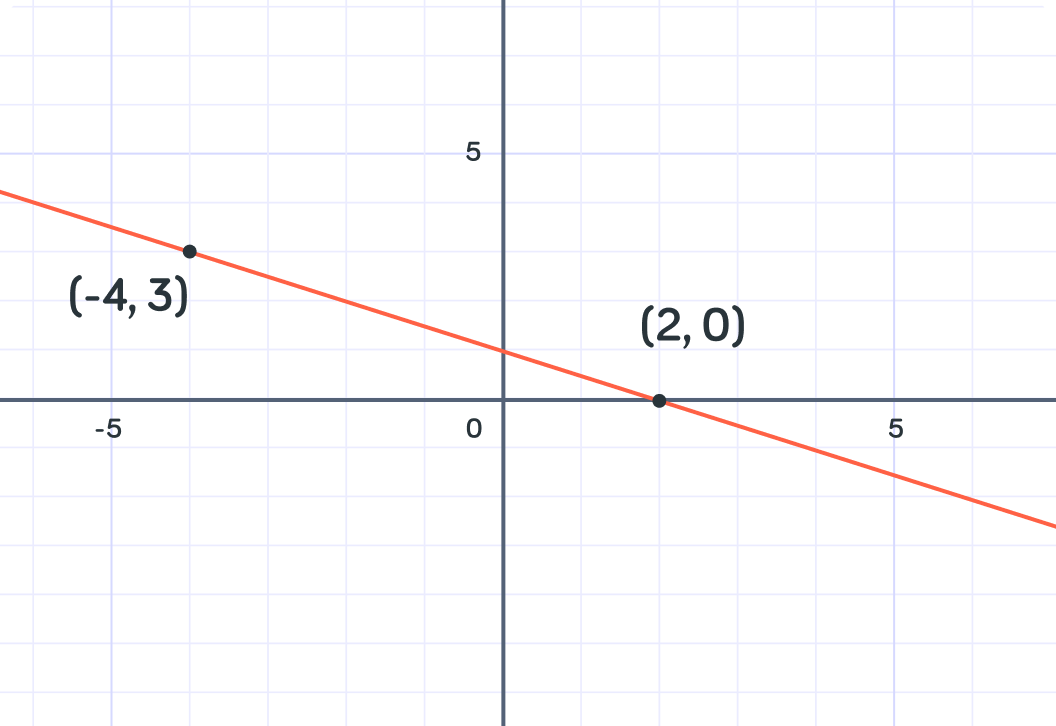
What is the gradient of the line which passes through the points (−4,3) and (2,0).

The standard form of the equation of a straight line is y=mx+c where m is the gradient and c is the y intercept. What is the y intercept on this straight line graph?


This is the same line whose gradient we found to be −0.5. Now we know the y intercept is 1, what is the equation of the line.


What is the gradient of the line with equation y−3x=5?

Now we know that the straight line has standard equation y=mx+c
we can find the equation of a line given the gradient and one point.
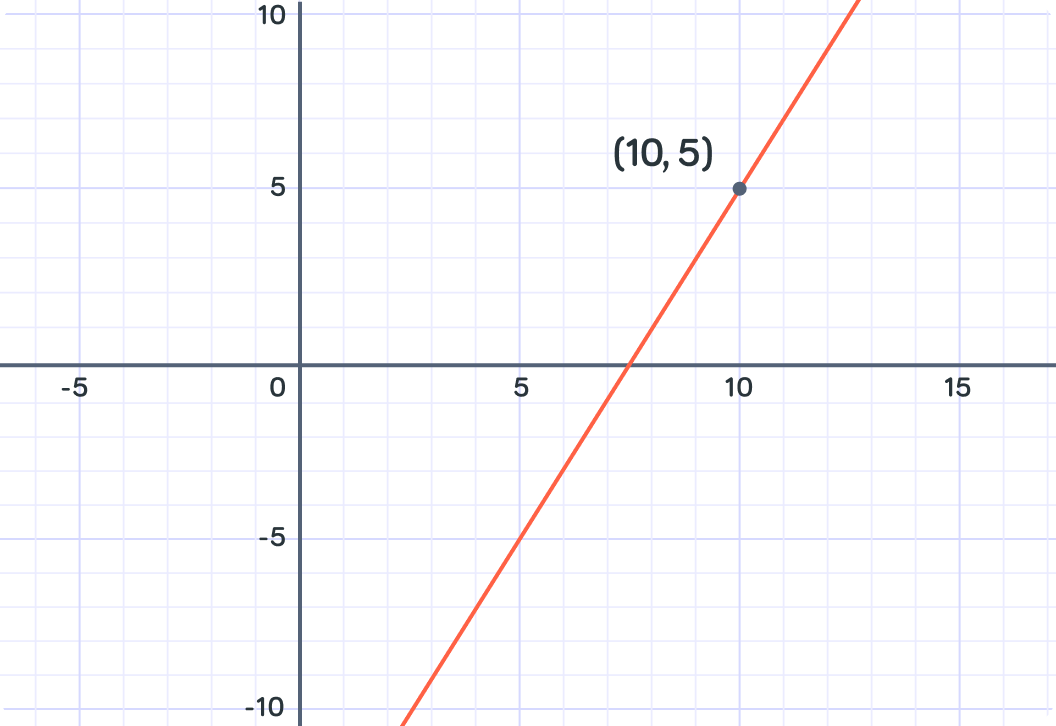
This line passes through the point (10,5) and has gradient 2. The first step is to take the standard form of the equation and put in the gradient. Select the correct option.


We now have part of our equation y=2x+c. We can use the point coordinates to work out c by substituting into our equation, 5=2×10+c. What is c?


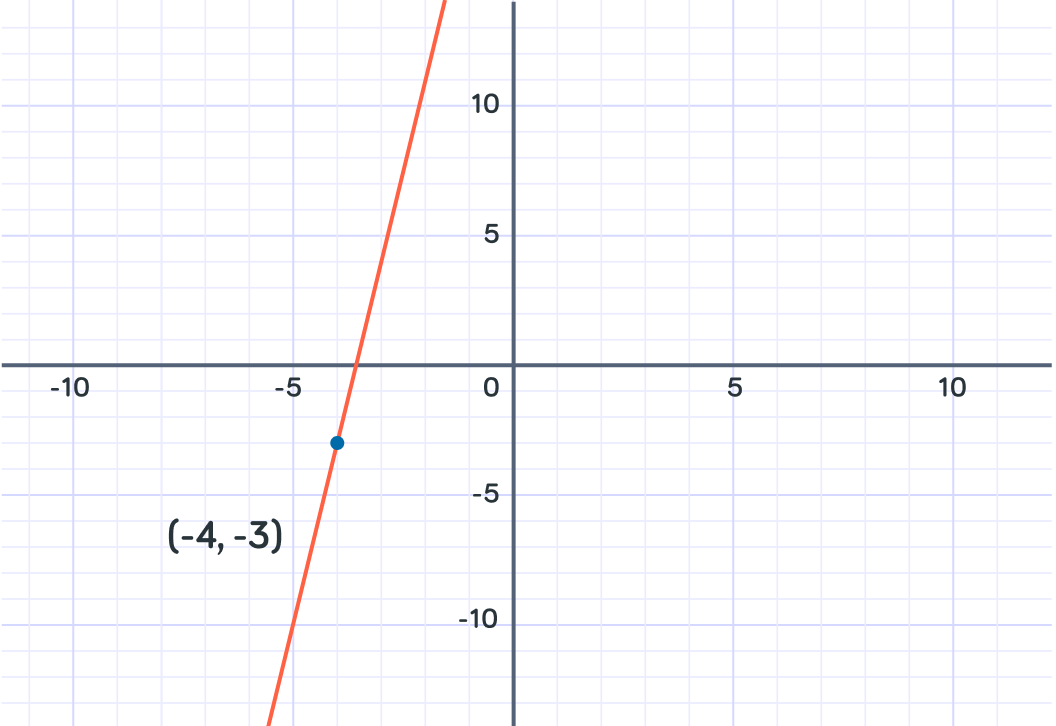
What is the equation of the line with gradient 7 and passes through the point (−4,−3)?

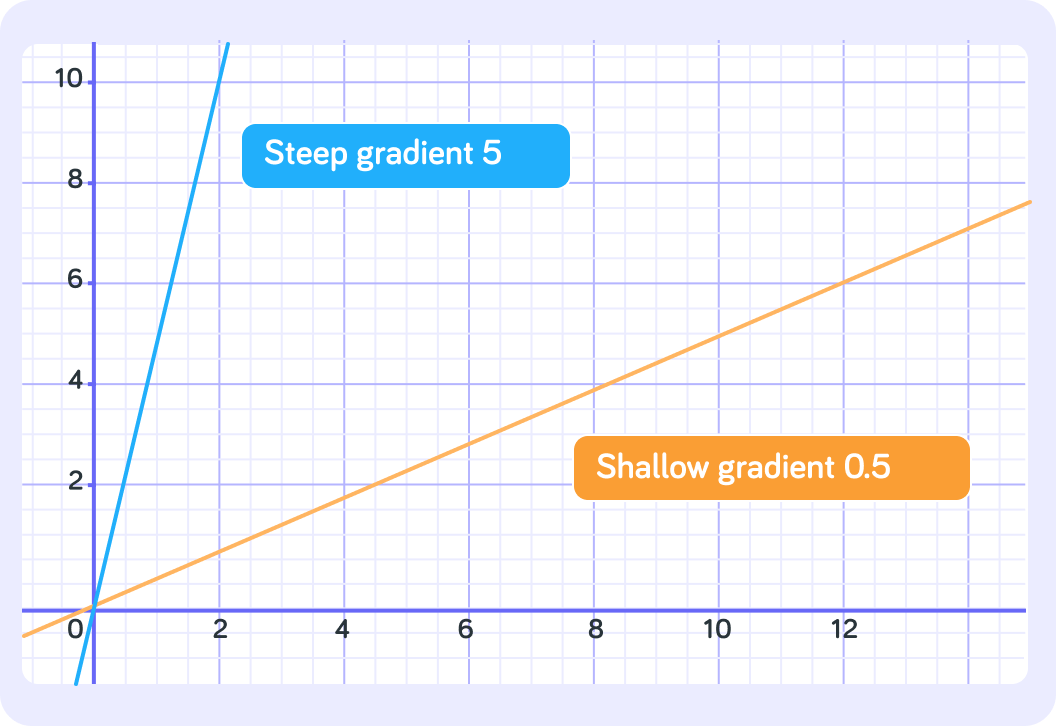
Summary! The gradient of the line is denoted by a number.
A positive gradient rises from left to right. A negative gradient descends from left to right.

The larger the number in the gradient, the steeper the line.
A gradient of 0.5 is quite shallow. A gradient of 5 is steep.
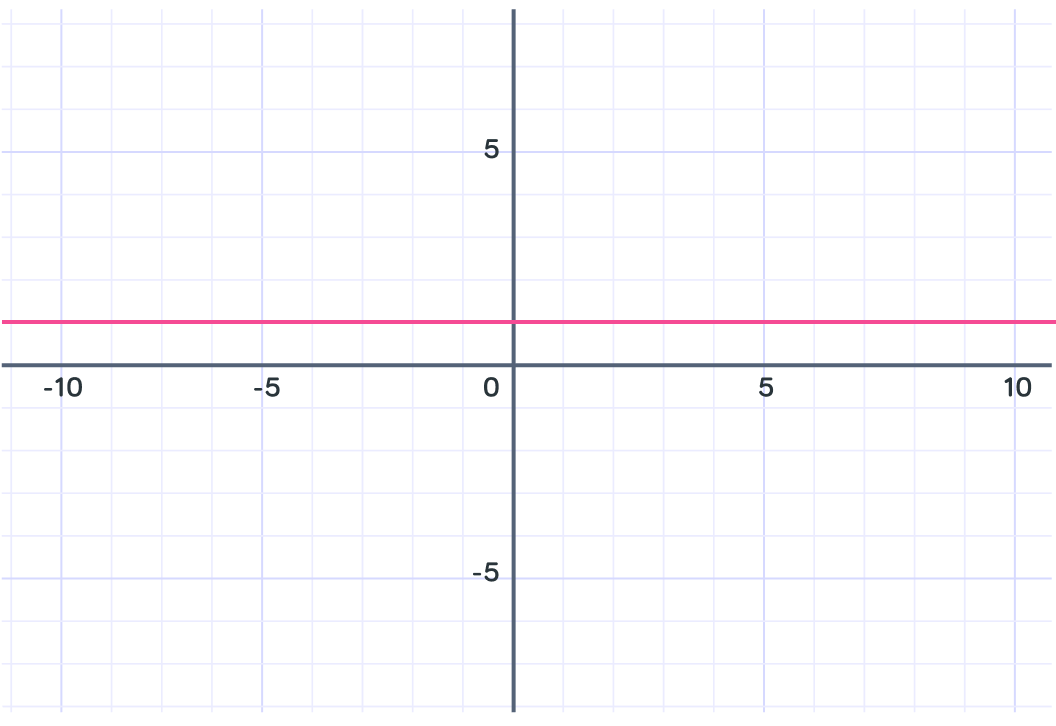
A horizontal line has a gradient of 0.
The line does not go up or down.
A vertical line has an infinite gradient.
The line only goes up.
We can calculate the gradient of a line if we know two points on that line.
The gradient of a line is normally shown by the letter m.

The standard equation of a straight line is y=mx+c
Here, m is the gradient and c is the y intercept.
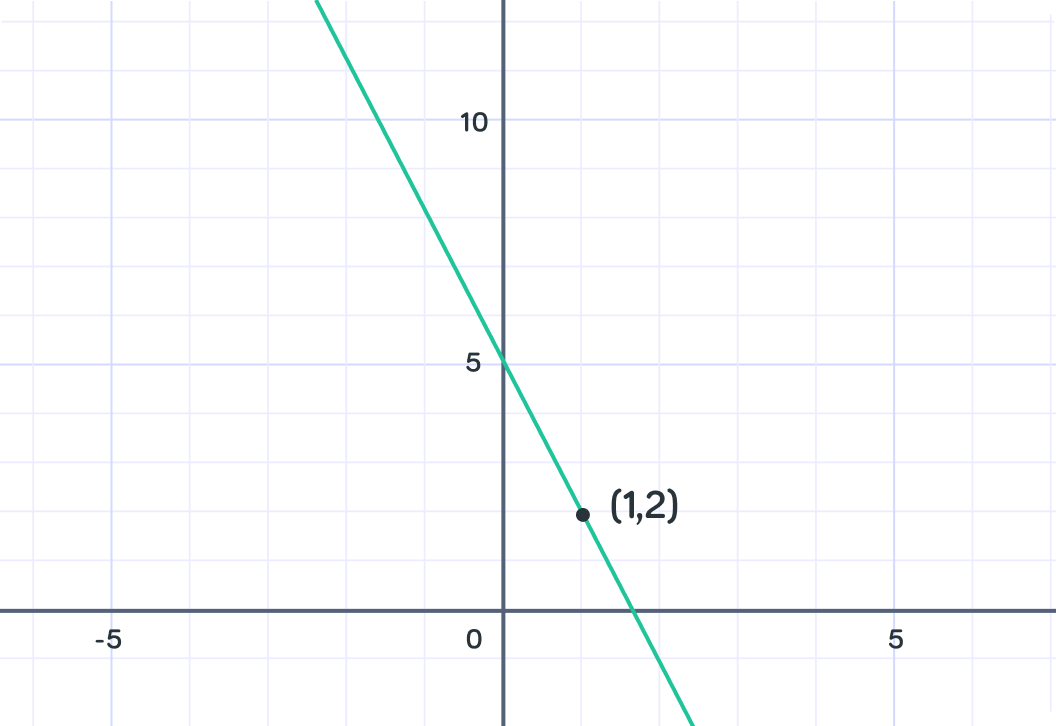
We can find the equation of a line with the gradient and one point here that is −3 and (1,2).
We start the equation y=−3x+c. Substitute the point, 2=−3×1+c and c=5 so the full equation is y=−3x+5.
Sometimes the equation of a straight line needs to be rearranged to put it into standard form.
The line with equation y−x=5. Rearrange to leave y on the left hand side, y=x−5 and this is standard form. The gradient is 1 and the y intercept is −5.
